Introduction
Baby boomers (classified in Australia as born between 1946 and 1965) are frequently cited, rightly or wrongly, as the lucky generation with a perception that they are better off financially, had enhanced education opportunities and are healthier than the preceding generations (Biggs et al. Reference Biggs, Phillipson, Money and Leach2006; Faulkner Reference Faulkner2007; Hamilton and Hamilton Reference Hamilton and Hamilton2006; Quine and Carter Reference Quine and Carter2006; Pinnegar and van den Nouwelant Reference Pinnegar and van den Nouwelant2012). Baby-boomer research is often centred on demographic changes, health, pensions, superannuation and retirement plans (Humple et al. Reference Humple, O'Loughlin, Wells and Kendig2010; Hunter, Wang and Worsely Reference Hunter, Wang and Worsely2007; Kubicek et al. Reference Kubicek, Korunka, Hoonakker and Raymo2010; Martin et al. Reference Martin, Freedman, Schoeni and Andreski2009; Quine and Carter Reference Quine and Carter2006; Taylor et al. Reference Taylor, Pilkington, Feist, Dal Grande and Hugo2014). While commentary on sea-change/tree-change moves (the move from major cities to an ‘easier’ life in rural/coastal communities) (Gurran and Blakely Reference Gurran and Blakely2007; Olsberg and Winters Reference Olsberg and Winters2005), downsizing (Wulff, Champion and Lobo Reference Wulff, Champion and Lobo2010) and reverse mortgages (Snoke, Kendig and O'Loughlin Reference Snoke, Kendig and O'Loughlin2011) are frequently addressed, other housing considerations, especially baby boomers who rent, are often overlooked as an important research and policy issue.
Pensions, superannuation (government-supported retirement savings based on employment income) and savings are the three funding mechanisms for retirees, although increasingly housing equity is seen as the ‘fourth pillar’ (Yates and Bradbury Reference Yates and Bradbury2010). Notwithstanding recent property devaluations and housing value volatility in most developed countries, baby boomers are a cohort who have experienced a property market that has escalated considerably across their housing career and their homes are frequently a considerable and critical asset (Beer and Faulkner Reference Beer and Faulkner2009; Harding, King and Kelly Reference Harding, King and Kelly2002; Ong et al. Reference Ong, Haffner, Wood, Jefferson and Austen2013; Snoke, Kendig and O'Loughlin Reference Snoke, Kendig and O'Loughlin2011). In the Australian Census, 75 per cent of baby boomers owned or were paying off their own home and 17 per cent were renting (either privately or via public housing) (Yates and Bradbury Reference Yates and Bradbury2010). Figures for baby boomers as home-owners of 70 per cent for Europe and 80 per cent for the United States of America are comparable (Angelini, Brugiavini and Weber Reference Angelini, Brugiavini and Weber2014; Laaksonen, Tarkiainen and Martikainen Reference Laaksonen, Tarkiainen and Martikainen2009). In Australia, public housing is for individuals or families on low to moderate incomes who are having difficulty securing housing in the private rental market. Due to the very high waiting lists and prioritisation system of offering to those with the greatest need, public housing is usually available for long-term existing tenants or for people in times of crisis, such as domestic violence sufferers, ex-prisoners or those at risk of homelessness. While some baby boomers have never owned a home, a proportion of baby boomers have also moved to rental accommodation as a result of changes in marital status (divorce, widowhood), changes in household composition (empty nest) or economic and health-related factors (sickness, disability, unemployment, retrenchment) (Angelini, Brugiavini and Weber Reference Angelini, Brugiavini and Weber2014; Faulkner Reference Faulkner2007; Pinnegar and van den Nouwelant Reference Pinnegar and van den Nouwelant2012; Wulff, Champion and Lobo Reference Wulff, Champion and Lobo2010). Home-ownership rates decline as age advances and equity is released as increased social and health-related support is required (such as entering aged care facilities or moving in with family members) but baby boomers have yet to reach the ‘advanced’ age where those forces more commonly come into play (Angelini, Brugiavini and Weber Reference Angelini, Brugiavini and Weber2014; Australian Housing and Urban Research Institute (AHURI) 2004).
