INTRODUCTION
Diabetes mellitus is an increasingly prevalent chronic disease, with estimates that up to 40% of adults may develop diabetes over their lifetime.Reference Hackethal 1 In the United States, it is the most prevalent chronic disease among all visitors to the emergency department (ED), with over 11 million visitors identifying themselves as diabetic and approximately 225,000 visitors with an ED discharge diagnosis of diabetes annually. 2 Patients with poorly controlled diabetes often visit the ED for management of hyperglycemic episodes, including diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state. In particular, patients with lower socioeconomic status or limited access to primary care may have higher ED utilization for diabetes management.Reference Curtis and Lee 3 - Reference Ford, Self and Slovis 5 The initial treatment and resuscitation of these patients are usually managed by ED physicians and carry a significant burden of disease due to the potentially life-threatening severity and recurrent nature of these hyperglycemic emergencies.Reference Alourfi and Homsi 6 , Reference Malone, Gennis and Goodwin 7
When evaluating hyperglycemic patients in the ED, physicians must consider identifying a precipitating factor for diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state.Reference Kitabchi, Umpierrez and Miles 8 The most common of these is infection, which may include respiratory, urinary, or skin and soft tissue sources.Reference Kitabchi, Umpierrez and Murphy 9 , Reference Ennis, Stahl and Kreisberg 10 Additional precipitants may include noncompliance or subtherapeutic administration of insulin therapy, pancreatitis, cardiac ischemia, cerebrovascular accident, and drugs.Reference Kitabchi, Umpierrez and Murphy 11 , Reference DeFronzo, Matzuda and Barret 12 These other medical conditions may worsen an individual’s glycemic control and subsequently trigger a hyperglycemic emergency, thus requiring the patient to return to the ED for further medical management. Many of these patients may ultimately require hospital or intensive care admission.
A sentinel visit can be defined as a visit to the ED, for any reason, within the 14 days preceding the attendance for hyperglycemia. To date, there are no descriptions in the literature as to whether patients presenting to the ED with hyperglycemia are likely to have had a sentinel visit for precipitating medical conditions prior to their visit for hyperglycemia. Furthermore, the clinical course of these patients is unknown with respect to the need for admission to the hospital for inpatient management of severe hyperglycemia following their repeat presentation to the ED. The objective of this study was to describe the epidemiology and outcomes of patients presenting with a sentinel ED visit prior to their visit for a hyperglycemic emergency. Secondary objectives were to describe the precipitating diagnoses, consultations in the ED, disposition, and outcomes of these patients on the hyperglycemia visits.
METHODS
We conducted a health records review of patients presenting to one of four academic tertiary care EDs (approximate combined annual census of 300,000) with a discharge diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, diabetic ketoacidosis, or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state over a 1-year period (January – December 2014). The study protocol was approved by the Health Sciences Research Ethics Boards at The Ottawa Hospital in Ottawa, Ontario and Western University in London, Ontario.
All visits of adult (≥18 years) ED patients with a final diagnosis of hyperglycemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state and its related codes under the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Revision (ICD-10), according to the treating physician were eligible to be included in the study. This included patients with either previously known or unknown diabetes and, if known to be diabetic, both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, regardless of whether they were insulin-dependent. We included all visits of patients who presented multiple times during the 12-month period. However, data on unique patient characteristics, excluding the repeat visits, were reported separately. Patients with co-morbid final diagnoses in addition to hyperglycemia, such as infection, cardiac ischemia, or adverse drug reaction, were also included. Patients were excluded if they had known advanced care directives for resuscitation involving refusal of treatment, or if they were initially assessed at a peripheral or community hospital and transferred to the study sites for ongoing management.
The primary outcome was the occurrence of a sentinel ED visit (within the preceding 14 days for any reason) prior to the hyperglycemia visit. Therefore, it is possible that a single visit for hyperglycemia could also be a sentinel visit for a subsequent hyperglycemia visit within the following 14 days. Secondary outcomes involved describing the reason for presentation and clinical course for these sentinel visits, as well as characterizing patient-important outcomes on the hyperglycemia visit such as consultations in the ED, patient disposition, and 30-day return visits (after the hyperglycemia visit) to the ED, hospital, or intensive care unit (ICU) admission.
