No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
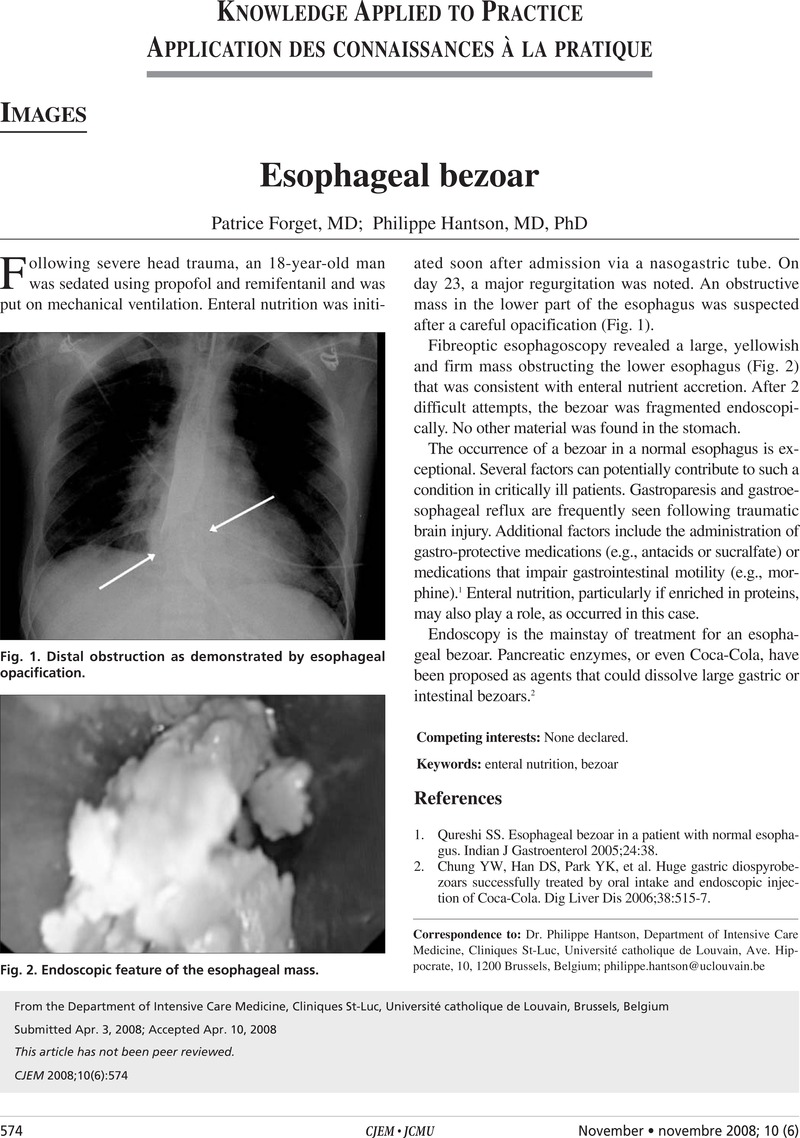
Esophageal bezoar
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 21 May 2015
Abstract
An abstract is not available for this content so a preview has been provided. As you have access to this content, a full PDF is available via the ‘Save PDF’ action button.
Keywords
- Type
- Knowledge Applied to Practice Application des connaissances à la pratique
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Canadian Association of Emergency Physicians 2008
References
1.Qureshi, SS. Esophageal bezoar in a patient with normal esophagus. Indian J Gastroenterol 2005;24:38.Google Scholar
2.Chung, YW, Han, DS, Park, YK, et al.Huge gastric diospyrobezoars successfully treated by oral intake and endoscopic injection of Coca-Cola. Dig Liver Dis 2006;38:515–7.Google Scholar


