Article contents
Représentations irréductibles bornées des groupes de Lie exponentiels
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
Abstract
Let  $G$ be a solvable exponential Lie group. We characterize all the continuous topologically irreducible bounded representations
$G$ be a solvable exponential Lie group. We characterize all the continuous topologically irreducible bounded representations
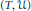 $(T,\mathcal{U})$
of
$(T,\mathcal{U})$
of  $G$ on a Banach space
$G$ on a Banach space
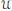 $\mathcal{U}$
by giving a
$\mathcal{U}$
by giving a  $G$-orbit in
$G$-orbit in
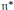 ${{n}^{*}}$
(
${{n}^{*}}$
(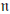 $\mathfrak{n}$ being the nilradical of
$\mathfrak{n}$ being the nilradical of 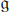 $\mathfrak{g}$), a topologically irreducible representation of
$\mathfrak{g}$), a topologically irreducible representation of
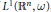 ${{L}^{1}}({{\mathbb{R}}^{n}},\,\,\omega )$
, for a certain weight
${{L}^{1}}({{\mathbb{R}}^{n}},\,\,\omega )$
, for a certain weight 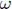 $\omega $ and a certain
$\omega $ and a certain 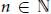 $n\,\in \,\mathbb{N}$, and a topologically simple extension norm. If
$n\,\in \,\mathbb{N}$, and a topologically simple extension norm. If  $G$ is not symmetric, i.e., if the weight
$G$ is not symmetric, i.e., if the weight 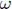 $\omega $ is exponential, we get a new type of representations which are fundamentally different from the induced representations.
$\omega $ is exponential, we get a new type of representations which are fundamentally different from the induced representations.
Résumé
Soit  $G$ un groupe de Lie résoluble exponentiel. Nous caractérisons toutes les représentations
$G$ un groupe de Lie résoluble exponentiel. Nous caractérisons toutes les représentations
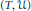 $(T,\mathcal{U})$
continues bornées topologiquement irréductibles de
$(T,\mathcal{U})$
continues bornées topologiquement irréductibles de  $G$ dans un espace de Banach
$G$ dans un espace de Banach
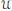 $\mathcal{U}$ à l’aide d’une
$\mathcal{U}$ à l’aide d’une  $G$-orbite dans
$G$-orbite dans 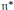 ${{n}^{*}}$
(
${{n}^{*}}$
(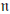 $\mathfrak{n}$ étant le radical nilpotent de
$\mathfrak{n}$ étant le radical nilpotent de 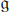 $\mathfrak{g}$), d’une représentation topologiquement irréductible de
$\mathfrak{g}$), d’une représentation topologiquement irréductible de 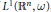 ${{L}^{1}}({{\mathbb{R}}^{n}},\,\,\omega )$, pour un certain poids
${{L}^{1}}({{\mathbb{R}}^{n}},\,\,\omega )$, pour un certain poids 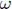 $\omega $ et un certain
$\omega $ et un certain 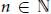 $n\,\in \,\mathbb{N}$, d’une norme d’extension topologiquement simple. Si
$n\,\in \,\mathbb{N}$, d’une norme d’extension topologiquement simple. Si  $G$ n’est pas symétrique, c. à d. si le poids
$G$ n’est pas symétrique, c. à d. si le poids 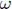 $\omega $ est exponentiel, nous obtenons un nouveau type de représentations qui sont fondamentalement différentes des représentations induites.
$\omega $ est exponentiel, nous obtenons un nouveau type de représentations qui sont fondamentalement différentes des représentations induites.
Keywords
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Canadian Mathematical Society 2001
References
Références
- 5
- Cited by