The advantage of owning a house into retirement is seen as insurance against rent increases, security if a future need arises and as a legacy for the next generation (Angelini, Brugiavini and Weber Reference Angelini, Brugiavini and Weber2014; Faulkner Reference Faulkner2007; Snoke, Kendig and O'Loughlin Reference Snoke, Kendig and O'Loughlin2011). Renting, either private or public, has been shown to be related to poor health outcomes in most developed countries (Hungerford Reference Hungerford2007; Laaksonen, Tarkiainen and Martikainen Reference Laaksonen, Tarkiainen and Martikainen2009). Renters more often report increased financial difficulties (Angelini, Brugiavini and Weber Reference Angelini, Brugiavini and Weber2014). While baby-boomer home-owners are willing to down size to release funds for lifestyle needs (AHURI 2004; Faulkner Reference Faulkner2007; Laaksonen, Tarkiainen and Martikainen Reference Laaksonen, Tarkiainen and Martikainen2009), renting baby boomers do not have that option to supplement their lifestyle choices if required (Ong et al. Reference Ong, Haffner, Wood, Jefferson and Austen2013).
Australia's current social policy context includes encouragement for ageing in place (continuing to live in the family home), extending the working years (with a non-compulsory retirement age) and increasing the age when one is eligible for the pension. Age pensions were accepted as the norm in previous retired generations (Hamilton and Hamilton Reference Hamilton and Hamilton2006; Harding, King and Kelly Reference Harding, King and Kelly2002). The baby-boomer cohort, as they approach retirement, with their wide range of experiences and expectations, have relatively large differences in superannuation, savings and housing assets (Biggs et al. Reference Biggs, Phillipson, Money and Leach2006; Faulkner Reference Faulkner2007; Quine and Carter Reference Quine and Carter2006). Over 30 per cent of baby boomers in Australia own more than one dwelling (Beer and Faulkner Reference Beer and Faulkner2009), while some, especially renters, are seen as being financially vulnerable and may experience economic hardships into old age (Hungerford Reference Hungerford2007; Hunter, Wang and Worsely Reference Hunter, Wang and Worsely2007). Vulnerability often exists with families headed by divorced women, or those who have never married or who have traditionally been low-income earners (Angelini, Brugiavini and Weber Reference Angelini, Brugiavini and Weber2014; Olsberg and Winters Reference Olsberg and Winters2005). Arguments have been made that although women will be over-represented in the renting group because of their substantially lower superannuation resources (Olsberg and Winters Reference Olsberg and Winters2005; Snoke, Kendig and O'Loughlin Reference Snoke, Kendig and O'Loughlin2011), low-income couple households will also be seeking assistance with their housing needs (AHURI 2008).
Previous studies have shown that being a renter in the pre-retirement years is associated with many later-year hardships, including health and wealth (Hungerford Reference Hungerford2007). As such, we assess the chronic conditions, risk factors, socio-economic factors and other health-related factors associated with renting, both private and public, to determine the profile of the renting group before they reach the normative retirement years. We also compare renters with home-owners.
Methods
The South Australian Monitoring and Surveillance System (SAMSS) is a telephone monitoring system designed to monitor systematically chronic disease, risk factors and other health-related issues on a regular and ongoing basis (Population Research and Outcome Studies 2004). Commencing in July 2002, a representative cross-sectional sample is randomly selected each month from all households in South Australia (SA) with a telephone connected and the number listed in the telephone directory. A letter of introduction is sent to the selected household and the person who was last to have a birthday within a 12-month period is chosen for interview.
A trained interviewer, via a computer-assisted telephone interview system, conducts the interviews. Data are collected by a contracted agency and interviews are conducted in English. Each interview takes approximately 15 minutes. At least ten call-backs are made to the telephone number selected. Replacement interviews for persons who could not be contacted or interviewed are not permitted. Interviews are conducted on a minimum of 600 randomly selected people (of all ages) each month. Of each interviewer's work, 10 per cent is selected at random for validation by a supervisor. The current analysis used data collected from January 2010 to December 2015. The median response rate was 63.8 per cent. No details were available for non-responders although the data were weighted to overcome potential response bias. All respondents gave informed consent to undertake the interview. Ethics approval was obtained from the ethics committee of the Department of Health and Ageing, SA (number 436/02/2014).