Trained research personnel collected data from paper and electronic medical records using a standardized data collection tool (see Supplementary Material). Electronic records were reviewed to determine whether the patient had a sentinel visit to the ED. Details surrounding both visits, including the reason for the visit, pertinent clinical findings, results of investigations, physician management, patient disposition, and final diagnoses, were collected. Data from the collection tool were then entered into a study-specific Microsoft Excel database (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA). Descriptive statistics were summarized using means and standard deviations with 95% confidence intervals (CI) where appropriate.
RESULTS
ED visits totalling 1,148 were screened for eligibility from January to December 2014. After applying the exclusion criteria and eliminating those visits that were incorrectly coded, 833 visits were ultimately included. These 833 hyperglycemia visits represented 645 unique patients, because 548 patients had only one visit while 97 patients had multiple visits accounting for the remaining 285 visits in the study period (Figure 1). Characteristics of the unique patients and all hyperglycemia visits are summarized in Table 1.
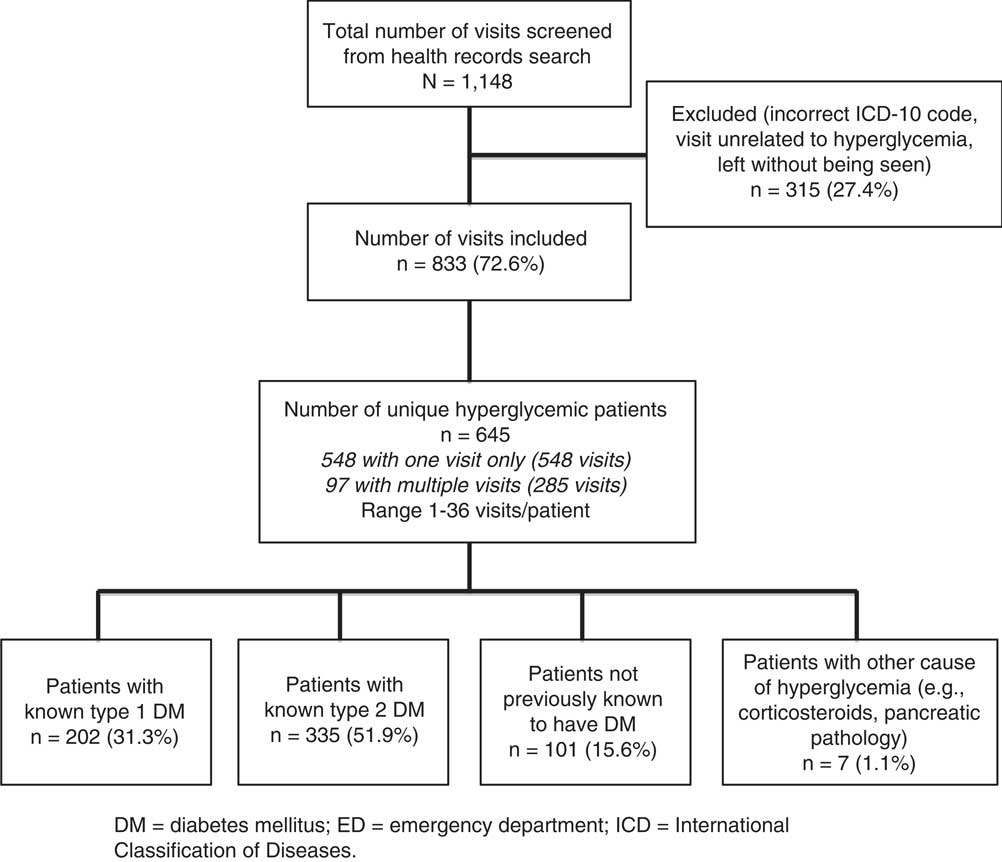
Figure 1 Flow diagram of eligible and enrolled patients. DM=diabetes mellitus; ED=emergency department; ICD=International Classification of Diseases.
