Colorectal cancer (CRC) is characterised by multiple chromosomal abnormalities. It is one of the best studied models representing the multistep nature of tumorigenesis. Sporadic CRC may develop through at least two independent pathways, i.e. the chromosomal instability (CIN) and the microsatellite instability (MIN) pathways. The CIN pathway is characterised by aneuploidy/polyploidy and mutations in APC, K-ras, p53 and DCC genes, and occasionally in SMAD2 and SMAD4 genes. The MIN pathway, on the other hand, is characterised by alterations in small stretches of short repetitive DNA sequences (microsatellites), and deficiency in DNA mismatch repair (MMR) which is often caused by promoter methylation of the MMR gene hMLH1 (Rashid et al. Reference Rashid, Zahurak, Goodman and Hamilton1999; Arnold et al. Reference Arnold, Goel and Compton2004). Colorectal carcinomas that evolve through the CIN or MIN pathways differ in several pathological features such as tumour sublocalisation, tumour differentiation and patient survival (Salahshor et al. Reference Salahshor, Kressner, Påhlman, Glimelius, Lindmark and Lindblom1999; Samowitz et al. Reference Samowitz, Holden and Curtin2001; Giaretti et al. Reference Giaretti, Venesio, Prevosto, Lombardo, Ceccarelli, Molinu and Risio2004; Lüchtenborg et al. Reference Lüchtenborg, Weijenberg, Wark, Saritas, Roemen, van Muijen, de Bruine, van den Brandt and de Goeij2005). This indicates that various environmental risk factors, such as dietary habits and lifestyle factors, may play a different role in the aetiology of CIN and MIN colorectal tumours.
The association between alcohol consumption and CRC has long been debated. Although alcohol itself is not carcinogenic, alcohol's first metabolite, acetaldehyde, is emerging as an important malefactor, being able to form stable DNA adducts, trigger mutations in tumour suppressors and oncogenes, and interfere with DNA repair (Poschl et al. Reference Poschl, Stickel, Wang and Seitz2004).
Several epidemiological studies have investigated associations between alcohol consumption and single genetic events involved in CRC, such as mutations in APC and K-ras genes, MIN and overexpression of p53 (Fredrikson et al. Reference Fredrikson, Axelson, Sun, Arbman, Nilsson, Nordenskjold, Sjodahl and Soderkvist1996; Slattery et al. Reference Slattery, Curtin, Anderson, Ma, Edwards, Leppert, Potter, Schaffer and Samowitz2000; Voskuil et al. Reference Voskuil, Kampman, Van Geloof, Grubben, Kok, Van Muijen, Nagengast, Vasen and van't Veer2000; Samowitz et al. Reference Samowitz, Holden and Curtin2001; Diergaarde et al. Reference Diergaarde, Braam, van Muijen, Ligtenberg, Kok and Kampman2003a, Reference Diergaarde, van Geloof, van Muijen, Kok and Kampmanb; Terry et al. Reference Terry, Neugut, Mansukhani, Waye, Harpaz and Hibshoosh2003). Although these studies focused merely on a single gene and their results are not consistent, all positive associations that were found linked alcohol consumption to colorectal carcinomas harbouring the mutated version of the studied gene, but not the wild-type version. What needs further elucidation are the aetiological pathway(s) by which alcohol consumption may contribute to colorectal tumorigenesis.
Our aim was to study the associations between alcohol consumption and the risk of CRC in subgroups of tumours, according to their genetic and molecular aberrations. We defined CIN+ tumours as colorectal tumours with either a truncating APC mutation, an activating K-ras mutation or overexpression of p53, since these genes can be considered as key genes of the CIN pathway. MIN+ tumours were defined according to a key feature of the MIN pathway, i.e. lack of hMLH1 expression. A third group of colorectal tumours was identified as CIN− /MIN− , i.e. tumours without the genetic and molecular aberrations characteristic for the CIN+ and MIN+ tumours.
The current study was conducted within the ongoing Netherlands Cohort Study on diet and cancer, and is the first to study alcohol consumption and subgroups of colorectal tumours, based on independent aetiological pathways of disease.
Materials and methods
Study population
In September 1986, the Netherlands Cohort Study on diet and cancer was initiated (van den Brandt et al. Reference van den Brandt, Goldbohm, van't Veer, Volovics, Hermus and Sturmans1990a). Briefly, 120 852 men and women, aged 55–69 years and originating from 204 municipal population registries throughout the country completed an extensive self-administered questionnaire on daily dietary habits, lifestyle and other risk factors for cancer. Newly diagnosed cancer cases were identified through annual record linkage to the Netherlands Cancer Registry and to PALGA, a nationwide database of histo- and cytopathology reports (van den Brandt et al. Reference van den Brandt, Schouten, Goldbohm, Dorant and Hunen1990b).