This analysis is limited to the responses from baby boomers only (N = 16,687). Respondents were asked if the dwelling was ‘owned or being purchased’, ‘rented from Housing SA’, ‘rented privately’ or ‘other’. Housing SA is the government department responsible for public housing rentals. The ‘other’ category covered community housing and retirement village accommodation and were excluded from the analysis (N = 114).
Descriptive analyses were undertaken using the following demographics, chronic diseases and risk factors.
Demographics
Demographic and socio-economic variables included in the descriptive analyses consisted of age, gender, work status, highest education obtained, marital status, country of birth, household annual income and Aboriginal/Torres Strait Islanders status. The single pension in Australia is less than Aus $20,000 per year. The lower amount was selected as the aim of the analysis was to examine vulnerable groups, especially those at the lower end of income levels. Two questions assessed the current household money situation and the family/household structure. Socio-economic status was assessed using postcodes classified into the Socio-economic Index for Areas (SEIFA) 2006 Index of Relative Socio-economic Disadvantage quintiles (Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) 2006). SEIFA ranks areas in Australia according to socio-economic advantage and disadvantage and is a composite score based on selected Census socio-economic variables. Questions on social capital-related factors included neighbourhood safety (yes/no), trust in the neighbourhood (yes/no), home safety (all of the time to none of the time), control over life decisions (strongly agree to strongly disagree) and transport problems (never to all of the time). Age (continuous), gender, household income and area (country SA or metropolitan Adelaide) were classified as confounders and used in the multivariate adjustments.
Chronic conditions
Respondents were asked whether a doctor had ever told them they had diabetes, cardiovascular disease (CVD), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), arthritis or osteoporosis, or if they had asthma symptoms in the previous 12 months. In addition, respondents were asked if they had ever been diagnosed with depression, anxiety, or a stress-related or other mental health problem. A multiple chronic condition variable was created from the seven chronic conditions assessed, with two or more chronic conditions indicating multiple chronic conditions.
Risk factors
Respondents were asked whether a doctor had ever told them they have or were currently receiving treatment or medication for high blood pressure or high cholesterol. Respondents were asked to provide the time they spent undertaking walking, moderate or vigorous physical activity over the past week. The time was summed, with the time spent undertaking vigorous activity multiplied by a factor of two to account for its greater intensity, in order to provide an indication as to whether respondents are undertaking a sufficient level of physical activity to provide a health benefit. This is defined as 150 minutes or more of activity each week (Department of Health and Ageing 1999) and has been recoded into insufficient activity (no activity, active but not sufficient) and sufficient activity.
Body mass index was derived from self-reported weight and height and recoded into three categories (underweight/normal, overweight and obese) (World Health Organization 2013). Respondents were asked how many servings of fruit and how many servings of vegetables they ate each day, with the recommendation being at least two servings of fruit and five servings of vegetables each day (National Health and Medical Research Council 2005).
Smoking status (current, ex or non) was also assessed. In addition, a multiple risk factor variable was created (physical inactivity, current smoking, inadequate consumption of fruit, inadequate consumption of vegetables, psychological distress, current high blood pressure, current high cholesterol and obesity) with a positive response to two or more risk factors indicating multiple risk factors. How respondents would rate their overall health was recoded, with fair or poor determined as low overall health status. For adjustment in the multivariate analysis only smoking status and sufficient physical activity were used, as these were the only risk factors deemed to be possible confounders.
Analysis
The weighting procedure known as ‘raking’ was used to weight the respondents by probability of selection within the household and by a range of socio-economic and demographic characteristics (age, gender, region, highest education level obtained, renting status, country of birth, marital status and employment status) (Dal Grande et al. Reference Dal Grande, Chittleborough, Campostrini and Taylor2015) using SA-specific ABS Census data so that the estimates are reflective of the structure of the population being assessed.
Data were analysed using SPSS for Windows version 24.0 and Stata version 13.0. Prevalence estimates were assessed for each risk factor and chronic condition by housing status. Chi-square tests were used to compare differences in the categorical variables. The association between housing status and the chronic conditions and risk factors were analysed using logistic regression models adjusting for multiple covariates. The multivariable models controlled for demographic variables (age (continuous), income, area and gender) and known risk factors (smoking and physical activity) and year of data collection.