Table 1 Characteristics of 645 included emergency department hyperglycemia patients and 833 total visits
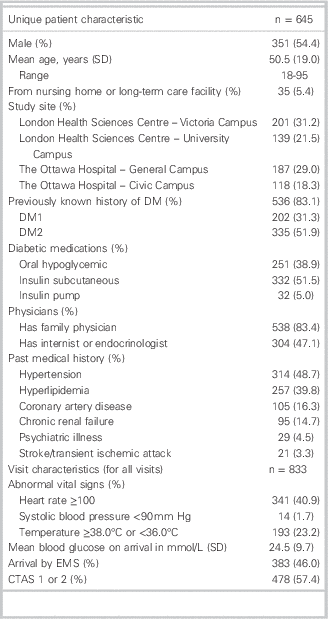
CTAS=Canadian Triage and Acuity Scale; DM=diabetes mellitus; ED=emergency department; EMS=emergency medical services; SD=standard deviation.
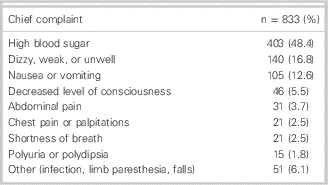
Table 2 summarizes the chief complaints of patients for all ED visits for hyperglycemia. Many patients (48.4%) presenting to the ED had a chief complaint of high blood sugar, because many were aware of their own hyperglycemia upon checking their own blood glucose at home or at another physician’s office. Other common complaints included nonspecific symptoms such as dizziness, weakness, feeling unwell (16.8%); or nausea and vomiting (12.6%).
Table 2 Chief complaints of all 833 emergency department visits for hyperglycemia
The most likely precipitating causes of hyperglycemia for these visits (Table 3) were medication or insulin noncompliance (35.8%), ongoing poor control or underdosing of medication or insulin (28.9%), and infection from various sources (21.7%). Of note, the emergency physician made a new diagnosis of diabetes mellitus in 12.1% of patients who were presenting to the ED with hyperglycemia.
Table 3 Likely precipitant of hyperglycemia for all 833 emergency department visits
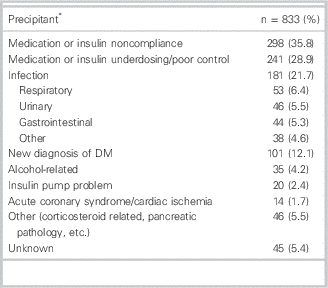
DM=diabetes mellitus.
* May have multiple precipitants of hyperglycemia.
The outcomes of all 833 ED hyperglycemic patient visits are outlined in Table 4. The final discharge diagnosis was hyperglycemia or diabetes in 463 (55.6%), diabetic ketoacidosis in 288 (34.6%), and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state in 79 (9.5%) of visitors. The vast majority of patients who had ED consultation for admission were referred to the internal medicine service. Physicians discharged 414 (49.7%) patients home from the ED, but 407 (48.9%) were admitted to the hospital, with 389 of these admitted to the ward and only 18 to the ICU. One patient died in the ED, and a total of six died in the hospital. Within 30 days of the hyperglycemia visit, 156 (18.7%) had a return visit to the ED for hyperglycemia, 73 (8.8%) required hospital admission, and only 2 of these (0.2%) were admitted to the ICU.
Table 4 Final diagnoses, consultations, disposition, and outcomes for all 833 emergency department hyperglycemia visits

DM=diabetes mellitus; ED=emergency department; ICU=intensive care unit.
Of 833 total visits for hyperglycemia in the 12-month period, 142 (17.0%; 95% CI: 14.5% to 19.6%) had a sentinel visit within the preceding 14 days. Characteristics of the sentinel visits are summarized in Table 5. Of the 142, 104 (73.2%) were discharged home from the sentinel ED visit, and 74 (52.1%) were discharged with a persistently elevated blood glucose (defined as a random blood glucose >11.0 mmol/L); 24 (16.9%) patients did not have a blood glucose checked at all during their sentinel visit, and 71 (50.0%) of patients did not have discharge instructions clearly documented on the chart. Of the 142 sentinel visits, 93 (65.5%) had a final diagnosis of diabetes, diabetic ketoacidosis, or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, and 22 (15.5%) had a diagnosis of infection. Of 142 patients with a sentinel visit, 61 (43.0%) were subsequently admitted for a hyperglycemic emergency upon returning to the ED.
