Article contents
Operators which Factor through Convex Banach Lattices
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
Extract
We investigate here classes of operators T between Banach spaces E and F, which have factorization of the form
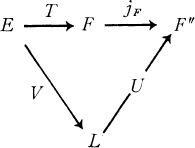
where L is a Banach lattice, V is a p-convex operator, U is a q-concave operator (definitions below) and jF is the cannonical embedding of F in F”. We show that for fixed p, q this class forms a perfect normed ideal of operators Mp, q, generalizing the ideal Ip,q of [5]. We prove (Proposition 5) that Mp, q may be characterized by factorization through p-convex and q-concave Banach lattices. We use this fact together with a variant of the complex interpolation method introduced in [1], to show that an operator which belongs to Mp, q may be factored through a Banach lattice with modulus of uniform convexity (uniform smoothness) of power type arbitrarily close to q (to p). This last result yields similar geometric properties in subspaces of spaces having G.L. – l.u.st.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Canadian Mathematical Society 1980
References
- 5
- Cited by


