A 69-year-old right-handed diabetic male with no prior history of transient ischemic attack (TIA) presented with two transient episodes of language disturbance and right hemiparesis on consecutive days. The first episode occurred at home prompting an urgent referral to the TIA Rapid Access Clinic. The second episode occurred while he was attending his clinic appointment. The examination at that time revealed a mild mixed aphasia, right pronator drift, and bilateral ideomotor apraxia (National Institute of Health Stroke Scale 2). The patient did not exhibit any autonomic features. Immediate multimodal computed tomography (CT) imaging was obtained (within 20 min). His non-contrast head CT was unremarkable except for the presence of leukoaraiosis (Figure 1A), and an arch-to-vertex CT angiography (CTA) showed no extra or intracranial arterial occlusion (Figure 1B) while the CT perfusion revealed left parieto-occipital hypoperfusion located predominantly in the white matter (Figure 1C). His symptoms resolved completely within 30 min and because his symptoms resolved intravenous thrombolysis was not given. The magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) on the following day showed no acute infarct. The patient was wearing a glucose monitoring device (FreeStyle Libre, Abbott Diabetes Care) which displayed a prolonged hypoglycemic (3.4 mmol/L) episodes concurrent with the duration and time of onset of his symptoms (second reading - Figure 1D). The data log from the glucose monitoring device revealed that the previous episode also was concurrent in terms of both duration and time of onset with an episode of hypoglycemia (also 3.4 mmol/L). The resolution of symptoms for each event occurred following the return of the blood glucose to the normal range. The patient had no further recurrence of symptoms and with no recorded episodes of hypoglycemia after the daily insulin dose was reduced.
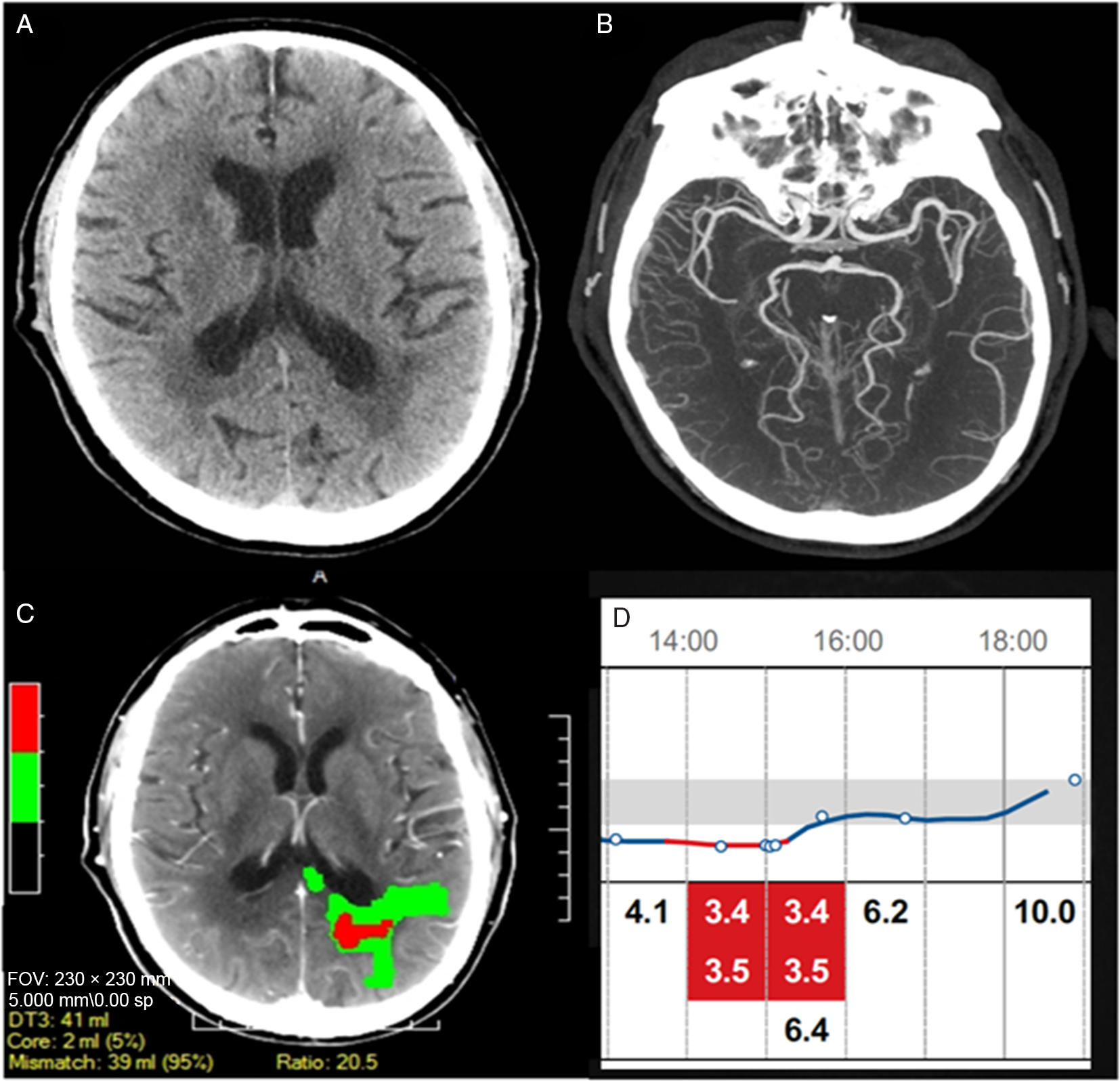
Figure 1: Acute imaging during the second episode: (A) Non-contrast head CT revealed no acute infarct. (B) No intracranial occlusions were noted on CTA. (C) CT perfusion demonstrated an area of reduced perfusion in the left parieto-occipital white matter. (D) Continuous recording of blood glucose (mmol/L) showed the 3-hour episode of hypoglycemia concurrent with the patient stroke symptoms.