Results
The demographic profile of the three groups (home-owners or buyers, private and public renters) are detailed in Table 1. Overall 16,687 baby-boomer respondents were included in the analysis (mean age = 54.1 years, standard deviation (SD) = 6.04), 49.2 per cent male with 17.4 per cent renting either privately (10.1%, 95% CI = 9.7–10.6) or publicly (7.3%, 95% CI = 6.9–7.7). The mean age was 56.5 years (SD = 5.9) for those owning or paying off their home, 55.6 years (SD = 5.9) for private renters and 57.2 years (SD = 6.2) for public renters. Increased proportion for public renters included those unable to work, the lower educated, those never married, those in the lowest SEIFA quintile, those earning < Aus $20,000 per year and adults living alone.
Table 1. Demographic profile of baby boomers by dwelling type, January 2010 to December 2015

Notes: The weighting of the data can result in rounding discrepancies or totals not adding. Refused were not reported. CI: confidence interval. SEIFA: Socio-economic Index for Areas. ATSI: Aboriginal/Torres Strait Islanders. 1. University education.
The relationship between housing status and the social capital-related variables is highlighted in Table 2. Public renters were more likely to report not living in a safe neighbourhood, not believing people in the neighbourhood trust one another and sometimes having problems with transport.
Table 2. Social capital profile of baby boomers by dwelling type, January 2010 to December 2015
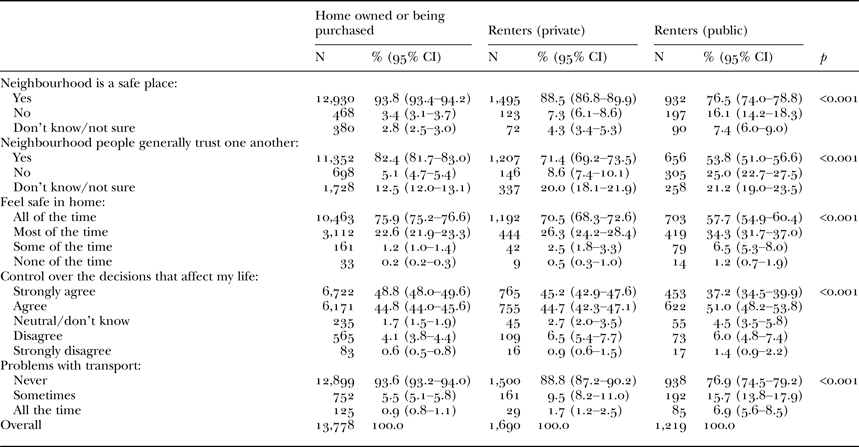
Notes: The weighting of the data can result in rounding discrepancies or totals not adding. Refused were not reported. CI: confidence interval.
The relationship between housing status and chronic conditions and risk factors are highlighted in Table 3. Public renters are more likely to have an increased risk of all of the chronic conditions and risk factors examined.
Table 3. Chronic condition and risk factor profile of baby boomers by dwelling type, January 2010 to December 2015

Notes: The weighting of the data can result in rounding discrepancies or totals not adding. Don't know/refused were not reported. Multiple risk factors included high blood pressure, high cholesterol, insufficient physical activity, obesity, current smoking and eating less than two servings of fruit or five servings of vegetables per day. CI: confidence interval. CVD: cardiovascular disease. COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Using multivariable analysis after adjustment, housing status was positively associated with CVD and mental health problems for both private and public renters and for diabetes, arthritis and COPD for public renters. The odds ratios increased from owning or buying own home to privately renting to public renting for all conditions except osteoporosis. The raw and adjusted estimates are presented in Table 4.
