Paraneoplastic neurologic syndromes (PNS) are immune-mediated diseases of the nervous system that occur as an indirect effect of malignancy. Patients with these syndromes often harbour onconeural antibodies, which target intracellular neural antigens and have a greater than 95% association with cancer.Reference Raspotnig, Vedeler and Storstein 1 This is in contrast to other autoantibodies that may be found in either paraneoplastic or primary autoimmune disease, bind to cell surface or synaptic proteins and are less predictive of malignancy (e.g. anti-voltage-gated calcium channel antibodies in patients with Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome, which are paraneoplastic in only 50%-60% of cases).Reference Nicolle 2 The presence of onconeural antibodies in a patient with neurologic symptoms reportedly strongly indicates the presence of a PNS, leading to extensive malignancy screening and consideration of immunotherapy. In 2015, London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC) became one of the first centres in Canada to perform in-house onconeural antibody testing. However, on informal review of this assay we noticed a seemingly high number of positive results compared with previous reports. As such, we performed a retrospective review to determine the positive predictive value (PPV) of onconeural antibody testing in the diagnosis of PNS.
We identified all patients who underwent serum onconeural antibody panel testing at LHSC from 2015 to 2017. All samples were analysed for onconeural antibodies (anti-Hu, Yo, Ri, Ma2, CV2 and amphiphysin) by two different methods: indirect immunofluorescence (IFA) on primate cerebellar and intestinal tissue with BIOCHIP Mosaics for Neurology and immunoblot (IB) with EUROLINE Neuronal Antigens Profile 2. The IFA was interpreted as negative or positive for a specific onconeural antibody fluorescence pattern, whereas the IB was read as negative or weakly (1+), moderately (2+) or strongly (3+) positive; an onconeural antibody was reported as positive if either IFA or IB was positive. A full chart review of the clinical history, examination, serum and cerebrospinal fluid testing, neuroimaging and electrophysiologic studies was performed on all patients who had a positive onconeural antibody result. The presence of an onconeural antibody was considered a false positive (FP) only if no malignancy was diagnosed and an alternative aetiology for the patient’s neurologic symptoms was identified clinically or pathologically. These patients were categorised as having non-paraneoplastic neurological syndromes (NPNS). The presence of an onconeural antibody was otherwise considered a true positive (TP), and these patients were classified as having a PNS. Using these data, the PPV of onconeural antibody testing for PNS was then calculated.
On review, 308 patients were identified who underwent onconeural antibody testing at our institution. Of these patients, 23 (7.5%) tested positive for an onconeural antibody (anti-Ma2=14, amphiphysin=5, CV2=3, Hu=1, Yo=1; one patient tested positive for both anti-Ma2 and CV2). Only 39% of these patients were positive by IFA, whereas 96% were positive by IB; 35% of patients were positive by both IFA and IB. The mean age was 59 years (range: 21-87), and 65% were men. Nine of 23 patients with various neurologic syndromes were considered TP, and categorised as having a PNS (see Table 1). An associated tumour was identified in five of these patients: four with anti-Ma2 antibodies (Hodgkin’s lymphoma, testicular teratoma, papillary thyroid carcinoma/medullary microcarcinoma and bronchoalveolar carcinoma) and one with anti-Hu antibodies (small-cell lung carcinoma). Out of the 23 patients, 14 were considered FP, with no malignancy found and an alternative diagnosis established clinically or pathologically; these patients were categorised as NPNS (see Table 1). The calculated PPV for onconeural antibody testing was 39%. When comparing PNS with NPNS, there was no significant difference in terms of age, sex, smoking history, symptom duration, antibody positivity, percentage positive by IFA, IB or both IFA and IB (see Table 2). However, only two patients were positive for both an onconeural antibody by IFA and had a strongly positive IB, both of whom were considered TP and classified as having a PNS.
Table 1 Neurologic syndromes in patients with paraneoplastic syndromes (PNS) and non-paraneoplastic neurological syndromes (NPNS)
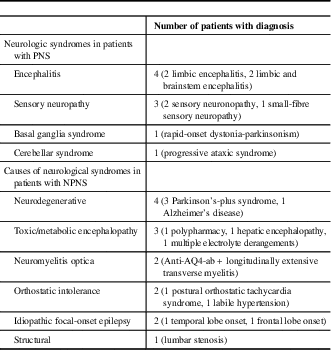
Table 2 Patient characteristics and onconeural antibodies identified
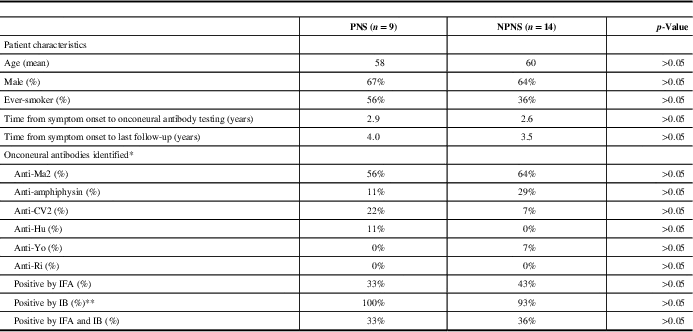
IB=immunoblot; IFA=indirect immunofluorescence; NPNS=non-paraneoplastic neurological syndromes; PNS=paraneoplastic syndromes.
* One patient was positive for both anti-Ma2 and CV2 antibodies.
