No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
On the Absolute Nörlund Summability of a Fourier Series
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
Extract
Core share and HTML view are not available for this content. However, as you have access to this content, a full PDF is available via the ‘Save PDF’ action button.
Let  be a given infinite series and {sn} the sequence of its partial sums. Let {pn} be a sequence of constants, real or complex, and let us write
be a given infinite series and {sn} the sequence of its partial sums. Let {pn} be a sequence of constants, real or complex, and let us write
(1.1)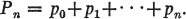
If
(1.2)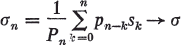
as n→∞, we say that the series  is summable by the Nörlund method (N,pn) to σ. The series
is summable by the Nörlund method (N,pn) to σ. The series  is said to be absolutely summable (N,pn) or summable |N,pn| if σn is of bounded variation, i.e.,
is said to be absolutely summable (N,pn) or summable |N,pn| if σn is of bounded variation, i.e.,
(1.3)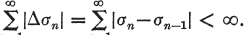
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Canadian Mathematical Society 1973
References
1.
Alexits, G., Convergence problems of orthogonal series, Pergamon Press, New York, 1961.Google Scholar
2.
Bhatt, S. N., An aspect of the local property of |N, pn| summability of a Fourier series, Indian J. Math.
5 (1963), 87–91.Google Scholar
3.
Hsiang, F. C., On the absolute Nörlund summability of a Fourier series, J. Austral. Math. Soc.
7 (1967), 252–256.Google Scholar