The present analyses were carried out over a 7·3-year period of follow-up, excluding the first 2·3 years. Hence, 925 histologically confirmed CRC cases were identified between January 1989 and January 1994, of whom 815 could be linked to a PALGA report of the lesion.
Data processing and analysis were done according to the case–cohort approach: cases were identified in the entire cohort, while a random sample of the cohort (subcohort) was used to estimate person-years at risk accumulating in the cohort. A subcohort of 5000 men and women was followed-up biennially to assess information on vital status and migration. Prevalent cancer cases, other than non-melanoma skin cancer, were excluded from the subcohort, as well as subjects who were deceased or were diagnosed with cancer during the first 2·3 years of follow-up. This left 4673 subcohort members for analyses.
Assessment of exposure
Information on alcohol consumption was obtained from the baseline questionnaire, which comprised a 150-item semi-quantitative FFQ. This questionnaire has been validated against a 9 d diet record (Goldbohm et al. Reference Goldbohm, van den Brandt, Brants, van't Veer, Al, Sturmans and Hermus1994). The Spearman correlation coefficient between mean daily alcohol consumption assessed by the questionnaire and estimated from the 9 d diet record was 0·89 for all subjects and 0·85 for users of alcoholic beverages. The absolute amount of alcohol consumption reported in the questionnaire by users of alcoholic beverages was, on average, 86 % of that reported in the 9 d diet record.
Tissue samples and molecular analyses
Of the 815 eligible CRC cases, 771 formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue blocks could be retrieved from Dutch pathology archives. Samples that did not contain carcinoma tissue were excluded. As previously described, tissue samples of 734 CRC cases were available for molecular analyses of K-ras (Brink et al. Reference Brink, de Goeij, Weijenberg, Roemen, Lentjes, Pachen, Smits, de Bruine, Goldbohm and van den Brandt2003) and APC (Lüchtenborg et al. Reference Lüchtenborg, Weijenberg, Roemen, de Bruïne, van den Brandt, Lentjes, Brink, van Engeland, Goldbohm and de Goeij2004) genes, and immunohistochemical staining of hMLH1 (Lüchtenborg et al. Reference Lüchtenborg, Weijenberg, Wark, Saritas, Roemen, van Muijen, de Bruine, van den Brandt and de Goeij2005) and p53.
Immunohistochemical staining for p53 was performed on archival adenocarcinoma specimens of all 734 CRC cases according to the avidin–biotin–peroxidase complex method, using the DO-7 mouse monoclonal antibody (DAKO A/S, Denmark). Immunostained slides and negative controls were evaluated semi-quantitatively and independently by two observers without knowledge of clinical parameters. We defined cases positive for overexpression of p53 if 20 % or more of the tumour cell nuclei showed positive staining with the antibody.
Statistical analysis
All subjects with complete information on alcohol consumption and confounding variables derived from the baseline questionnaire, and CRC cases for whom information on APC, K-ras, p53 and hMLH1 status was also known, were included in the statistical analysis (4076 subcohort members and 573 CRC cases).
Incidence risk ratios (RR) and corresponding 95 % confidence intervals (CI) were estimated using Cox proportional hazards models. Total alcohol consumption was divided into three categories: 0, < 30·0 and ≥ 30·0 g/d, in line with the results of a recent pooled analysis that suggested a threshold in alcohol consumption above which the risk of CRC increases (Cho et al. Reference Cho, Smith-Warner and Ritz2004). Consumption of beer, wine and liquor were considered dichotomously. Analyses were adjusted for age at baseline (years), sex, BMI (kg/m2), family history of CRC (yes v. no), daily intakes of total energy (kJ/d), linoleic acid (g/d) and calcium (mg/d), and smoking (never, ex, current smoker). The analyses of the alcoholic beverages were additionally adjusted for total alcohol intake (categorised as 0, < 30·0 and ≥ 30·0 g/d), to evaluate the role of the specific beverage independently of its alcoholic content. The analyses were performed using the STATA statistical software package (version 9.1).
Results
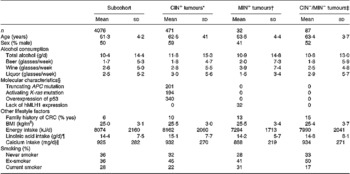
Table 1 shows drinking habits and baseline characteristics of the subcohort and CRC cases classified according to the studied genetic and molecular defects. Of the 471 CIN+ colorectal tumours, 38 (8 %) tumours only had a truncating APC mutation, 46 (9 %) only had an activating K-ras mutation and 168 (36 %) tumours only showed overexpression of p53. In addition, 174 (37 %) of the CIN+ tumours had two of the described aberrations and 45 (10 %) had all three aberrations. Compared with the CIN+ cases, the MIN+ cases comprised significantly more female cases, had fewer liquor consumers and a lower daily intake of total energy. No differences in drinking habits or baseline characteristics between the CIN− /MIN− cases and both CIN+ and MIN+ cases were observed.
