Physical fitness is associated with decreased risks of high blood pressure, dyslipidaemia and insulin resistance in children(Reference Froberg and Andersen1), which in turn result in lowered risk of CVD and metabolic disorders during adulthood. Physical fitness during adolescence has also been related to a healthier cardiovascular profile in adulthood(Reference Twisk, Kemper and van Mechelen2).
National standardised physical fitness tests for children are conducted in many countries(Reference Malina and Katzmarzyk3). A battery of tests is often included to evaluate both aerobic and anaerobic performance-related fitness. According to reviews of studies in children worldwide, performance in these tests has declined during the past three decades(Reference Tomkinson4, Reference Tomkinson and Olds5). This may be partly attributed to the increased prevalence of overweight and obesity that many countries are experiencing.
In several countries that are undergoing the nutritional transition, the increasing prevalence of overweight and obesity coexists with substantial rates of malnutrition(Reference Doak, Adair and Monteiro6, Reference Duran, Caballero and de Onis7). The role that marginal malnutrition could play in performance-related fitness of children has not been studied extensively. Stunted children have short lower extremities that may have a negative impact on performance in run or jump tests, but they may also have low muscle mass or poor micronutrient status that could negatively affect performance. Lower performance scores in fitness tests have been reported among stunted children compared with non-stunted children(Reference Benefice, Fouere and Malina8, Reference Prista, Ribeiro Maia and Damasceno9). Fe-deficiency anaemia results in reduced performance(Reference Hinton, Giordano and Brownlie10, Reference Rowland, Deisroth and Green11), and physical training can decrease body Fe stores(Reference Beard and Tobin12). However, few studies have examined other micronutrients that are associated with anaemia, such as folate or vitamin B12, in relation to performance-related fitness. In adolescents, elevated homocysteine, which is associated with folate and vitamin B12 deficiencies, was related to reduced cardiovascular fitness(Reference Ruiz, Sola and Gonzalez-Gross13). Children receiving a fortified beverage that provided Fe, folate, vitamin B12 and other micronutrients showed significantly improved fitness compared with children receiving a beverage without micronutrients(Reference Solon, Sarol and Bernardo14).
We conducted a cross-sectional study to examine the associations between anaerobic performance-related fitness and anthropometric and micronutrient status indicators in schoolchildren from Bogotá, Colombia. Colombia is a country undergoing a nutritional transition, from high rates of under-nutrition to increasing rates of overweight. Non-negligible rates of stunting, overweight or obesity and micronutrient deficiencies in this cohort of children have previously been reported(Reference Arsenault, Mora-Plazas and Forero15–Reference Dekker, Mora-Plazas and Marín18). We hypothesised that children with suboptimal nutritional status (stunting, overweight or low micronutrient status) would have lower scores on anaerobic fitness tests than children with adequate nutritional status.
Experimental methods
Study population
The present study is part of a project on children's health and nutritional status in primary public schools of Bogotá, Colombia, which was initiated in 2006. Details of the study design have been reported previously(Reference Arsenault, Mora-Plazas and Forero19). In brief, we randomly selected a representative sample of 3202 primary schoolchildren of age 5–12 years, using a cluster sampling strategy in which all primary public schools in the city were included. The sampling units were the classrooms. Recruitment occurred at the beginning of the school year, in February 2006. The sample is representative of low- and middle-income families from Bogotá, since the public primary school system enrols the majority of school-age children, and close to 90 % of them belong to low- and middle-socioeconomic strata. The present study was conducted according to the guidelines laid down in the Declaration of Helsinki, and all procedures involving human subjects were approved by the Ethics Committee of the National University of Colombia Medical School. The Human Subjects Committee at the Harvard School of Public Health approved the use of data from the study. Written informed consent was obtained from the children's primary care providers before enrolment.
Field procedures
At the time of enrolment, information was obtained on the parents' sociodemographic characteristics, including age, marital status, education level and indicators of the household socio-economic status, using a self-administered questionnaire that was completed and returned by 2466 households, representing 81 % of enrolled children's families. During the 3 weeks following recruitment, teams of trained research assistants visited the schools to obtain a fasting blood specimen by venepuncture from enrolled children and to collect anthropometric measurements using standardised techniques(Reference Lohman, Roche and Martorell20). Weight was measured to the nearest 0·1 kg on Tanita HS301 electronic scales (Tanita, Tokyo, Japan), while height was measured to the nearest 1 mm using wall-mounted portable Seca 202 stadiometers (Seca, Hamburg, Germany). Arm circumference was measured to the nearest 0·1 cm using a non-extensible tape. Triceps skinfolds were measured to the nearest 0·5 mm using Slim Guide Skinfold Calipers (Creative Health Products, Inc., Plymouth, MI, USA).
