Article contents
Estimating parameters associated with monotone properties
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 March 2020
Abstract
There has been substantial interest in estimating the value of a graph parameter, i.e. of a real-valued function defined on the set of finite graphs, by querying a randomly sampled substructure whose size is independent of the size of the input. Graph parameters that may be successfully estimated in this way are said to be testable or estimable, and the sample complexity qz = qz(ε) of an estimable parameter z is the size of a random sample of a graph G required to ensure that the value of z(G) may be estimated within an error of ε with probability at least 2/3. In this paper, for any fixed monotone graph property 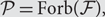 $\mathcal{P}= \text{Forb}\!(\mathcal{F}),$ we study the sample complexity of estimating a bounded graph parameter z that, for an input graph G, counts the number of spanning subgraphs of G that satisfy
$\mathcal{P}= \text{Forb}\!(\mathcal{F}),$ we study the sample complexity of estimating a bounded graph parameter z that, for an input graph G, counts the number of spanning subgraphs of G that satisfy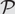 $\mathcal{P}$. To improve upon previous upper bounds on the sample complexity, we show that the vertex set of any graph that satisfies a monotone property
$\mathcal{P}$. To improve upon previous upper bounds on the sample complexity, we show that the vertex set of any graph that satisfies a monotone property 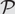 $\mathcal{P}$ may be partitioned equitably into a constant number of classes in such a way that the cluster graph induced by the partition is not far from satisfying a natural weighted graph generalization of
$\mathcal{P}$ may be partitioned equitably into a constant number of classes in such a way that the cluster graph induced by the partition is not far from satisfying a natural weighted graph generalization of 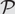 $\mathcal{P}$. Properties for which this holds are said to be recoverable, and the study of recoverable properties may be of independent interest.
$\mathcal{P}$. Properties for which this holds are said to be recoverable, and the study of recoverable properties may be of independent interest.
Information
- Type
- Paper
- Information
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press 2020
References
- 4
- Cited by