Table 5 Characteristics of 142 sentinel visits within the previous 14 days of emergency department hyperglycemia visit
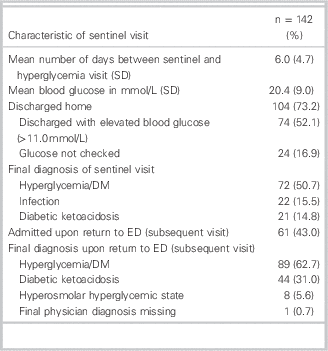
DM=diabetes mellitus; ED=emergency department; SD=standard deviation.
DISCUSSION
The results of this large descriptive study demonstrate that 17.0% of patients presenting to the ED with a hyperglycemic emergency had a sentinel visit within the preceding 14 days, usually for hyperglycemia or infection. Although the majority (73.2%) of patients may not have required admission upon their initial sentinel ED visit, some returned shortly thereafter with worsening hyperglycemia secondary to possible noncompliance, ongoing poor control, or severe infection. Furthermore, 43.0% of these patients required admission upon their repeat visit to the ED. This study suggests that the sentinel visits may be a warning sign to patients and health care providers of worsening disease, and that there may be an opportunity for prevention or intervention if those who are at higher risk of a subsequent ED visit or hospital admission can be identified.
At a minimum, clinicians should be encouraged to check the blood glucose of patients with diabetes during their ED visits and give clear discharge instructions for tighter glycemic control and follow-up if they are found to be hyperglycemic.
Many studies have attempted to identify the variables that predict short-term unplanned recurrent visits to the ED for any reason, including risk factors such as older age, higher triage scores, alcohol abuse, painful conditions, and history of cancer or cardiac or psychiatric disease.Reference Hu, Lu and Lin 13 - Reference Sauvin, Freund and Saidi 16 Research on recurrent visits, specifically for hyperglycemia and diabetes, is more limited, particularly within the ED setting. One study by Sykes et al. demonstrated that factors associated with readmission to the critical care unit for recurrent diabetic ketoacidosis within 1 year include older age, female gender, concurrent sepsis, anemia, and increased anion gap on admission.Reference Sykes, Pimentel and Santos 17 However, this study was ICU-based, rendering the conclusions difficult to generalize to patients seen within the ED who may not be critically ill. One ED-based health records review by Driver et al. determined that discharge glucose levels and amount of glucose reduction were not associated with short-term adverse outcomes in discharged patients with type 2 diabetes and severe hyperglycemia.Reference Driver, Olives and Bischof 18 The authors in this study defined short-term adverse outcomes as any unplanned return visit to the ED for hyperglycemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, hospitalization for any reason, and death within 7 days of initial presentation. Unfortunately, this study excluded all patients with type 1 diabetes who may be at higher risk of experiencing an adverse outcome or returning to the ED more frequently in the short-term. Furthermore, both of these studies were retrospective in nature and were thus subject to similar limitations as the present study.
In a large multicentre study by Rowe et al., the management and outcomes of 1,039 adult patients with diabetes mellitus presenting to the ED with hypoglycemia were examined.Reference Rowe, Singh and Villa-Roel 19 This health records review concluded that ED visits for hypoglycemia consumed considerable health care resources, including the need for prehospital transportation, medical treatment, diagnostic testing, and a significant rate of hospital admission (26.5%). Furthermore, diabetic follow-up was infrequent (<20%) for these patients, and discharge instructions were documented for only 55.5% of those enrolled, similar to the frequency of documented discharge instructions in the present study (50.0%). Another retrospective study by Ginde et al. confirmed that ED written discharge instructions appeared inadequate in providing recommended education for patients with severe hypoglycemia.Reference Ginde, Pallin and Camarga 20 Although these studies examined patients with low blood glucose rather than those with hyperglycemia, it is evident across studies that health care providers can improve their documentation of discharge instructions and follow-up for all patients with diabetes who are presenting to the ED for glucose management.
