Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Butzer, Paul L.
1956.
On the singular integral of de la Vallée-Poussin.
Archiv der Mathematik,
Vol. 7,
Issue. 4,
p.
295.
de Leeuw, Karel
1959.
On the degree of approximation by Bernstein polynomials.
Journal d’Analyse Mathématique,
Vol. 7,
Issue. 1,
p.
89.
Leviatan, D.
and
Müller, M.
1969.
Some applications of the Gamma-operators.
Archiv der Mathematik,
Vol. 20,
Issue. 6,
p.
638.
Varma, A.K.
1971.
On a new interpolation process.
Journal of Approximation Theory,
Vol. 4,
Issue. 2,
p.
159.
Rathore, R. K. S.
1974.
On a Sequence of Linear Trigonometric Polynomial Operators.
SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 6,
p.
908.
Ditzian, Z.
and
May, C. P.
1976.
A saturation result for combinations of Bernstein polynomials.
Tohoku Mathematical Journal,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 3,
Weston Meyer, W
and
Thomas, Donald H
1976.
Variations on a theme by Schoenberg.
Journal of Approximation Theory,
Vol. 18,
Issue. 1,
p.
39.
May, C.P
1977.
On Phillips operator.
Journal of Approximation Theory,
Vol. 20,
Issue. 4,
p.
315.
Ditzian, Z
1979.
A global inverse theorem for combinations of Bernstein polynomials.
Journal of Approximation Theory,
Vol. 26,
Issue. 3,
p.
277.
Wimp, Jet
1979.
Computing values of a function on [0,1] from its moments.
Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Section A Mathematics,
Vol. 82,
Issue. 3-4,
p.
273.
Felbecker, G�nter
1979.
Linearkombinationen von iterierten Bernsteinoperatoren.
Manuscripta Mathematica,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 2-4,
p.
229.
Stark, Eberhard L.
1981.
Functional Analysis and Approximation.
p.
443.
Satô, Kunio
1981.
Global approximation theorems for some exponential-type operators.
Journal of Approximation Theory,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 1,
p.
32.
Greaves, G.
1982.
An algorithm for the Hausdorff moment problem.
Numerische Mathematik,
Vol. 39,
Issue. 2,
p.
231.
Wood, B
1985.
Order of approximation by linear combinations of positive linear operators.
Journal of Approximation Theory,
Vol. 45,
Issue. 4,
p.
375.
Naiko, D. A.
1988.
Approximation of the derivatives of some combinations of operators of class B.
Ukrainian Mathematical Journal,
Vol. 39,
Issue. 5,
p.
473.
Sablonnière, Paul
1989.
Multivariate Approximation Theory IV.
p.
287.
Martinez, Francisco Luquin
1989.
Some properties of two-dimensional Bernstein polynomials.
Journal of Approximation Theory,
Vol. 59,
Issue. 3,
p.
300.
Vogt, L
1989.
Approximation by linear combinations of positive convolution integrals.
Journal of Approximation Theory,
Vol. 57,
Issue. 2,
p.
178.
Zhengchang, Wu
1991.
Norm of the Bernstein left quasi-interpolant operator.
Journal of Approximation Theory,
Vol. 66,
Issue. 1,
p.
36.


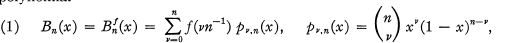
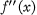 exists (Voronowskaja [7], see also [5])
exists (Voronowskaja [7], see also [5])