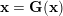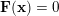Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Medrano-Sánchez, Carlos
Igual-Catalán, Raul
Rodríguez-Ontiveros, Victor H.
and
Plaza-García, Inmaculada
2019.
Circuit Analysis of Matrix-Like Resistor Networks for Eliminating Crosstalk in Pressure Sensitive Mats.
IEEE Sensors Journal,
Vol. 19,
Issue. 18,
p.
8027.
Pollock, Sara
Rebholz, Leo G.
and
Xiao, Mengying
2019.
Anderson-Accelerated Convergence of Picard Iterations for Incompressible Navier--Stokes Equations.
SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis,
Vol. 57,
Issue. 2,
p.
615.
Burdin, Vladimir A.
Bourdine, Anton V.
Bourdine, Anton V.
Burdin, Vladimir A.
Morozov, Oleg G.
Sultanov, Albert H.
and
Andreev, Vladimir A.
2019.
Solution for the twomode propagation of LP01 and LP11 modes in a step-index optical fiber with the Kerr nonlinearity taking into account.
p.
48.
Evans, Claire
Pollock, Sara
Rebholz, Leo G.
and
Xiao, Mengying
2020.
A Proof That Anderson Acceleration Improves the Convergence Rate in Linearly Converging Fixed-Point Methods (But Not in Those Converging Quadratically).
SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis,
Vol. 58,
Issue. 1,
p.
788.
Kelley, C.T.
Bernholc, J.
Briggs, E.L.
Hamilton, Steven
Lin, Lin
and
Yang, Chao
2020.
Mesh independence of the generalized Davidson algorithm.
Journal of Computational Physics,
Vol. 409,
Issue. ,
p.
109322.
Pollock, Sara
and
Schwartz, Hunter
2020.
Benchmarking results for the Newton–Anderson method.
Results in Applied Mathematics,
Vol. 8,
Issue. ,
p.
100095.
Wicht, Daniel
Schneider, Matti
and
Böhlke, Thomas
2020.
On Quasi‐Newton methods in fast Fourier transform‐based micromechanics.
International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering,
Vol. 121,
Issue. 8,
p.
1665.
Burdin, V.A.
Bourdine, A.V.
and
Gubareva, O.Yu.
2020.
Necessary conditions for the propagation of two modes, LP01 and LP11, in a step-index optical fiber with a Kerr nonlinearity.
Computer Optics,
Vol. 44,
Issue. 4,
Fang, Lidong
Majumdar, Apala
and
Zhang, Lei
2020.
Surface, size and topological effects for some nematic equilibria on rectangular domains.
Mathematics and Mechanics of Solids,
Vol. 25,
Issue. 5,
p.
1101.
Bui, Quan M.
and
Elman, Howard C.
2020.
Semi-smooth Newton methods for nonlinear complementarity formulation of compositional two-phase flow in porous media.
Journal of Computational Physics,
Vol. 407,
Issue. ,
p.
109163.
Morrow, Zachary
Kwon, Hyuk-Yong
Kelley, C. T.
and
Jakubikova, Elena
2021.
Efficient Approximation of Potential Energy Surfaces with Mixed-Basis Interpolation.
Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 9,
p.
5673.
Gong, Wenyin
Liao, Zuowen
Mi, Xianyan
Wang, Ling
and
Guo, Yuanyuan
2021.
Nonlinear Equations Solving with Intelligent Optimization Algorithms: A Survey.
Complex System Modeling and Simulation,
Vol. 1,
Issue. 1,
p.
15.
Yang, Yunwen
2021.
Parallel performance analysis of nonlinear equations algorithm based on hybrid genetic algorithm.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series,
Vol. 1982,
Issue. 1,
p.
012108.
Fabiani, Gianluca
Calabrò, Francesco
Russo, Lucia
and
Siettos, Constantinos
2021.
Numerical solution and bifurcation analysis of nonlinear partial differential equations with extreme learning machines.
Journal of Scientific Computing,
Vol. 89,
Issue. 2,
Pollock, Sara
Rebholz, Leo G.
and
Xiao, Mengying
2021.
Acceleration of nonlinear solvers for natural convection problems.
Journal of Numerical Mathematics,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 4,
p.
323.
Jasiulek, Michael
2021.
Solving nonlinear integral equations for laser pulse retrieval with Newton's method.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 103,
Issue. 5,
Luo, Xin-long
and
Xiao, Hang
2021.
Generalized Continuation Newton Methods and the Trust-Region Updating Strategy for the Underdetermined System.
Journal of Scientific Computing,
Vol. 88,
Issue. 3,
Laiu, M. Paul
Endeve, Eirik
Chu, Ran
Harris, J. Austin
and
Messer, O. E. Bronson
2021.
A DG-IMEX Method for Two-moment Neutrino Transport: Nonlinear Solvers for Neutrino–Matter Coupling*
.
The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series,
Vol. 253,
Issue. 2,
p.
52.
Pollock, Sara
and
Rebholz, Leo G
2021.
Anderson acceleration for contractive and noncontractive operators.
IMA Journal of Numerical Analysis,
Vol. 41,
Issue. 4,
p.
2841.
Rebholz, Leo G.
Vargun, Duygu
and
Xiao, Mengying
2021.
Enabling convergence of the iterated penalty Picard iteration with O(1) penalty parameter for incompressible Navier–Stokes via Anderson acceleration.
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,
Vol. 387,
Issue. ,
p.
114178.