Several recent studies have attempted to describe ED-based interventions for hyperglycemic or newly diagnosed diabetic patients prior to discharge.Reference Jornsay, Garnett and Bolte 21 - Reference Munoz, Villanueva and Fogg 23 One interventional study by Dubin et al. evaluated the implementation of a program involving education and medication management to achieve better control of diabetes and reduce the frequency of repeat ED visits for hyperglycemia.Reference Dubin, Nassar and Sharretts 22 Of 86 patients enrolled, subsequent ED visits and hospitalizations for glycemic control were reduced by 78% among study group patients. They concluded that formal diabetes teaching and medication management introduced in the ED could significantly reduce hyperglycemia and reduce the frequency of ED visits for uncontrolled diabetes. Furthermore, the medication algorithm used to manage hyperglycemia, which included starting basal insulin in the ED, was safe and effective. Another study by Munoz et al. involving an ED protocol of using subcutaneous insulin for 54 diabetic patients until discharge or hospital admission also demonstrated the safety of ED-based medical interventions for hyperglycemic patients.Reference Munoz, Villanueva and Fogg 23 Although the results of these studies have been promising, all have included very small sample sizes. Additionally, it is yet unclear whether all patients presenting with hyperglycemia would benefit from these treatments or whether these ED interventions should be directed toward a certain subset of this population.
LIMITATIONS
Although the present study had a large sample size and was conducted at two academic centres consisting of four tertiary care EDs in Ontario, Canada, the results may not be generalizable to community settings or EDs outside of this geographical location. Additionally, it is possible that patients may have sought care at community EDs surrounding our study sites. However, if this were true, the outcome rates reported in this study would actually be an underestimate of the true incidence in the population. As a result, the occurrence of sentinel or recurrent ED visits and subsequent admission may in fact be more frequent than our results would suggest.
Due to the retrospective nature of this health records review, this study is limited by the data that were recorded on patient charts. We are thus unable to establish any causal links with respect to outcomes in our study and cannot comment on additional variables that may not have been explicitly recorded. It is possible that some patients in our study period were missed if the treating physician’s final diagnoses did not include an ICD-10 code related to hyperglycemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, particularly if they were perceived to have a more important diagnosis such as cardiac arrest, acute coronary syndrome, or stroke. However, we attempted to mitigate this limitation by reviewing both primary and secondary diagnoses on all eligible ED visits. Furthermore, although we were able to determine whether patients had a family physician, internist, or endocrinologist, we were unable to ascertain whether patients were able to access these health care professionals in follow-up after their ED visits unless they were seen within the hospital’s outpatient clinics. It is possible that those who were successful in seeing their physicians for follow-up may not have needed to return to the ED for a subsequent hyperglycemia visit. Finally, a final discharge diagnosis of “hyperglycemia” without diabetic ketoacidosis or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state may not be clinically meaningful or patient-important, especially if patients had a long history of poor control and were chronically hyperglycemic.
CONCLUSIONS
This multicentre ED-based study demonstrates that 17.0% of patients with diabetes presenting with a hyperglycemic emergency had a sentinel visit to the ED within the previous 14 days. These sentinel visits for hyperglycemia or infection may be a warning sign of worsening glucose control that may trigger a hyperglycemic emergency requiring subsequent admission to the hospital. Patients are often discharged home from these sentinel visits with an elevated blood glucose or without their blood glucose being checked at all. For patients presenting to the ED with a history of diabetes, clinicians should be vigilant in checking blood glucose and provide clear discharge instructions for follow-up and glucose management to prevent further hyperglycemic emergencies from occurring. Future prospective research is needed to further elucidate the variables that might predict which patients are at higher risk for return ED visits for hyperglycemia and how these factors might be mitigated.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors wish to thank Alla Iansavitchene, Angela Marcantonio, Catherine Clement, Dr. Jonathan Dreyer, John Teefy, Patrick Macos, and Paul Prochazka for their assistance and support for this study.
Competing interests: None declared.








