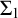Refine search
Actions for selected content:
44 results
Change and Tensions in Non-profit Organizations: Beyond the Isomorphism Trajectory
-
- Journal:
- Voluntas: International Journal of Voluntary and Nonprofit Organizations / Volume 29 / Issue 5 / October 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2026, pp. 898-910
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nonprofit Isomorphism: An Australia–United States Comparison
-
- Journal:
- Voluntas: International Journal of Voluntary and Nonprofit Organizations / Volume 19 / Issue 1 / March 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2026, pp. 67-91
-
- Article
- Export citation
Managing Expectations, Demands and Myths: Swedish Study Associations Caught Between Civil Society, the State and the Market
-
- Journal:
- Voluntas: International Journal of Voluntary and Nonprofit Organizations / Volume 24 / Issue 3 / September 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2026, pp. 537-558
-
- Article
- Export citation
An Industry Fields Approach to Isomorphism Involving Australian Nonprofit Organizations
-
- Journal:
- Voluntas: International Journal of Voluntary and Nonprofit Organizations / Volume 24 / Issue 4 / December 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2026, pp. 1037-1070
-
- Article
- Export citation
Processes of Institutionalization and Differentiation in the Italian Third Sector
-
- Journal:
- Voluntas: International Journal of Voluntary and Nonprofit Organizations / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / September 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2026, pp. 409-427
-
- Article
- Export citation
Structural Isomorphism in Australian Nonprofit Organizations
-
- Journal:
- Voluntas: International Journal of Voluntary and Nonprofit Organizations / Volume 16 / Issue 1 / March 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2026, pp. 1-31
-
- Article
- Export citation
Institutional isomorphism in Chinese development finance regimes: a comparative study of the AIIB, the NDB, and the two policy banks
-
- Journal:
- Japanese Journal of Political Science , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2025, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 1 - Introduction
-
- Book:
- Composite Predicates in English
- Published online:
- 09 May 2025
- Print publication:
- 15 May 2025, pp 1-17
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 10 - Conclusion and outlook
-
- Book:
- Composite Predicates in English
- Published online:
- 09 May 2025
- Print publication:
- 15 May 2025, pp 193-202
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 9 - Theoretical discussion
-
- Book:
- Composite Predicates in English
- Published online:
- 09 May 2025
- Print publication:
- 15 May 2025, pp 173-192
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Isomorphism-inspired theorising about optionality and variation: no empirical support from English grammar
-
- Journal:
- English Language & Linguistics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2025, pp. 1-21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Framing the first-price auction
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Economics / Volume 10 / Issue 1 / March 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2025, pp. 37-51
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chapter One - Chinese Companies in the US Legal System
-
- Book:
- Negotiating Legality
- Published online:
- 13 June 2024
- Print publication:
- 27 June 2024, pp 10-44
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
ON UNSUPERSTABLE THEORIES IN GDST
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Symbolic Logic / Volume 89 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 1720-1746
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
15 - Gestalt Psychology
- from Part II - Systems of Psychology
-
- Book:
- History and Systems of Psychology
- Published online:
- 04 November 2022
- Print publication:
- 17 November 2022, pp 301-317
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
ON SHAVRUKOV’S NON-ISOMORPHISM THEOREM FOR DIAGONALIZABLE ALGEBRAS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Review of Symbolic Logic / Volume 17 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 September 2022, pp. 206-243
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation

Universal Grammar and Iconicity
-
- Published online:
- 03 February 2022
- Print publication:
- 03 February 2022
Chapter 2 - The Serial Verb Constructions
-
- Book:
- Universal Grammar and Iconicity
- Published online:
- 03 February 2022
- Print publication:
- 03 February 2022, pp 17-100
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
7 - The Development of the ICC Arbitration System
- from Part II - The Age of Institutionalization
-
- Book:
- The Three Ages of International Commercial Arbitration
- Published online:
- 16 December 2021
- Print publication:
- 16 December 2021, pp 154-190
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 7 - Language Development: A General Perspective
-
- Book:
- English around the World
- Published online:
- 25 September 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 July 2020, pp 199-220
-
- Chapter
- Export citation