Also during this period, teams of physical trainers administered two standardised physical fitness tests in a subgroup of 1945 students: the shuttle run and the standing long jump. These tests are part of the ‘Eurofit’ battery of fitness tests that include endurance, strength, speed, flexibility and balance(21). The shuttle run is a test of speed and agility, and the standing long jump is a test of explosive power and leg strength; both are measures of anaerobic performance-related fitness primarily. For the shuttle run, children were instructed to stand on a line, run a distance of 9 m at maximum speed to a reference point and pick up a block, turn and run back to the starting line, place the block down, and repeat this course a second time (for a total distance of 36 m). The run time was recorded to the nearest 0·01 s using digital stopwatches when the child returned to the starting line and placed the second block down. For the standing long jump, children were instructed to stand on a marked line and jump as far as possible from the standing position, using their arms for balance. The jump distance was recorded to the nearest 1·0 cm. Each test was administered three times, and results from the three attempts were recorded.
Laboratory methods
Approximately 4 ml of blood were collected in EDTA tubes following a protocol to avoid haemolysis. On the same day of collection, the aliquots were protected from sunlight and transported on ice to the National Institute of Health in Bogotá, where all biochemistry analyses took place. Complete blood counts were obtained, and Hb concentrations were determined using the haemiglobincyanide method. An aliquot was centrifuged at 1500 g for 15 min, and plasma was separated. Plasma ferritin and vitamin B12 concentrations were measured using competitive chemiluminescent immunoassay in an ADVIA Centaur analyser (Bayer Diagnostics, Tarrytown, NY, USA). C-reactive protein was measured using a turbidimetric immunoassay on an ACS180 analyser (Bayer Diagnostics). The packed erythrocyte volume was haemolysed by dilution in a hypotonic aqueous solution of 1 % ascorbic acid. Erythrocyte folate was measured on the erythrocyte lysates using chemiluminescent immunoassay.
Data analyses
Outcomes were the shuttle run score (s) and the standing long jump score (cm). We chose the best result from each child's three attempts for analyses. Both outcomes were treated as continuous variables. Henceforth, a ‘higher’ score refers to a lower run time or a further jump distance.
The main exposures of interest were anthropometric and micronutrient status indicators. Anthropometric indicators included stunting, thinness, overweight, obesity, and arm muscle and fat area. Child stunting was defined as height-for-age < − 2 standard deviations from the sex- and age-specific median of the National Center for Health Statistics/WHO reference population(22). Thinness was defined based on the BMI-for-age and sex cut-off point corresponding to < 18·5 kg/m2 in adults as proposed by Cole et al. (Reference Cole, Flegal and Nicholls23). Overweight or obese was defined according to BMI cut-off points for age and sex corresponding to ≥ 25 kg/m2 in adults, following the International Obesity Task Force recommendations(Reference Cole, Bellizzi and Flegal24). Mid-upper arm muscle area (an index of total body muscle mass) and arm fat area (an index of body fat) were calculated using equations that include the arm circumference and triceps skinfold measures(Reference Gibson25). Age- and sex-adjusted z-scores for the arm muscle and fat areas were calculated using the study population as the reference and then were categorised into quartiles. Indicators of micronutrient status were anaemia, ferritin (an indicator of Fe stores), vitamin B12 serostatus and erythrocyte folate concentrations. Anaemia was defined as Hb < 115 g/l, after subtracting 12 g/l from the individual values as an adjustment for an altitude of 2500 m(Reference Nestle26). Low ferritin was defined as < 15 μg/l if C-reactive protein ≤ 10 mg/l or < 30 μg/l if C-reactive protein >10(Reference Zimmermann and Hurrell27). Vitamin B12 status was defined as normal (>221 pmol/l) or marginal or low ( ≤ 221 pmol/l)(Reference Jones, Ramirez-Zea and Zuleta28). Erythrocyte folate concentrations were categorised into quartiles since only two children were below 305 nmol/l, a cut-off point suggested by the Institute of Medicine(29) to define deficiency.
