Direct visualization of his airway using fiber optics is shown in Figure 1. Computed tomography imaging was obtained (Figure 2). The diagnosis was laryngeal injury resulting in avulsion of the left false cord.

Figure 1 Direct visualization of patient airway using fiber optics.
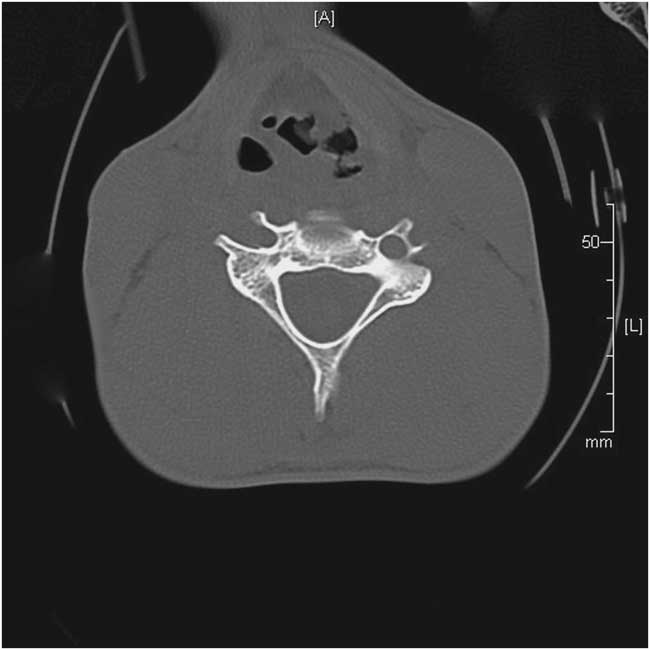
Figure 2 Computed tomography scan of laryngeal injury resulting in avulsion of the left false cord.
Discussion
Blunt neck trauma occurs in 5% of traumas and is more common than penetrating neck injuries.Reference Levy 1 The most common mechanism is a motor vehicle collision where rapid acceleration or deceleration occurs. Laryngotracheal injuries in blunt neck trauma are second only to intracranial hemorrhage as cause of death among patients with head and neck trauma. Mortality has been reported from 2% to 15% and increases with advancing age.Reference Jewett, William and Rutledge 2 The most common presenting symptom in these patients is hoarseness.Reference Juutilainen, Vintturi and Robinson 3
Airway control in these patients should be a priority.Reference Rathlev, Medzon and Bracken 4 Cervical spine control should be maintained. Intubation may be difficult, secondary to additional facial injuries. High suspicion for pharyngeal, esophageal, cervical spine, and head injuries needs to be maintained.
This patient was taken to the operating room for tracheostomy placement and repair of laryngeal injury and mandibular fixation. He did well postoperatively, and the tracheostomy was eventually removed.




