Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Manon, Christopher
2010.
Presentations of semigroup algebras of weighted trees.
Journal of Algebraic Combinatorics,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 4,
p.
467.
Manon, Christopher
2012.
Gorenstein semigroup algebras of weighted trees and ordered points on the projective line.
Journal of Algebra,
Vol. 354,
Issue. 1,
p.
110.
Nohara, Yuichi
and
Ueda, Kazushi
2014.
Toric degenerations of integrable systems on Grassmannians and polygon spaces.
Nagoya Mathematical Journal,
Vol. 214,
Issue. ,
p.
125.
Cantarella, Jason
Deguchi, Tetsuo
and
Shonkwiler, Clayton
2014.
Probability Theory of Random Polygons from the Quaternionic Viewpoint.
Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics,
Vol. 67,
Issue. 10,
p.
1658.
Manon, Christopher
2015.
Newton-Okounkov polyhedra for character varieties and configuration spaces.
Transactions of the American Mathematical Society,
Vol. 368,
Issue. 8,
p.
5979.
Nohara, Yuichi
and
Ueda, Kazushi
2015.
Goldman Systems and Bending Systems.
Canadian Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 67,
Issue. 5,
p.
1109.
Cantarella, Jason
and
Shonkwiler, Clayton
2016.
The symplectic geometry of closed equilateral random walks in 3-space.
The Annals of Applied Probability,
Vol. 26,
Issue. 1,
Hilgert, Joachim
Manon, Christopher
and
Martens, Johan
2016.
Contraction of Hamiltonian $K$-Spaces.
International Mathematics Research Notices,
p.
rnw191.
Deguchi, Tetsuo
and
Uehara, Erica
2017.
Statistical and Dynamical Properties of Topological Polymers with Graphs and Ring Polymers with Knots.
Polymers,
Vol. 9,
Issue. 7,
p.
252.
Shonkwiler, Clayton
2018.
The Geometry of Constrained Randomwalks and an Application to Frame Theory.
p.
343.
Manon, Christopher
2018.
Toric Geometry ofSL2(ℂ) Free Group Character Varieties from Outer Space.
Canadian Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 70,
Issue. 2,
p.
354.
Cantarella, Jason
Chapman, Kyle
Reiter, Philipp
and
Shonkwiler, Clayton
2018.
Open and closed random walks with fixed edgelengths in $ \newcommand{\m}{\mathcal} \newcommand{\R}{\mathbb{R}} \R^d$.
Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical,
Vol. 51,
Issue. 43,
p.
434002.
Cantarella, Jason
Needham, Tom
Shonkwiler, Clayton
and
Stewart, Gavin
2019.
Random Triangles and Polygons in the Plane.
The American Mathematical Monthly,
Vol. 126,
Issue. 2,
p.
113.
Ilten, Nathan
and
Manon, Christopher
2019.
Rational Complexity-One $\boldsymbol{T}$-Varieties Are Well-Poised.
International Mathematics Research Notices,
Vol. 2019,
Issue. 13,
p.
4198.
Hake, Kathleen
2019.
Knotting probability of equilateral hexagons.
Journal of Knot Theory and Its Ramifications,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 07,
p.
1950040.
Needham, Tom
and
Shonkwiler, Clayton
2022.
Admissibility and frame homotopy for quaternionic frames.
Linear Algebra and its Applications,
Vol. 645,
Issue. ,
p.
237.
Manon, Christopher
and
Yang, Jihyeon Jessie
2022.
Tropical geometry and Newton–Okounkov cones for Grassmannian of planes from compactifications.
Canadian Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 74,
Issue. 1,
p.
199.
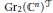 $\text{G}{{\text{r}}_{2}}{{({{\mathbb{C}}^{n}})}^{\mathcal{T}}}$ of
$\text{G}{{\text{r}}_{2}}{{({{\mathbb{C}}^{n}})}^{\mathcal{T}}}$ of 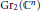 $\text{G}{{\text{r}}_{2}}{{({{\mathbb{C}}^{n}})}^{{}}}$ with each trivalent tree
$\text{G}{{\text{r}}_{2}}{{({{\mathbb{C}}^{n}})}^{{}}}$ with each trivalent tree 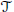 $\mathcal{T}$ having
$\mathcal{T}$ having  $n$ leaves. These degenerations induce toric degenerations
$n$ leaves. These degenerations induce toric degenerations 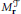 $M_{r}^{\mathcal{T}}$ of
$M_{r}^{\mathcal{T}}$ of 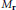 ${{M}_{r}}$, the space of
${{M}_{r}}$, the space of  $n$ ordered, weighted (by
$n$ ordered, weighted (by  $\mathbf{r}$) points on the projective line. Our goal in this paper is to give a geometric (Euclidean polygon) description of the toric fibers and describe the action of the compact part of the torus as “bendings of polygons”. We prove the conjecture of Foth and Hu that the toric fibers are homeomorphic to the spaces defined by Kamiyama and Yoshida.
$\mathbf{r}$) points on the projective line. Our goal in this paper is to give a geometric (Euclidean polygon) description of the toric fibers and describe the action of the compact part of the torus as “bendings of polygons”. We prove the conjecture of Foth and Hu that the toric fibers are homeomorphic to the spaces defined by Kamiyama and Yoshida.