Child and maternal characteristics were considered as covariates in the analysis. Child characteristics included age, sex and time spent playing outdoors as a measure of habitual physical activity. Maternal characteristics included age, education level and parity. Household socio-economic indices included the daily income per capita (household income divided by the household size) and the household socio-economic stratum according to the city's classification of the neighbourhoods’ public service fees.
We first compared the distribution of run and jump scores by categories of each sociodemographic characteristic using univariate linear regression models, in which the physical performance test score was introduced as the outcome and each characteristic as the predictor. For ordinal predictors, a test for trend was conducted by introducing a variable representing the ordinal categories of the predictor in the linear model as a continuous covariate. In order to identify sociodemographic covariates that were independently associated with fitness scores and thus could potentially confound their associations with nutritional status indicators, we constructed a multivariate model including the variables that were significantly associated with each test at P < 0·10 in univariate analyses. Predictors were retained in the model if they remained statistically significant at P < 0·05 or were considered to be relevant from a mechanistic viewpoint.
We then examined the associations between each of the anthropometric or micronutrient status indicators and the physical performance tests. Based on established sex differences in physical performance(Reference Benefice, Fouere and Malina8, Reference Prista, Ribeiro Maia and Damasceno9), which we verified with the present results, the analyses were stratified by sex. Differences in test scores and 95 % CI were calculated between categories of each nutritional predictor using multivariate linear models, which included significant sociodemographic correlates of each test as adjustment covariates. Micronutrient status indicators were included simultaneously into the same model to obtain estimates that were independent of each other. Finally, interactions were assessed among micronutrients on test scores by introducing into the models cross-product terms between the indicators and testing them with the likelihood-ratio test. CI were constructed with robust estimates of the variance, which do not require normality assumptions. In all models, an exchangeable correlation matrix (PROC GENMOD, SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA) was specified to account for potential correlations within households among siblings. The effect of clustering from the sampling strategy was also considered in the models, but it was negligible and excluded for parsimony. All tests were double-sided and considered to be statistically significant if P ≤ 0·05. Analyses were performed using the Statistical Analysis System (release 9.1; SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA).
Results
Among the 1945 children in whom fitness tests were conducted, shuttle run and long jump scores were available in 1894 and 1939, respectively. Some of the tests could not be administered in all schools for logistical reasons. On average, children in whom tests were performed were 0·3 years older (P < 0·0001), played outside 0·9 h/week less (P = 0·01) and had mothers who were 1 year older (P = 0·0005) than children in whom performance tests were not done. There were no differences regarding sex or socio-economic factors. The mean age of the children was 8·9 years. Each of the test scores was positively associated with age (P for trend < 0·0001). Boys ran faster (P < 0·0001) and jumped further (P < 0·0001) than girls (Table 1). Performance in both tests was positively associated with indicators of socio-economic status. In addition, jump scores were positively associated with time spent playing outdoors (P for trend = 0·02). The scores from the two tests were positively correlated with each other, independent of age and sex (partial r − 0·36, P < 0·0001; coefficient term is negative because a lower run time is a ‘higher’ score).
Table 1 Sociodemographic correlates of shuttle run and standing long jump scores in schoolchildren from Bogotá, Colombia
(Mean values, standard deviations, number of children and 95 % confidence intervals)

Q, quartile; Ref, reference.
* Estimates are from a multivariate linear generalised estimating equation model. Only estimates for variables retained in the final model are presented. Note: Negative estimates for the shuttle run time correspond to ‘faster’ run times and are considered as ‘higher’ scores.
† Standard error for a 1-year change in age.
Stunted children of both the sexes ran significantly slower than non-stunted children (0·4 s; P = 0·0002), after adjustment for age, socio-economic status, BMI and arm muscle area (Table 2). Stunted boys scored 6 cm lower in the standing long jump test than non-stunted boys (P = 0·003; Table 3). Children who were either thin, overweight or obese ran 0·3 s slower than normal-weight children (P < 0·01). Thin girls scored significantly lower in the jump test than normal-weight children of the same sex (P = 0·01). Arm fat area was negatively associated with run performance in both girls (P for trend = 0·002) and boys (P for trend = 0·0004). Overweight or obesity was negatively associated with jump scores in boys (P < 0·0001). Boys in the highest quartile of arm fat area had lower jump scores than those in the lowest quartile (P < 0·0001).
