No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
D-Spaces and Resolution
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
Abstract
Core share and HTML view are not available for this content. However, as you have access to this content, a full PDF is available via the ‘Save PDF’ action button.
A space X is a D-space if, for every neighborhood assignment f there is a closed discrete set D such that 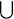 f(D) = X. In this paper we give some necessary conditions and some sufficient conditions for a resolution of a topological space to be a D-space. In particular, if a space X is resolved at each x ∊ X into a D-space Y x by continuous mappings fx : X − {x} → Yx , then the resolution is a D-space if and only if
f(D) = X. In this paper we give some necessary conditions and some sufficient conditions for a resolution of a topological space to be a D-space. In particular, if a space X is resolved at each x ∊ X into a D-space Y x by continuous mappings fx : X − {x} → Yx , then the resolution is a D-space if and only if 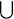 {x} × Bd(Yx ) is a D-space.
{x} × Bd(Yx ) is a D-space.
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Canadian Mathematical Society 1997
References
1.
van Douwen, E. K. and Pfeffer, W. F., Some Properties of the Sorgenfrey Line and Related Spaces. Pacific J. Math. (2) 81 (1979).Google Scholar
3.
Watson, S., The Construction of Topological Spaces. Recent Progress in General Topology, North-Holland, 1992.Google Scholar

