Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Stancu, A.
2011.
Centro-Affine Invariants for Smooth Convex Bodies.
International Mathematics Research Notices,
Reisner, Shlomo
Schütt, Carsten
and
Werner, Elisabeth M.
2012.
Mahler's Conjecture and Curvature.
International Mathematics Research Notices,
Vol. 2012,
Issue. 1,
p.
1.
Böröczky, K.
Makai, E.
Meyer, M.
and
Reisner, S.
2013.
On the volume product of planar polar convex bodies — Lower estimates with stability.
Studia Scientiarum Mathematicarum Hungarica,
Vol. 50,
Issue. 2,
p.
159.
Ivaki, Mohammad N.
2014.
On the Stability of the p-Affine Isoperimetric Inequality.
The Journal of Geometric Analysis,
Vol. 24,
Issue. 4,
p.
1898.
Kim, Jaegil
2014.
Minimal volume product near Hanner polytopes.
Journal of Functional Analysis,
Vol. 266,
Issue. 4,
p.
2360.
Jesús Jerónimo Castro
2015.
The Volume of the Convex Hull of a Body and its Homothetic Copies.
The American Mathematical Monthly,
Vol. 122,
Issue. 5,
p.
486.
Rademacher, Luis
2016.
A SIMPLICIAL POLYTOPE THAT MAXIMIZES THE ISOTROPIC CONSTANT MUST BE A SIMPLEX.
Mathematika,
Vol. 62,
Issue. 1,
p.
307.
Rebollo Bueno, Jesus
2021.
Stochastic reverse isoperimetric inequalities in the plane.
Geometriae Dedicata,
Vol. 215,
Issue. 1,
p.
401.
Alexander, Matthew
Fradelizi, Matthieu
García-Lirola, Luis C.
and
Zvavitch, Artem
2021.
Geometry and volume product of finite dimensional Lipschitz-free spaces.
Journal of Functional Analysis,
Vol. 280,
Issue. 4,
p.
108849.
Florentin, D.
Schütt, C.
Werner, E.
and
Zhang, N.
2022.
Convex floating bodies of equilibrium.
Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society,
Vol. 150,
Issue. 7,
p.
3037.
G. Horváth, Ákos
and
Lángi, Zsolt
2022.
On the convex hull and homothetic convex hull functions of a convex body.
Geometriae Dedicata,
Vol. 216,
Issue. 1,
Liu, Chunyan
Werner, Elisabeth M.
Ye, Deping
and
Zhang, Ning
2025.
Archimedes’ principle of flotation and floating bodies: construction, extensions and related problems.
Acta Mathematica Scientia,
Vol. 45,
Issue. 1,
p.
237.
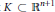 $K\,\subset \,{{\mathbb{R}}^{n+1}}$ be a convex body of class
$K\,\subset \,{{\mathbb{R}}^{n+1}}$ be a convex body of class 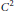 ${{C}^{2}}$ with everywhere positive Gauss curvature. We show that there exists a positive number
${{C}^{2}}$ with everywhere positive Gauss curvature. We show that there exists a positive number 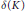 $\delta \left( K \right)$ such that for any
$\delta \left( K \right)$ such that for any 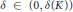 $\delta \,\in \,\left( 0,\,\delta \left( K \right) \right)$ we have
$\delta \,\in \,\left( 0,\,\delta \left( K \right) \right)$ we have 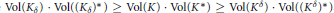 $\text{Vol}\left( {{K}_{\delta }} \right)\,\cdot \,\text{Vol}\left( {{\left( {{K}_{\delta }} \right)}^{*}} \right)\,\ge \,\text{Vol}\left( K \right)\,\cdot \,\text{Vol}\left( {{K}^{*}} \right)\,\ge \,\text{Vol}\left( {{K}^{\delta }} \right)\,\cdot \,\text{Vol}\left( {{\left( {{K}^{\delta }} \right)}^{*}} \right)$, where
$\text{Vol}\left( {{K}_{\delta }} \right)\,\cdot \,\text{Vol}\left( {{\left( {{K}_{\delta }} \right)}^{*}} \right)\,\ge \,\text{Vol}\left( K \right)\,\cdot \,\text{Vol}\left( {{K}^{*}} \right)\,\ge \,\text{Vol}\left( {{K}^{\delta }} \right)\,\cdot \,\text{Vol}\left( {{\left( {{K}^{\delta }} \right)}^{*}} \right)$, where 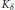 ${{K}_{\delta }}$,
${{K}_{\delta }}$, 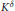 ${{K}^{\delta }}$ and
${{K}^{\delta }}$ and 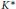 ${{K}^{*}}$ stand for the convex floating body, the illumination body, and the polar of
${{K}^{*}}$ stand for the convex floating body, the illumination body, and the polar of 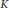 $K$, respectively. We derive a few consequences of these inequalities.
$K$, respectively. We derive a few consequences of these inequalities.