No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Obtaining remainder term estimates by an inversion technique
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 July 2016
Abstract
Let  be a double sequence of random variables such that there exists a ‘dual' sequence
be a double sequence of random variables such that there exists a ‘dual' sequence  satisfying
satisfying  , and that
, and that  can be expressed as a sum of independent random variables. If
can be expressed as a sum of independent random variables. If 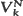 (suitably centered and rescaled) is approximately normally distributed as k and N → ∞ in some fashion, we can use this fact to obtain a remainder-term estimate for the asymptotic normality of
(suitably centered and rescaled) is approximately normally distributed as k and N → ∞ in some fashion, we can use this fact to obtain a remainder-term estimate for the asymptotic normality of 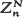 as n and N → ∞ in some prescribed manner. The result in the general theorem is used in two specific situations: (i) classical occupancy where the balls can fall through the boxes, (ii) a capture-recapture problem where tagging affects catchability.
as n and N → ∞ in some prescribed manner. The result in the general theorem is used in two specific situations: (i) classical occupancy where the balls can fall through the boxes, (ii) a capture-recapture problem where tagging affects catchability.
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Applied Probability Trust 1984
References
Van Beek, P. (1972) An application of Fourier methods to the problem of sharpening the Berry-Esseen inequality. Z. Wahrscheinlichkeitsth.
23, 187–196.Google Scholar
Englund, G. (1979) Remainder term estimate for the asymptotic normality of the number of renewals. J. Appl. Prob.
17, 1108–1113.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Englund, G. (1980) A remainder term estimate for the normal approximation in classical occupancy when the balls can fall through the boxes. Tech. Report TRITA-1981-18, Royal Inst. of Technology, Stockholm.Google Scholar
Englund, G. (1981) A remainder term estimate for the normal approximation in classical occupancy. Ann. Prob.
9, 684–692.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Farm, A. (1971) Asymptotic normality in a capture-recapture problem when catchability is affected by the tagging procedure. Tech. Report TRITA-MAT-1971-10, Royal Inst. of Technology, Stockholm.Google Scholar
Johnson, N. L. and Kotz, S. (1977) Urn Models and their Applications.
Wiley, New York.Google Scholar
Park, C. J. (1972) A note on the classical occupancy problem, Ann. Math. Statist.
43, 1698–1701.Google Scholar
Rényi, A. (1962) Three new proofs and a generalization of a theorem by Irving Weiss. Publ. Math. Inst. Hung. Acad. Sci.
7, 203–214.Google Scholar
Samuel-Cahn, E. (1974) Asymptotic distributions for occupancy and waiting time problems with positive probability of falling through the cells. Ann. Prob.
2, 515–521.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Samuel-Cahn, E. (1975) Asymptotic distribution for the coupon-collector's and sampling-tagging problems when tagging affects catchability. J. Appl. Prob.
12, 625–628.Google Scholar

