Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
BOEHNLEIN, EDWARD
and
JIANG, TAO
2012.
Set Families With a Forbidden Induced Subposet.
Combinatorics, Probability and Computing,
Vol. 21,
Issue. 4,
p.
496.
Axenovich, Maria
Manske, Jacob
and
Martin, Ryan
2012.
Q 2-free Families in the Boolean Lattice.
Order,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 1,
p.
177.
Griggs, Jerrold R.
Li, Wei-Tian
and
Lu, Linyuan
2012.
Diamond-free families.
Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A,
Vol. 119,
Issue. 2,
p.
310.
Griggs, Jerrold R.
and
Li, Wei-Tian
2013.
The partition method for poset-free families.
Journal of Combinatorial Optimization,
Vol. 25,
Issue. 4,
p.
587.
Katona, Gyula O.H.
2013.
Sperner type theorems with excluded subposets.
Discrete Applied Mathematics,
Vol. 161,
Issue. 9,
p.
1251.
Manske, Jacob
and
Shen, Jian
2013.
Three Layer Q 2-Free Families in the Boolean Lattice.
Order,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 2,
p.
585.
Kramer, Lucas
Martin, Ryan R.
and
Young, Michael
2013.
On diamond-free subposets of the Boolean lattice.
Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A,
Vol. 120,
Issue. 3,
p.
545.
Lu, Linyuan
2014.
On crown-free families of subsets.
Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A,
Vol. 126,
Issue. ,
p.
216.
Sarkis, Ghassan
and
Shahriari, Shahriar
2014.
Diamond-Free Subsets in the Linear Lattices.
Order,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 3,
p.
421.
Johnston, Travis
Lu, Linyuan
and
Milans, Kevin G.
2015.
Boolean algebras and Lubell functions.
Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A,
Vol. 136,
Issue. ,
p.
174.
Czabarka, Éva
Dutle, Aaron
Johnston, Travis
and
Székely, László A.
2015.
Abelian groups yield many large families for the diamond problem.
European Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 1,
Issue. 2,
p.
320.
Katona, Gyula O. H.
and
Nagy, Dániel T.
2015.
Incomparable Copies of a Poset in the Boolean Lattice.
Order,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 3,
p.
419.
Griggs, Jerrold R.
and
Li, Wei-Tian
2015.
Poset-free families and Lubell-boundedness.
Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A,
Vol. 134,
Issue. ,
p.
166.
Lu, Linyuan
and
Milans, Kevin G.
2015.
Set families with forbidden subposets.
Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A,
Vol. 136,
Issue. ,
p.
126.
Patkós, Balázs
2015.
Supersaturation and stability for forbidden subposet problems.
Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A,
Vol. 136,
Issue. ,
p.
220.
Gu, Ran
Li, Xueliang
Peng, Yuejian
and
Shi, Yongtang
2016.
Some Motzkin–Straus type results for non-uniform hypergraphs.
Journal of Combinatorial Optimization,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 1,
p.
223.
Peng, Yuejian
Peng, Hao
Tang, Qingsong
and
Zhao, Cheng
2016.
An extension of the Motzkin–Straus theorem to non-uniform hypergraphs and its applications.
Discrete Applied Mathematics,
Vol. 200,
Issue. ,
p.
170.
METHUKU, ABHISHEK
and
PÁLVÖLGYI, DÖMÖTÖR
2017.
Forbidden Hypermatrices Imply General Bounds on Induced Forbidden Subposet Problems.
Combinatorics, Probability and Computing,
Vol. 26,
Issue. 4,
p.
593.
Cox, Christopher
and
Stolee, Derrick
2018.
Ramsey Numbers for Partially-Ordered Sets.
Order,
Vol. 35,
Issue. 3,
p.
557.
Nagy, Dániel T.
2018.
Forbidden subposet problems with size restrictions.
Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A,
Vol. 155,
Issue. ,
p.
42.
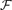 ⊂ 2[n] be a family of subsets of {1, 2,. . ., n}. For any poset H, we say
⊂ 2[n] be a family of subsets of {1, 2,. . ., n}. For any poset H, we say 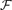 is H-free if
is H-free if 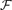 does not contain any subposet isomorphic to H. Katona and others have investigated the behaviour of La(n, H), which denotes the maximum size of H-free families
does not contain any subposet isomorphic to H. Katona and others have investigated the behaviour of La(n, H), which denotes the maximum size of H-free families 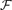 ⊂ 2[n]. Here we use a new approach, which is to apply methods from extremal graph theory and probability theory to identify new classes of posets H, for which La(n, H) can be determined asymptotically as n → ∞ for various posets H, including two-end-forks, up-down trees, and cycles C4k on two levels.
⊂ 2[n]. Here we use a new approach, which is to apply methods from extremal graph theory and probability theory to identify new classes of posets H, for which La(n, H) can be determined asymptotically as n → ∞ for various posets H, including two-end-forks, up-down trees, and cycles C4k on two levels.