Table 1 Drinking habits and baseline characteristics (mean and sd) of the subcohort members and subgroups of CRC characterized by specific genetic and molecular aberrations, the Netherlands Cohort Study (1986–1993)(Mean values and standard deviations)
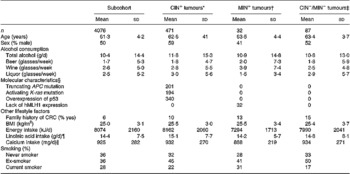
CRC, colorectal cancer; CIN, chromosome instability; MIN, microsatellite instability.
* Defined as colorectal tumours presenting either a truncating APC mutation, an activating K-ras mutation or overexpression of p53.
† Defined as colorectal tumours presenting lack of hMLH1 expression only.
‡ Defined as colorectal tumours presenting no truncating APC mutation, nor an activating K-ras mutation, overexpression of p53 or lack of hMLH1 expression.
§ Of the CIN+ tumours, thirty-eight harboured a truncating APC mutation only, forty-six an activating K-ras mutation only and 168 only showed overexpression of p53. In addition, 174 CIN+ tumours harboured two of these aberrations and forty-five harboured all three aberrations.
¶ Adjusted for total energy intake.
∥ Adjusted for energy intake from dairy products.
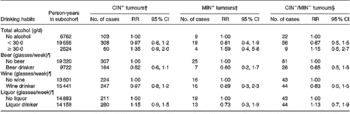
Table 2 reports the RR and 95 % CI for total alcohol consumption and different types of alcoholic beverages, and the risk of CRC according to the presence or absence of specific genetic and molecular aberrations. Compared with abstaining, consumption levels of total alcohol ≥ 30 g/d were associated with an increased risk of CRC irrespective of genetic or molecular aberrations present, although statistical significance was not reached (RR: 1·35 (95 % CI: 0·9–2·0) for the CIN+ tumours, RR: 1·59 (95 % CI: 0·4–5·8) for the MIN+ tumours and RR: 1·15 (95 % CI: 0·5–2·7) for the CIN− /MIN− tumours). Beer, wine and liquor consumption, after adjustment for total alcohol intake, showed no clear relationship with CIN+, MIN+ and CIN− /MIN− tumours.
Table 2 Incidence rate ratios for subgroups of colorectal cancer characterized by specific genetic and molecular aberrations, according to drinking habits, adjusted for confounders*, the Netherlands Cohort Study (1986–1993)
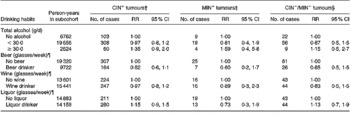
CIN, chromosome instability; MIN, microsatellite instability; RR, rate ratio; CI, confidence interval.
* Adjusted for age (years), sex, BMI (kg/m2), family history of colorectal cancer (yes/no), daily energy intake (kJ/d), daily linoleic acid intake (g/d), daily calcium intake (mg/d) and smoking (never, ex, current).
† Defined as colorectal tumours presenting either a truncating APC mutation, an activating K-ras mutation or overexpression of p53.
‡ Defined as colorectal tumours presenting lack of hMLH1 expression only.
§ Defined as colorectal tumours presenting no truncating APC mutation, nor an activating K-ras mutation, overexpression of p53 or lack of hMLH1 expression.
¶ Additionally adjusted for categories of total alcohol consumption (0, < 30·0, ≥ 30·0 g/d).
Discussion
We investigated associations between alcohol consumption and the risk of CRC by involvement of the CIN and MIN aetiological pathways in a large prospective study. In this study, we defined CIN+ tumours as tumours harbouring either a truncating APC mutation, an activating K-ras mutation or overexpression of p53, and the MIN+ tumours as tumours lacking expression of hMLH1. A third group of colorectal tumours did not harbour any of these defects and was defined as CIN− /MIN− . Our results indicate that, compared with abstaining, alcohol consumption levels ≥ 30 g/d were associated with an increased risk of CRC, which was observed in all three subgroups, although statistical significance was not reached. Within all three subgroups, no associations were observed between different alcoholic beverages adjusted for total alcohol consumption, and the risk of CRC.
