Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Cénac, Peggy
de Loynes, Basile
Offret, Yoann
and
Rousselle, Arnaud
2020.
Recurrence of multidimensional persistent random walks. Fourier and series criteria.
Bernoulli,
Vol. 26,
Issue. 2,
Bhimaraju, Akhil
Zacharias, Atul A.
and
Chatterjee, Avhishek
2022.
Multichannel Resource Allocation for Smooth Streaming: Non-Convexity and Bandits.
IEEE Transactions on Communications,
Vol. 70,
Issue. 8,
p.
5085.
Hervé, Loïc
and
Ledoux, James
2023.
Robustness of iterated function systems of Lipschitz maps.
Journal of Applied Probability,
Vol. 60,
Issue. 3,
p.
921.

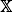 with transition kernel
with transition kernel 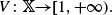 The Markov kernel
The Markov kernel 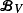 associated with
associated with 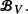 A general procedure to compute ρ
A general procedure to compute ρ