Article contents
The Dunford-Pettis Property for Symmetric Spaces
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
Abstract
A complete description of symmetric spaces on a separable measure space with the Dunford-Pettis property is given. It is shown that 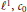 ${{\ell }^{1}},{{c}_{0}}$ and
${{\ell }^{1}},{{c}_{0}}$ and 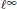 ${{\ell }^{\infty }}$ are the only symmetric sequence spaces with the Dunford- Pettis property, and that in the class of symmetric spaces on
${{\ell }^{\infty }}$ are the only symmetric sequence spaces with the Dunford- Pettis property, and that in the class of symmetric spaces on 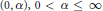 $(0,\,\alpha ),\,0\,<\,\alpha \,\le \,\infty$, the only spaces with the Dunford-Pettis property are
$(0,\,\alpha ),\,0\,<\,\alpha \,\le \,\infty$, the only spaces with the Dunford-Pettis property are 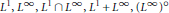 ${{\text{L}}^{1}},{{\text{L}}^{\infty }},{{\text{L}}^{1}}\cap {{\text{L}}^{\infty }},{{\text{L}}^{1}}+{{\text{L}}^{\infty }},{{({{\text{L}}^{\infty }})}^{\text{o}}}$ and
${{\text{L}}^{1}},{{\text{L}}^{\infty }},{{\text{L}}^{1}}\cap {{\text{L}}^{\infty }},{{\text{L}}^{1}}+{{\text{L}}^{\infty }},{{({{\text{L}}^{\infty }})}^{\text{o}}}$ and 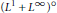 ${{({{\text{L}}^{1}}+{{\text{L}}^{\infty }})}^{\text{o}}}$, where
${{({{\text{L}}^{1}}+{{\text{L}}^{\infty }})}^{\text{o}}}$, where 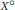 ${{\text{X}}^{\text{o}}}$ denotes the norm closure of
${{\text{X}}^{\text{o}}}$ denotes the norm closure of 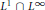 ${{\text{L}}^{1}}\cap {{\text{L}}^{\infty }}$ in
${{\text{L}}^{1}}\cap {{\text{L}}^{\infty }}$ in 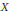 $X$. It is also proved that all Banach dual spaces of
$X$. It is also proved that all Banach dual spaces of 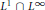 ${{\text{L}}^{1}}\cap {{\text{L}}^{\infty }}$ and
${{\text{L}}^{1}}\cap {{\text{L}}^{\infty }}$ and 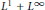 ${{\text{L}}^{1}}+{{\text{L}}^{\infty }}$ have the Dunford-Pettis property. New examples of Banach spaces showing that the Dunford-Pettis property is not a three-space property are also presented. As applications we obtain that the spaces
${{\text{L}}^{1}}+{{\text{L}}^{\infty }}$ have the Dunford-Pettis property. New examples of Banach spaces showing that the Dunford-Pettis property is not a three-space property are also presented. As applications we obtain that the spaces 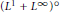 ${{({{\text{L}}^{1}}+{{\text{L}}^{\infty }})}^{\text{o}}}$ and
${{({{\text{L}}^{1}}+{{\text{L}}^{\infty }})}^{\text{o}}}$ and 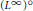 ${{({{\text{L}}^{\infty }})}^{\text{o}}}$ have a unique symmetric structure, and we get a characterization of the Dunford-Pettis property of some Köthe-Bochner spaces.
${{({{\text{L}}^{\infty }})}^{\text{o}}}$ have a unique symmetric structure, and we get a characterization of the Dunford-Pettis property of some Köthe-Bochner spaces.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Canadian Mathematical Society 2000
References
- 11
- Cited by