** Of the nine patients with PNS who had positive onconeural antibodies by IB, 4 were 1+ positive, 3 were 2+ positive and 2 were 3+ positive. Of the 13 patients with NPNS who had positive onconeural antibodies by IB, 10 were 1+ positive, 2 were 2+ positive and 1 was 3+ positive.
The Euronetwork PNS diagnostic criteria considers the presence of a well-characterised onconeural antibody sufficient for the diagnosis of PNS, even in patients with non-classical neurologic presentations and no malignancy.Reference Graus, Delattre and Antoine 3 It is therefore challenging to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of onconeural antibody testing owing to incorporation bias, which occurs when the diagnostic test under study is incorporated into the diagnostic criteria of the disease.Reference Worster and Carpenter 4 In our retrospective review of onconeural antibody testing, we found that 7.5% of patients tested had a reported positive result. This is in contrast to previous studies that have found onconeural antibodies in only 1%-2% of patients screened for suspected PNS.Reference Karim, Hughes, Winer, Williams and Bradwell 5 , Reference Pittock, Kryzer and Lennon 6 Although this could theoretically be because of improved patient selection at our institution, the findings of our study are concerning for a high proportion of FP. Interestingly, anti-Ma2 accounted for the majority (61%) of all positive results in our review, followed by anti-amphiphysin (22%) and anti-CV2 (13%). This is in contrast to previously reported onconeural antibody frequencies in the largest database on PNS, wherein the most frequently reported onconeural antibody was anti-Hu (39%) followed by anti-Yo (13%).Reference Giometto, Grisold and Vitaliani 7
The discrepancies between our findings and previous studies may at least partially be due to the fact that the majority of our reported positive onconeural antibody test results were positive by IB but negative by IFA. This is in contrast to the term “well-characterised onconeural antibodies” as defined in the Euronetwork PNS diagnostic criteria, which requires initial positivity by immunohistochemistry followed by positive immunoblotting to confirm antibody specificity.Reference Graus, Delattre and Antoine 3 It has been recommended not to rely solely on IB for the identification of onconeural antibodies, without confirmation by another method such as IFA.Reference Raspotnig, Vedeler and Storstein 1 , Reference Zoccarato, Gastaldi and Zuliani 8 This is of particular relevance as onconeural antibody testing becomes available to generalist laboratories, which may lack the expertise required to interpret IFA and therefore overly rely on IB when reporting a positive result. Although in our study there was no statistically significant difference in the number of patients who were positive by both IFA and IB when comparing PNS with NPNS, it is worth noting that only two patients were both positive by IFA and had a strongly positive IB result. Both of these patients had a malignancy identified and were classified as TP, suggesting that concordant positivity by IFA and strong positivity by IB remains highly indicative of PNS.
Our study has several limitations. Owing to its retrospective nature, there were no criteria used to select who underwent onconeural antibody testing. Performing a test on patients who are highly unlikely to have a positive result may lower the PPV of the test, which decreases alongside the prevalence of a disease in a tested population. Our study reflects clinical practice, however, as healthcare providers frequently order onconeural antibody testing even in patients with atypical neurologic presentations once an autoimmune or paraneoplastic aetiology is entertained. Another limitation to our study is that we only reviewed the charts of patients with positive onconeural antibody testing. This precludes calculation of sensitivity, specificity or negative predictive value of this test, which all require separating true negative (TN) from false negative (FN) results. It bears emphasising, however, that patients with PNS may have non-classical neurologic presentations, and that onconeural antibody detection may precede the diagnosis of an occult malignancy by years. As such, even in a patient with neurologic symptoms that are atypical for a PNS and no identified malignancy, it remains challenging to assert that a negative onconeural antibody panel is a TN (i.e. the patient truly does not have a PNS). Conversely, a patient may have a syndrome that is clearly paraneoplastic but not typically associated with onconeural antibodies, such as a young woman with opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome and an ovarian teratoma.Reference Armangue, Titulaer and Sabater 9 Although her onconeural antibody panel would probably be negative in the presence of a PNS, it would seem inappropriate to consider this result a FN.
Given these difficulties in distinguishing between TN and FN, and the fact that our primary concern was a seemingly high number of positive onconeural antibody test results, we focused on distinguishing between TP and FP in order to calculate the PPV. The PPV of onconeural antibody testing has a major impact on clinical decision-making, as it represents the percentage of patients with a positive test result who actually have PNS. Owing to the lack of a non-pathologic diagnostic gold standard for PNS, we opted to exercise caution in determining which patients we classified as NPNS, by requiring that no malignancy be present and that an alternative diagnosis be identified. Although this method probably resulted in patients with NPNS being classified as PNS simply because of the lack of an alternative diagnosis, it avoids overestimation of FP and artificial lowering of the PPV. Despite this conservative approach, the calculated PPV of onconeural antibody testing for PNS in our study was only 39%. Our study suggests that the PPV of onconeural antibody testing for PNS may be lower than appreciated by healthcare providers. In particular, onconeural antibody detection by immunoblotting alone, without confirmatory testing by a second assay such as IFA, should be viewed critically. Recognising the potential diagnostic pitfalls of onconeural antibody testing is essential to avoid unnecessary repeated malignancy screening, inappropriate administration of immunotherapy and delayed identification of correct alternative diagnoses.
Disclosures
The authors declare that they have nothing to disclose.
Statement of Authorship
AB analysed the data and drafted the manuscript. MWN reviewed the manuscript for intellectual content. LY analysed the data and reviewed the manuscript for intellectual content.