Table 2 Anthropometric correlates of shuttle run scores in schoolchildren from Bogotá, Colombia
(Mean values, standard deviations, number of children and 95 % confidence intervals)
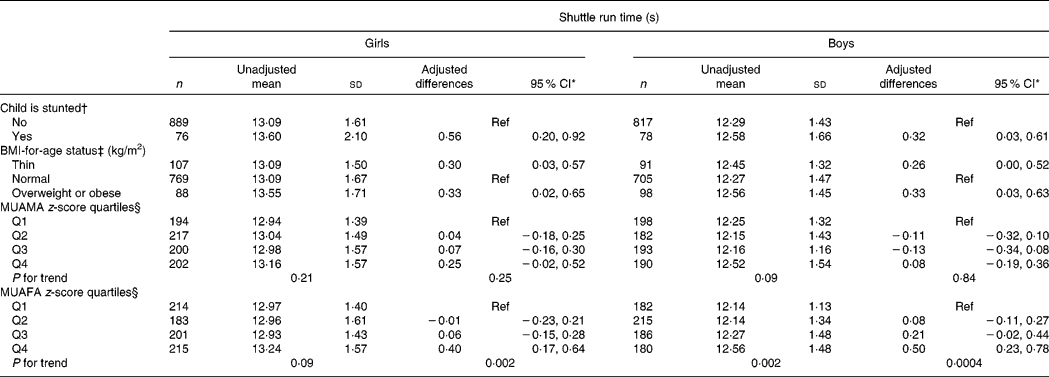
Ref, reference; MUAMA, mid-upper arm muscle area; MUAFA, mid-upper arm fat area; HAZ, height-for-age.
* Estimates are from linear generalised estimating equation models with covariates that included age and household socio-economic stratum. Other covariates included in models with each anthropometric status indicator were as follows: BMI status and MUAMA z-score in the model with ‘child is stunted’; HAZ and MUAMA z-score in the model with ‘BMI-for-age status’; HAZ and MUAFA z-score in the model with ‘MUAMA z-score quartiles’; HAZ and MUAMA z-score in the model with ‘MUAFA z-score quartiles’. Note: negative estimates for the shuttle run time correspond to ‘faster’ run times and are considered as ‘higher’ scores.
† Stunted is defined as HAZ < − 2 from the sex- and age-specific median of the National Center for Health Statistics/WHO reference population(22).
‡ Thinness is defined as BMI-for-age and sex below the cut-off point corresponding to < 18·5 kg/m2 in adults(Reference Cole, Flegal and Nicholls23); overweight and obese are defined according to BMI cut-off points for age and sex corresponding to ≥ 25 kg/m2 in adults(Reference Cole, Bellizzi and Flegal24).
§ MUAMA and MUAFA were calculated based on arm circumference and triceps skinfolds and standardised for age and sex using the study population.
Table 3 Anthropometric correlates of standing long jump scores in schoolchildren from Bogotá, Colombia
(Mean values, standard deviations, number of children and 95 % confidence intervals)

Ref, reference; MUAMA, mid-upper arm muscle area; MUAFA, mid-upper arm fat area; HAZ, height-for-age.
* Estimates are from linear generalised estimating equation models with covariates that included age, household socio-economic stratum, hours spent playing outdoors per week and household per capita income. Other covariates included in models with each anthropometric status indicator were as follows: BMI status and MUAMA z-score in the model with ‘child is stunted’; HAZ and MUAMA z-score in the model with ‘BMI-for-age status’; HAZ and MUAFA z-score in the model with ‘MUAMA z-score quartiles’; HAZ and MUAMA z-score in the model with ‘MUAFA z-score quartiles’.
† Stunted is defined as HAZ < − 2 from the sex- and age-specific median of the National Center for Health Statistics/WHO reference population(22).
‡ Thinness is defined as BMI-for-age and sex below the cut-off point corresponding to < 18·5 kg/m2 in adults(Reference Cole, Flegal and Nicholls23); overweight and obese are defined according to BMI cut-off points for age and sex corresponding to ≥ 25 kg/m2 in adults(Reference Cole, Bellizzi and Flegal24).
§ MUAMA and MUAFA were calculated based on arm circumference and triceps skinfolds and standardised for age and sex using the study population.
