Article contents
EPIDEMIC DYNAMICS ON RANDOM AND SCALE-FREE NETWORKS
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 30 January 2013
Abstract
Random networks were first used to model epidemic dynamics in the 1950s, but in the last decade it has been realized that scale-free networks more accurately represent the network structure of many real-world situations. Here we give an analytical and a Monte Carlo method for approximating the basic reproduction number 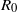 ${R}_{0} $ of an infectious agent on a network. We investigate how final epidemic size depends on
${R}_{0} $ of an infectious agent on a network. We investigate how final epidemic size depends on 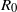 ${R}_{0} $ and on network density in random networks and in scale-free networks with a Pareto exponent of 3. Our results show that: (i) an epidemic on a random network has the same average final size as an epidemic in a well-mixed population with the same value of
${R}_{0} $ and on network density in random networks and in scale-free networks with a Pareto exponent of 3. Our results show that: (i) an epidemic on a random network has the same average final size as an epidemic in a well-mixed population with the same value of  ${R}_{0} $; (ii) an epidemic on a scale-free network has a larger average final size than in an equivalent well-mixed population if
${R}_{0} $; (ii) an epidemic on a scale-free network has a larger average final size than in an equivalent well-mixed population if 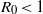 ${R}_{0} \lt 1$, and a smaller average final size than in a well-mixed population if
${R}_{0} \lt 1$, and a smaller average final size than in a well-mixed population if 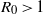 ${R}_{0} \gt 1$; (iii) an epidemic on a scale-free network spreads more rapidly than an epidemic on a random network or in a well-mixed population.
${R}_{0} \gt 1$; (iii) an epidemic on a scale-free network spreads more rapidly than an epidemic on a random network or in a well-mixed population.
MSC classification
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright ©2013 Australian Mathematical Society
References
- 7
- Cited by