The case highlights three important aspects related to stroke diagnosis and management. First, acute focal neurological deficits are highly suggestive but do not always represent stroke and common stroke mimics need to be considered. Second, as this case shows hypoglycemia can present with focal symptoms and should be tested for routinely in the context of all stroke patients. Reference Malouf and Brust1,Reference Moulin and Leys2 Third, focal hypoperfusion as identified by clinical neuroimaging such as CT or MRI can be caused by common metabolic abnormalities, in this case hypoglycemia, and therefore should be carefully interpreted to avoid inappropriate administration of thrombolysis. Reference Wing and Markus3 Our patient presented with acute-onset of focal neurologic deficits and CT hypoperfusion suggestive of an acute ischemic stroke. However, the presence of concurrent and recurrent low glucose with symptoms in the absence of vascular occlusion and infarct on follow-up MRI provide compelling evidence that hypoglycemia was the cause of the symptoms. In the absence of continuous glucose recording or in the case of a more equivocal scenario, controlled hypoglycemia by a test such as a glucose clamp study Reference Simonson, Tamborlane, DeFronzo and Sherwin4 can provide supportive evidence for hypoglycemia as a cause of recurrent focal neurological symptoms.
Encephalopathy is the most frequent manifestation of hypoglycemia but focal presentations are rarely reported. Reference Malouf and Brust1 The mechanism of cerebral dysfunction causing focal deficits in hypoglycemia remain speculative but could be due regional neuronal vulnerability, Reference Montgomery and Pinner5 vasospam, Reference MacDonald and Brown6 steal phenomenon in the presence of fixed stenosis, Reference Sontineni, Lee and Porter7 redistribution of cerebral blood flow, Reference Jarjour, Ryan and Becker8 or aggravation of underlying neurological disease, such as leukoaraiosis which was present in this case. Other common stroke mimics include seizure causing postictal negative focal symptoms but the absence of observed ictal phenomenon such as involuntary motor movements or reduced awareness made this diagnosis unlikely. Vascular imaging excluded fixed arterial stenosis and parenchymal imaging (CT and MRI) was negative for pre-existing cerebral injury except leukoaraiosis. Therefore, regional neuronal vulnerability related to small vessel disease is the likely explanation in our case. The role of pre-existing microangiopathic changes and chronic low-grade ischemia, leukoaraiosis in this case, could have increased white matter and/or the microvasculature susceptibility to hypoglycemia. White matter, in particular appears susceptible to hypoglycemic injury/dysfunction as observed in previous reports Reference Mori, Nishie, Houzen, Yamaguchi and Wakabayashi9 and also in our patient. It is important to note that in cases where leukoaraisosis is very asymmetrical (unlike our case) and symptoms do not correspond to the hypoperfused area, repeating a second perfusion study when the patient is asymptomatic would be useful to exclude pre-existing and unrelated (chronic) hypoperfusion and misattributing the acute symptoms to them. As perfusion is increasingly becoming a part of standard acute stroke imaging protocols, familiarity with local CT perfusion software and common causes of artefacts is also important to correctly interpret the perfusion imaging.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blood glucose should always be checked in patients with stroke-like symptoms. Perfusion imaging does not always exclude stroke mimics and requires careful interpretation in the appropriate clinical context.
Acknowledgement
We thank our patient for sharing glucose monitoring data and consenting to publish his case.
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Statement of Authorship
RJS: the clinical data collection, interpretation of the data, writing the first draft, editing of the manuscript; DD: interpretation of the data, image formatting, editing of the manuscript; PAB: study concept, the clinical data collection, interpretation of the data, editing of the manuscript