Anaemic children did not differ significantly from non-anaemic children in test scores (Table 4). Girls with low ferritin, an indicator of Fe stores, scored significantly lower in the run test than girls with normal ferritin (0·6 s; P = 0·02), but in boys the difference did not reach significance (0·5 s; P = 0·06). Boys with low ferritin had 7 cm lower jump scores than boys with normal ferritin (P = 0·03; Table 5). Erythrocyte folate concentrations were significantly, independently and linearly related to higher run scores in both girls (P for trend = 0·0005) and boys (P for trend = 0·009). Erythrocyte folate concentrations were also linearly associated with jump scores in both girls (P for trend = 0·01) and boys (P for trend = 0·003). Children in the highest quartile of folate jumped 4 cm further than children in the lowest quartile of the same sex (females, P = 0·02; males, P = 0·007). Boys who had marginal or low vitamin B12 status had 4 cm lower jump scores (P = 0·01) than boys with normal B12 status.
Table 4 Micronutrient status correlates of shuttle run scores in schoolchildren from Bogotá, Colombia
(Mean values, standard deviations, number of children and 95 % confidence intervals)
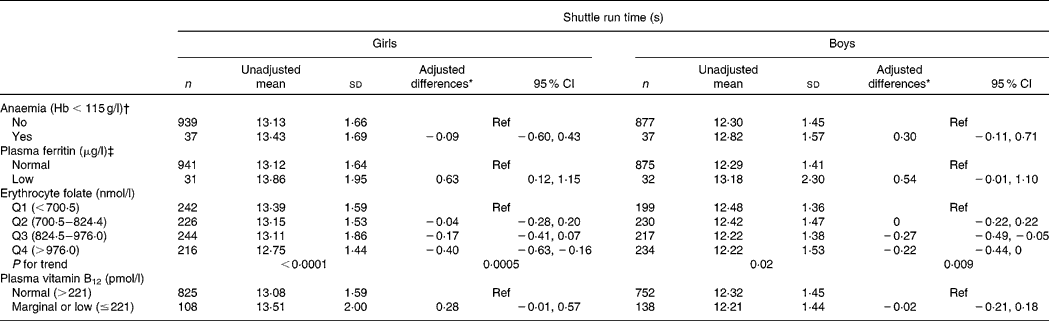
Q, quartile; Ref, reference; HAZ, height-for-age; CRP, C-reactive protein.
* Estimates are from a multivariate linear general estimating equation model with covariates that include age, household socio-economic stratum, HAZ, BMI-for-age status, plasma ferritin, folate quartiles and plasma vitamin B12. Note: Negative estimates for shuttle run time correspond to ‘faster’ run times and are considered as ‘higher’ scores.
† After subtracting 12 g/l from the individual values as an adjustment for an altitude of 2500 m(Reference Nestle26).
‡ Low ferritin was defined as < 15 μg/l if the concentration of CRP was ≤ 10 mg/l or < 30 μg/l if CRP >10 mg/l(Reference Zimmermann and Hurrell27).
Table 5 Micronutrient status correlates of standing long jump scores in schoolchildren from Bogotá, Colombia
(Mean values, standard deviations, number of children and 95 % confidence intervals)
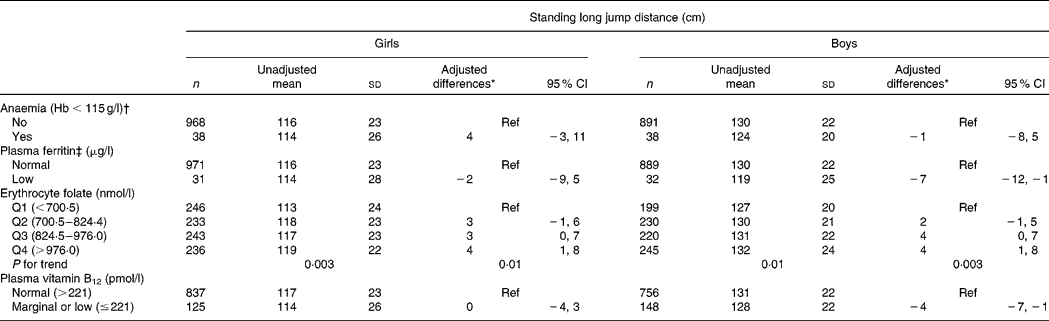
Q, quartile; Ref, reference; HAZ, height-for-age; CRP, C-reactive protein.
