Article contents
Powers in Orbits of Rational Functions: Cases of an Arithmetic Dynamical Mordell–Lang Conjecture
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 January 2019
Abstract
Let 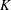 $K$ be a finitely generated field of characteristic zero. For fixed
$K$ be a finitely generated field of characteristic zero. For fixed 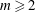 $m\geqslant 2$, we study the rational functions
$m\geqslant 2$, we study the rational functions 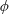 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$ defined over
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$ defined over 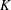 $K$ that have a
$K$ that have a 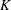 $K$-orbit containing infinitely many distinct
$K$-orbit containing infinitely many distinct 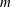 $m$-th powers. For
$m$-th powers. For 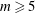 $m\geqslant 5$ we show that the only such functions are those of the form
$m\geqslant 5$ we show that the only such functions are those of the form 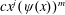 $cx^{j}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(x))^{m}$ with
$cx^{j}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(x))^{m}$ with 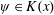 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}\in K(x)$, and for
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}\in K(x)$, and for 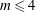 $m\leqslant 4$ we show that the only additional cases are certain Lattès maps and four families of rational functions whose special properties appear not to have been studied before.
$m\leqslant 4$ we show that the only additional cases are certain Lattès maps and four families of rational functions whose special properties appear not to have been studied before.
With additional analysis, we show that the index set 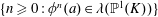 $\{n\geqslant 0:\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}^{n}(a)\in \unicode[STIX]{x1D706}(\mathbb{P}^{1}(K))\}$ is a union of finitely many arithmetic progressions, where
$\{n\geqslant 0:\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}^{n}(a)\in \unicode[STIX]{x1D706}(\mathbb{P}^{1}(K))\}$ is a union of finitely many arithmetic progressions, where 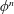 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}^{n}$ denotes the
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}^{n}$ denotes the  $n$-th iterate of
$n$-th iterate of  $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$ and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$ and 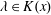 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}\in K(x)$ is any map Möbius-conjugate over
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}\in K(x)$ is any map Möbius-conjugate over 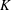 $K$ to
$K$ to 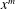 $x^{m}$. When the index set is infinite, we give bounds on the number and moduli of the arithmetic progressions involved. These results are similar in flavor to the dynamical Mordell–Lang conjecture, and motivate a new conjecture on the intersection of an orbit with the value set of a morphism. A key ingredient in our proofs is a study of the curves
$x^{m}$. When the index set is infinite, we give bounds on the number and moduli of the arithmetic progressions involved. These results are similar in flavor to the dynamical Mordell–Lang conjecture, and motivate a new conjecture on the intersection of an orbit with the value set of a morphism. A key ingredient in our proofs is a study of the curves 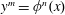 $y^{m}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}^{n}(x)$. We describe all
$y^{m}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}^{n}(x)$. We describe all 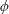 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$ for which these curves have an irreducible component of genus at most 1, and show that such
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$ for which these curves have an irreducible component of genus at most 1, and show that such 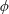 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$ must have two distinct iterates that are equal in
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$ must have two distinct iterates that are equal in 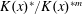 $K(x)^{\ast }/K(x)^{\ast m}$.
$K(x)^{\ast }/K(x)^{\ast m}$.
Keywords
MSC classification
Information
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Canadian Mathematical Society 2018
Footnotes
Authors J. C. and J. S. research was supported by Carleton College’s HHMI grant for undergraduate science education and the Carleton College department of Mathematics and Statistics.
References
- 3
- Cited by

