Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 July 2024
The most prominent authigenic reaction in Holocene tuffaceous sediments at Teels Marsh, Nevada, is the hydration of rhyolitic glass by interstitial brines and the subsequent formation of phillipsite. This reaction has the form: rhyolitic glass + H2O → hydrous alkali alumninosilicate gel → phillipsite. Phillipsite is the most abundant authigenic phase in the tuffaceous sediments (>95%), analcime is the next most abundant phase, and clinoptilolite occurs as a trace mineral in the <2-mm fraction. Analcime forms by the reaction of phillipsite and Na+. Gaylussite and searlesite also are common authigenic phases at Teels Marsh. The concentration of silica in the interstitial brines is controlled by one or more of the authigenic reactions at less than 100 ppm. A stoichiometric equation for the reaction of phillipsite to analcime at Teels Marsh is:
Sodium and potassium activities of brines associated with both phillipsite and analcime were used to estimate the equilibrium constant for this reaction as 3.04 × 10−5. The ΔG0 value for the reaction is +6.2 kcal/mole at 25°C and 1 atm pressure. The estimated ΔG0 value of phillipsite, using this reaction, is −1072.8 kcal/mole at 25°C and 1 atm.
Наиболее рельефной аутигенной реакцией в голоценовых туфовых осадках в Тиилс Марш, Невада является гидрация риолитового стекла трещинной соленой водой и последующее образование филлипсита. Эта реакция протекает следующим образом: риолитовое стекло + H2O → воднощелочный алюминосиликатный гель → филлипсит. Филлипсит является наиболее распространенной аутигенной фазой в туфовых осадках (>95%), за ним идет анальцим, тогда как следы клиноптилолита появляются во фракции размером <2 мм. Анальцим образуется путем реакции филлипсита и Na+. Гейлюсит и сирлесит являются также популярными аутогенными фазами в Тиилс Марш. Концентрация кремнезема в трещинных соленых водах контролируется одной или более аутигенными реакциями при менее чем 100 милионных. Стехиометрическое уравнение для реакции преобразования филлипсита в анальцим: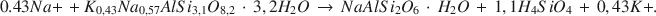
Натриевые и калиевые активности соленой воды, связанные с обоими, филлипситом и анальцимом, были использованы для определения константы равновесия для этой реакции, равной 3,04 × 10-5. Величина ΔG0 для реакйии равна +6,2 ккал/моль при 25°С и давлении 1 атм. Величина ΔG0 для филлипсита, определенная при использовании этой реакции, равна −1072,8 ккал/моль при 25°C и 1 атм. [E.C.]
Die wichtigste authigene Reaktion in holozänen tuffhaltigen Sedimenten von Teels Marsh, Nevada, ist die Hydratation von Rhyolithglas durch Porenlösungen und die darauf folgende Bildung von Phillipsit. Diese Reaktion verläuft folgendermaßen: Rhyolithglas + H2O → wasserhaltiges Alkali-Alumosilikat-Gel → Phillipsit. Phillipsit ist die häufigste authigene Phase in den tuffhaltigen Sedimenten (>95%), Analcim ist die nächsthäufige Phase. Klinoptilolith kommt nur in Spuren in der Fraktion <2 mm vor. Analcim bildet sich durch die Reaktion von Phillipsit mit Na+. Gaylussit and Searlesit sind ebenfalls authigene Phasen in Teels Marsh. Die Konzentration an Siliziumdioxid in den Porenlösungen wird durch eine oder mehrere der authigenen Reaktionen kontrolliert und beträgt weniger als 100 ppm. Eine stöchiometrische Gleichung für die Reaktion von Phillipsit zu Analcim in Teels Marsh lautet: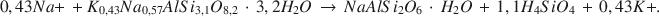
Die Natrium- und Kaliumaktivitäten der Porenlösungen, die sowohl mit Phillipsit als auch mit Analcim im Gleichgewicht stehen, wurden verwendet, um die Gleichgewichtskonstante für diese Reaktion abzuschätzen. Sie beträgt 3,04 × 10−5. Der ΔG0-Wert für die Reaktion beträgt +6,2 kcal/mol bei 25°C und 1 atm Druck. Der geschätzte ΔG0-Wert von Phillipsit beträgt, bei Verwendung dieser Reaktion, −1072,8 kcal/mol bei 25°C und 1 atm. [U.W.]
La réaction authigénique la plus proéminente dans les sédiments holocènes tufacés à Teels Marsh, au Nevada, est l'hydration du verre rhyolitique par des saumures interstitiales et la formation ultérieure de phillipsite. Cette réaction a la forme suivante: verre rhyolitique + H2O → gel alkali aluminosilicate hydre → phillipsite. La phillipsite est la phase authigénique la plus abondante dans les sédiments tufacés (>95%), suivie par la phase analcime, seconde en abondance, et la clinoptilolite apparait comme trace minérale dans la fraction <2 mm. L'analcime est produite par la réaction de phillipsite et de Na+. La gaylussite et la searlesite sont aussi des phases authigéniques courantes à Teels Marsh. La concentration de silice dans les saumures interstitiales est controlée par une ou plusieurs réactions authigéniques à moins de 100 ppm. Une équation stoichiométrique pour la réaction de phillipsite en analcime à Teels Marsh est: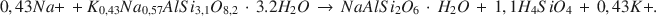
Les activités du sodium et du potassium des saumures avec à la fois la phillipsite et l'analcime ont été employées pour estimer comme constante d’équilibre pour cette réaction 3,04 × 10−5. La valeur ΔG0 pour la réaction est +6,2 kcal/mole à 25°C et à 1 atm de pression. La valeur estimée de ΔG0 pour la phillipsite, utilisant cette réaction, est −1072 kcal/mole à 25°C et 1 atm. [D.J.]