* Estimates are from a multivariate linear general estimating equation model with covariates that include age, household socio-economic stratum, hours spent playing outdoors per week, household per capita income, HAZ, BMI-for-age status, plasma ferritin, folate quartiles and plasma vitamin B12.
† After subtracting 12 g/l from the individual values as an adjustment for an altitude of 2500 m(Reference Nestle26).
‡ Low ferritin was defined as < 15 μg/l if the concentration of CRP was ≤ 10 mg/l or < 30 μg/l if CRP >10 mg/l(Reference Zimmermann and Hurrell27).
There were no significant interactions between micronutrients for any of the outcomes among all the children; there were too few children in some of the categories to test for interactions by sex. In supplemental analysis, we examined whether the associations between stunting and the test scores were confounded by micronutrient status, given that micronutrient deficiencies could cause linear growth retardation. After controlling for micronutrient concentrations, the associations between stunting and fitness scores remained unchanged. In addition, there were no interactions between stunting and the micronutrients.
Discussion
In the present study, we examined cross-sectional associations of anthropometric indices and biomarkers of micronutrient status with performance-related fitness indicators in a large representative sample of low- and middle-income schoolchildren from Bogotá, Colombia. We found negative associations between stunting, overweight or obesity, and arm fat area and anaerobic performance. With respect to micronutrients, there were significant trends in higher run and jump scores with higher erythrocyte folate concentrations, despite negligible folate deficiency. In male children, marginal or low vitamin B12 status was associated with lower long jump scores than children with normal status.
Our finding of a positive association between folate status and anaerobic performance-related fitness is novel. The few studies that have been reported on folate status and exercise performance have focused on aerobic performance. Higher serum folate concentrations were reported in more highly trained athletes compared with less trained athletes(Reference Konig, Bisse and Deibert30), yet folate supplementation of folate-deficient female marathon runners had no effect on aerobic capacity or running time(Reference Matter, Stittfall and Graves31). Despite the lack of folate deficiency in the present study population, presumably due to folic acid fortification of wheat flour in Colombia, we found a linear association between erythrocyte folate and anaerobic performance indicators. Although it is unclear how folate could affect anaerobic performance, one possible mechanism may be via creatine, a reservoir for high-energy phosphate bonds that are needed for ATP synthesis at the onset of intense exercise, because folate is needed for the methylation of S-adenosylmethionine, which serves as a methyl donor for creatine biosynthesis.
Vitamin B12 could also potentially affect both aerobic and anaerobic performance-related fitness through the same mechanisms as folate. We found a positive association between vitamin B12 status and jump scores among boys only but no associations with shuttle run scores. The jump test is a test of explosive power and may require more muscle strength than the run, consistent with a possible role of vitamin B12 in creatine synthesis and muscle function. Supplementation studies conducted so far do not support a role of vitamin B12 on fitness tests. A study of 18–21-year-old men receiving vitamin B12 or placebo injections for 6 weeks found no effects on aerobic capacity, standing jump, hand grip or coordination tasks(Reference Tin-May-Than, Ma-Win-May and Skin-Sann-Aung32). Montoye et al. (Reference Montoye, Spata and Pinckney33) supplemented boys aged 12–17 years with vitamin B12 or placebo for 7 weeks and found no effects on a half-mile run or a step test. These studies did not assess baseline vitamin B12 status and were of short duration. Whether longer supplementation studies in populations with high prevalence of vitamin B12 deficiency may yield positive effects on performance-related fitness deserves future investigation.
Our finding that stunted children scored lower in both the run and long jump tests than non-stunted children is consistent with previous studies(Reference Benefice, Fouere and Malina8, Reference Prista, Ribeiro Maia and Damasceno9). For the long jump test, this relationship was only found in boys, consistent with another study in schoolchildren from Mozambique(Reference Prista, Ribeiro Maia and Damasceno9). Stunting is thought to be caused by impaired growth of long leg bones during later infancy(Reference Cole34). We found that stunting was negatively associated with both performance tests independent of muscle mass, suggesting that shorter leg length rather than less muscle mass may be responsible for the performance deficits. We did not find associations between arm muscle area and performance; however, Davies had found a linear relationship between lean leg volume and standing long jump distance in 12–13-year-old children(Reference Davies35). We did not measure lean leg volume, and it is possible that arm muscle area estimated from the arm circumference and triceps skinfold is not as valid an indicator of leg muscle mass as lean leg volume. We also found that the effect of stunting was independent of micronutrient status.