Table 4. Odds ratio (95% confidence interval) for chronic diseases according to housing status among baby boomers
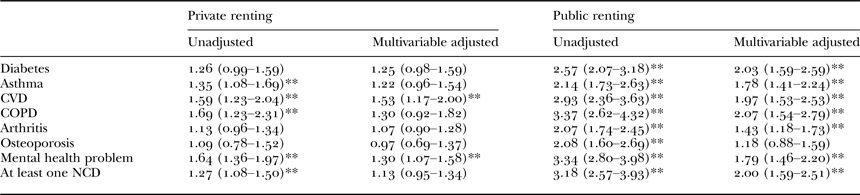
Notes: Multivariable models adjusted for age, gender, smoking status, income, sufficient physical activity, area, year of survey. Reference category = home owned or being purchased. COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. CVD: cardiovascular disease. NCD: non-communicable disease.
Significance level: ** p < 0.01.
Discussion
This analysis has shown that there are major differences in the demographic and health profiles of baby-boomer renters and non-renters, with those renting from the government more likely to be living alone, report being unable to work as their work status, have low education levels, be in the lowest quintile of socio-economic disadvantage, have a low income and have just enough money to exist each pay period. The health profile of renters (both private and public) was poorer overall, with renters more likely to have an increased risk of having all of the chronic conditions (except osteoporosis) and risk factors assessed. In most instances there was a trend from home-owners to private renters to public renters with, in all instances, the public renters having the worst health outcomes. For those publicly renting these relationships were maintained even after controlling for socio-economic and risk factor variables, while for those privately renting the relationships for CVD and mental health problems were maintained after adjustment.
The overall prevalence of baby-boomer renters (17.4%) is in line with ABS published figures, adding reliability to these results (ABS 2011). Of concern is the large number of dwellings this represents. As argued by Yates and Bradbury (Reference Yates and Bradbury2010), public housing is decreasing in number and scale and while private rental might have more attributes, affordability will be a major issue (AHURI 2008). While market forces determine renting costs, baby boomers will be indebted to this private market with little or no fall back, with the Australian Commonwealth Rent Assistance programme limited and not covering the gap when the more expensive private rental housing market is assessed (Cartwright Reference Cartwright2007). The demand for government-funded housing will increase, as will the need to diversify housing for this heterogeneous group. One questions whether the suitability, number, location, amenities, quality and variety of public housing in Australia will be sufficient to cover the requirements of this population into the future. These issues are compounded by current government policy aimed at keeping older people in their home rather than in a nursing home or similar accommodation offering assistance. Research has indicated that Australian baby boomers will want to live independently and within the community rather than residential aged care or retirement villages (Quine and Carter Reference Quine and Carter2006). They also do not want to be institutionalised or live with their children (Olsberg and Winters Reference Olsberg and Winters2005; Quine and Carter Reference Quine and Carter2006).
In common with other studies was the large proportion of one-person households who are renting (40.5 and 58.2% for private and government renters, respectively). As argued by Demey et al. (Reference Demey, Berrington, Evandrou and Falkingham2013), this group regularly lack social, economic and family resources; this is often particularly true for men in this situation. Notwithstanding, single women, frequently affected by inadequate superannuation funds, are also vulnerable (Snoke, Kendig and O'Loughlin Reference Snoke, Kendig and O'Loughlin2011). Research has shown that relationship breakdown is one of the most important reasons for renting status later in life and although women who are living alone are often satisfied with the arrangement, this is limited to those owning their home whereas women baby boomers who are renters are fearful for their future (Beer and Faulkner Reference Beer and Faulkner2009; Olsberg and Winters Reference Olsberg and Winters2005). Other major differences were also found between renters and home-owners in terms of family structure. The differences have implications for many other issues, including care-giving status, social isolation, availability of informal care and shared financial resources, indicating a need for further research in this area.
While health is a major concern for pre-retirement baby boomers, it is usually centred on maintaining optimal health for as long as possible (Hamilton and Hamilton Reference Hamilton and Hamilton2006; Humple et al. Reference Humple, O'Loughlin, Wells and Kendig2010; Hunter, Wang and Worsely Reference Hunter, Wang and Worsely2007). As this research has shown, the health of baby-boomer renters is already compromised. Comparisons with the latest Australian Census (2011/12) data indicate that the overall prevalence estimates obtained in this analysis for baby boomers are similar to Australian and SA estimates. What is of concern is the high prevalence estimates for all of the variables assessed for both of the renting groups. While baby-boomer renters may have future financial concerns regarding housing options, the concerns regarding decline in health should already have manifested. As argued by Hamilton and Hamilton (Reference Hamilton and Hamilton2006), lower-income retirees, including renters, will not be looking forward to a ‘golden age of freedom and relaxation’ as will the more affluent baby boomers.
