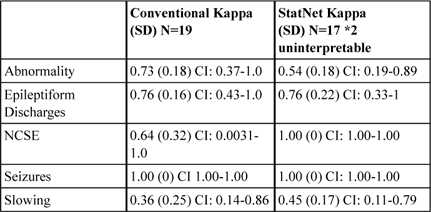
Table 1 Results: Interobserver Reliability
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 17 June 2016
Background: NCSE dramatically increases morbidity and mortality. It is clinically subtle, which makes it difficult to diagnose without EEG. StatNet EEG provides a quick alternative to conventional EEG, which is often unavailable after hours. Methods: Each patient received a StatNet EEG by a neurology resident and a conventional EEG by an EEG technologist. Blinded studies were compared for delay between the studies, setup time, artifact, and abnormality detection using conventional EEG as controls. Nonparametric Mann-Whitney two-sample T-test was used. Results are expressed in mean minutes +/- SD. Kappa score assessed inter-observer reliability. Results: 19 patients were collected. Two StatNet EEGs were not interpretable and excluded. The mean delay between studies was 26h53min. Electrode placement is significantly shorter: 13:14±5:24 StatNet EEG vs 18:07±5:35 conventional EEG (p=0.02).
Conclusions: There is high inter-rater reliability between the conventional and StatNet EEG groups (table 1) demonstrating that StatNet is a reliable and effective tool, aiding in early recognition and management of NCSE.
Table 1 Results: Interobserver Reliability


Table 1 Results: Interobserver Reliability