We found that children who were classified as thin ran slightly but significantly slower than children with normal weight, independent of height. This finding is in agreement with another study in 12–15-year-old children from the Republic of Seychelles, where children with low BMI ran slower than those with normal BMI(Reference Bovet, Auguste and Burdette36). Thin children in the Republic of Seychelles also had lower jump scores, which agrees with our findings among girls only. Thin boys in our population may have differed in other nutritional characteristics, such as micronutrient status, from the children in the Republic of Seychelles. The negative effects of thinness may be due to less muscle mass, which we may have measured with some error by using arm muscle area.
Our finding that overweight or obese children had lower scores in the shuttle run and long jump than normal-weight children is consistent with previous observational studies(Reference Bovet, Auguste and Burdette36, Reference Malina, Beunen and Claessens37). The reason why overweight children tend to perform less well on physical tasks that require projection of the body through space, such as runs and jumps, may be related with the fact that excess fat represents an additional load that must be moved(Reference Malina and Katzmarzyk3). The finding that arm fat area was associated with poorer performance independent of muscle area suggests that excess fat mass among overweight children impairs performance. It is unclear why the negative relationship between arm fat area and long jump scores was only present in boys; however, another study in schoolchildren found that subcutaneous fat in boys only was associated with lower long jump scores(Reference Benefice, Fouere and Malina8). Weight reduction interventions in obese children and adolescents have resulted in improvements of both anaerobic and aerobic performance(Reference Dao, Frelut and Peres38–Reference Knöpfli, Radtke and Lehmann40).
Differences in fitness scores among anaemic v. non-anaemic children in the present study did not reach statistical significance. The prevalence of anaemia in our population was low (4 %), which may have limited statistical power. Although Fe status would be expected to affect aerobic more than anaerobic performance due to Hb's role in oxygen transport, we found a significant association between low Fe stores assessed by ferritin and anaerobic performance-related fitness. Some studies have demonstrated improved aerobic capacity and endurance performance in non-anaemic women with low ferritin concentrations who received Fe supplements(Reference Hinton, Giordano and Brownlie10, Reference Rowland, Deisroth and Green11). The effect of Fe supplementation on anaerobic performance-related fitness tests such as those in the present study is not known and deserves consideration in future studies.
A limitation of the present study is its cross-sectional design, which limits the possibility of drawing causal inferences. We were not able to assess motivation of the children, which is a major determinant of performance in fitness tests(Reference Cairney, Hay and Faught41). It is conceivable that Fe and vitamin B12 deficiencies could affect motivation via their effects on cognition, and thus their potential effects on these tests would not be direct but mediated through improved motivation. We were also not able to assess the children's prior physical training as a predictor of performance in the fitness tests; however, we did find a positive association between the children's jump scores and reported time spent playing outdoors, a factor that has been correlated with children's physical activity(Reference Sallis, Prochaska and Taylor42, Reference Cleland, Crawford and Baur43). Our finding of associations between long jump scores and anthropometric and micronutrient status indicators were independent of the association with time spent playing outdoors.
In conclusion, the present study suggests that there might be negative effects of suboptimal anthropometric and micronutrient status on anaerobic performance-related fitness of children from settings undergoing the nutritional transition. Further studies are needed to determine the effect of nutritional interventions on performance-related fitness of children in these settings.
Acknowledgements
The present study was supported by the Secretary of Education of Bogotá, the David Rockefeller Center for Latin American Studies at Harvard University, the National University of Colombia and the National Institute of Health of Colombia. J. E. A. was supported by training grant T32DK07703 from the National Institutes of Health. None of the authors has any conflicts of interest. The authors’ contributions were as follows: J. E. A. was involved in the data analyses, interpretation of the results and writing of the first draft of the manuscript; M. M.-P. contributed to the study design and implementation of tests in the field; Y. F. contributed to the study implementation and laboratory analyses; S. L.-A. contributed to the study implementation and data management; G. J. was responsible for the implementation of physical performance tests in the field; A. B. participated in the study design and interpretation of the data; P. M. G. contributed to the interpretation of the data; E. V. contributed to the study design, data analyses, interpretation of the results and preparation of the manuscript. All authors critically reviewed the manuscript.