Overall, self-reported health also shows marked variation by housing status, with nearly 50 per cent of government renters reporting fair or poor self-reported health. Previous research has found this question to be a strong indicator of future health-care use and mortality (Gill et al. Reference Gill, Taylor, Broderick, Avery and Dal Grande2009). Seen as a perceived health status measure, studies have shown relationships between social gradients of health and health equity although others have argued that self-reporting poor health is a justification for early retirement from the workforce or as an excuse for low income (Hungerford Reference Hungerford2007). Our cross-sectional study shows both high levels of non-employment and low income for the renting group but the study is not able to determine what came first – the poor health or the renting status.
The five social capital-related questions assessed in this research were not meant to cover the broad gamut of social capital but rather serve as indications of community and social life. The fact that a trend from home-ownership to private renter to public renters existed for the variables examined is reinforced by previous research that shows often renters are less connected to their neighbourhood and this can indicate some level of social exclusion (Hungerford Reference Hungerford2007). Coupled with this is the fact that budget rental accommodation is often not in sought-after areas, with the result that services can be compromised. Previous Australian research has shown dissatisfaction with safety and overall neighbourhoods for all renters (Parkinson et al. Reference Parkinson, Ong, Cigdem and Taylor2014), while our research has particularly indicated the dissatisfaction of the public housing renters.
Weaknesses of the study include the inability to determine the length of the renting experience, and the lack of measures of wealth and other financial determinants as opposed to income (Snoke, Kendig and O'Loughlin Reference Snoke, Kendig and O'Loughlin2011). While renting can be an indication of hardship, it does not provide information on the social and economic environment in which the person lives or the level of wealth. In addition, the cross-sectional nature of the data collection and the fact that the implications of cause and effect cannot be examined, is a weakness. This is important in this study, as we have no knowledge of whether the move to rental accommodation occurred so as to release funds for medical, health and personal care expenses. Beer and Faulker (Reference Beer and Faulkner2009) report that up to 85 per cent of private renters have previously been a home-owner or were paying off a home prior to their renting; this could not be assessed in this study. A further weakness of the study is the inability to determine whether the respondent was living rent-free or was paying rent to a friend or family who owned the dwelling. This would imply that the number renting privately may be an under-estimation. A strength of this study is being able to distinguish between private and public renters. While public renters are often seen as disadvantaged (Laaksonen, Tarkiainen and Martikainen Reference Laaksonen, Tarkiainen and Martikainen2009), we were able to show that the associations were apparent even after adjustment by socio-economic factors and, in most cases, the private rental group were also experiencing poor health outcomes.
Affordable, accessible and appropriate housing contributes to health and wellbeing (Demey et al. Reference Demey, Berrington, Evandrou and Falkingham2013). This research has provided empirical evidence of the considerable differences in health, socio-economic indicators and risk factors between baby boomers who rent and those who own, or are buying, their own homes. This analysis has added to the notion, as argued by others, that home-ownership status should be regarded as important an indicator as other commonly cited indicators, such as education level and income, when assessing health (Laaksonen, Tarkiainen and Martikainen Reference Laaksonen, Tarkiainen and Martikainen2009). The results of this research will fill important gaps for this sub-group of baby boomers who are going to put increased pressure on formal government support networks including health, housing and welfare (Martin et al. Reference Martin, Freedman, Schoeni and Andreski2009). This may be in conflict with the current government policy of increasing individual responsibility for old-age needs and support (Hamilton and Hamilton Reference Hamilton and Hamilton2006; Quine and Carter Reference Quine and Carter2006).
Acknowledgements
SAMSS is owned by the Department of Health and Ageing, SA, Australia. All collected source data are maintained and managed by Population Research & Outcome Studies, University of Adelaide. The opinions expressed in this work are those of the authors and may not represent the position or policy of the Department for Health and Ageing.