In line with the present results, positive associations between alcohol consumption and CRC with single genetic or molecular aberrations have been reported for colorectal tumours that showed overexpression of p53 and colon tumours with MIN (Fredrikson et al. Reference Fredrikson, Axelson, Sun, Arbman, Nilsson, Nordenskjold, Sjodahl and Soderkvist1996; Samowitz et al. Reference Samowitz, Holden and Curtin2001; Diergaarde et al. Reference Diergaarde, Braam, van Muijen, Ligtenberg, Kok and Kampman2003a; Terry et al. Reference Terry, Neugut, Mansukhani, Waye, Harpaz and Hibshoosh2003), but not for colon tumours harbouring mutations in the APC and K-ras genes (Slattery et al. Reference Slattery, Curtin, Anderson, Ma, Edwards, Leppert, Potter, Schaffer and Samowitz2000; Diergaarde et al. Reference Diergaarde, van Geloof, van Muijen, Kok and Kampman2003b). We performed additional analyses for alcohol consumption and the risk of CRC in which we considered each genetic or molecular aberration independently of any other simultaneously present genetic or molecular aberration(s), but the results of these analyses did not alter our present conclusions.
The pathological effects of alcohol consumption on the colorectal tract have been extensively investigated but still remain largely unclear. Evidence exists for the involvement of acetaldehyde (Taylor & Rehm, Reference Taylor and Rehm2005), but also other mechanisms have been linked to CRC, e.g. the induction of reactive oxygen species through the induction of cytochrome P-450 2E (Badger et al. Reference Badger, Ronis, Seitz, Albano, Ingelman-Sundberg and Lieber2003; Seitz et al. Reference Seitz, Maurer and Stickel2005; Boffetta & Hashibe, Reference Boffetta and Hashibe2006). Other molecular changes seen in CRC involve alterations in DNA methylation, e.g. induction of expression of oncogenes and silencing of tumour suppressor genes. Choi et al. (Reference Choi, Stickel, Baik, Kim, Seitz and Mason1999) demonstrated that chronic alcohol consumption causes genomic DNA hypomethyation in rats, whereas no effect was seen on the methylation status of the tumour suppressor gene p53. Next to effects at the genomic level, alcohol may also affect the colorectal mucosa. As shown in experimental studies, decreasing cell numbers in the functional compartment of the colonic crypt through acetaldehyde, trigger compensatory hyper-regeneration with increased crypt cell production rates and extension of the proliferative compartment towards the lumen of the crypt (Seitz et al. Reference Seitz, Simanowski, Garzon, Rideout, Peters, Koch, Berger, Einecke and Maiwald1990; Simanowski et al. Reference Simanowski, Homann, Knuhl, Arce, Waldherr, Conradt, Bosch and Seitz2001). Mucosal hyper-regeneration, regardless of the underlying cause, is strongly associated with CRC risk. Many of the above-described processes have been observed in heavy or chronic alcohol consumers. The amount of damage related to alcohol tends to follow a dose–response relationship and, as such, (very) high levels of daily alcohol intake may be needed for genetic mutations to occur. Moderate consumption levels, as in our study population, might thus not be able to increase CRC risk through causing specific genetic or molecular aberrations. In addition, besides adverse effects of alcohol consumption, the entire nutritional status in heavy drinkers may be impaired due to malnutrition and intestinal absorption, increasing the cancer risk even more.
The strengths of our study include a population-based and prospective design. In addition, the high completeness of follow-up of cancer incidence and subcohort members precluded minimal recall and selection biases. Although the CIN and MIN pathways also involve aberrations other than the ones that were included in the current study, APC, K-ras and p53 are key genes of the CIN pathway, as hMLH1 is a key gene of the MIN pathway. Our study is currently the first prospective study that investigated the association between alcohol consumption and distinct CRC subgroups. Nevertheless, it should be noted that the numbers of CRC cases in certain subgroups are small and results should be interpreted with caution.
In conclusion, our results indicate that a daily alcohol consumption of ≥ 30 g is positively associated with the risk of CRC. This increase in risk was observed independent of the presence or absence of the genetic and molecular aberrations we studied to distinguish between aetiological pathways.
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to the participants of this study and further thank the regional cancer registries (IKA, IKL, IKMN, IKN, IKO, IKR, IKST, IKW, IKZ and VIKC), and the Netherlands nationwide registry of pathology (PALGA). We also thank all the Dutch pathology laboratories for their cooperation in providing the tissue blocks, Dr M. Brink for the collection of tissue samples, Dr A. de Bruïne for expert pathological advice, Dr M. Brink, Dr M. Lüchtenborg, P. Wark, G. Roemen, K. Wouters and Dr M van Engeland for molecular analyses, Dr L. Schouten, S. van de Crommert, H. Brants, J. Nelissen, C. de Zwart, M. Moll, W. van Dijk, M. Jansen and A. Pisters for data management, and H. van Montfort, T. van Moergastel, L. van den Bosch and R. Schmeitz for programming assistance. Finally, we thank Dr A. Volovics and Dr A. Kester for statistical advice. Financial support for collection of tumour material and mutation analyses was provided by a grant from the Dutch Cancer Society and financial support for the current study is provided by a grant from the European Research Advisory Board (ERAB).