Article contents
On fields of rationality for automorphic representations
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 September 2014
Abstract
This paper proves two results on the field of rationality 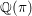 $\mathbb{Q}({\it\pi})$ for an automorphic representation
$\mathbb{Q}({\it\pi})$ for an automorphic representation  ${\it\pi}$, which is the subfield of
${\it\pi}$, which is the subfield of 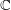 $\mathbb{C}$ fixed under the subgroup of
$\mathbb{C}$ fixed under the subgroup of 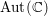 $\text{Aut}(\mathbb{C})$ stabilizing the isomorphism class of the finite part of
$\text{Aut}(\mathbb{C})$ stabilizing the isomorphism class of the finite part of  ${\it\pi}$. For general linear groups and classical groups, our first main result is the finiteness of the set of discrete automorphic representations
${\it\pi}$. For general linear groups and classical groups, our first main result is the finiteness of the set of discrete automorphic representations  ${\it\pi}$ such that
${\it\pi}$ such that  ${\it\pi}$ is unramified away from a fixed finite set of places,
${\it\pi}$ is unramified away from a fixed finite set of places, 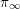 ${\it\pi}_{\infty }$ has a fixed infinitesimal character, and
${\it\pi}_{\infty }$ has a fixed infinitesimal character, and 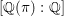 $[\mathbb{Q}({\it\pi}):\mathbb{Q}]$ is bounded. The second main result is that for classical groups,
$[\mathbb{Q}({\it\pi}):\mathbb{Q}]$ is bounded. The second main result is that for classical groups, 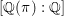 $[\mathbb{Q}({\it\pi}):\mathbb{Q}]$ grows to infinity in a family of automorphic representations in level aspect whose infinite components are discrete series in a fixed
$[\mathbb{Q}({\it\pi}):\mathbb{Q}]$ grows to infinity in a family of automorphic representations in level aspect whose infinite components are discrete series in a fixed 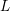 $L$-packet under mild conditions.
$L$-packet under mild conditions.
MSC classification
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s) 2014
References
- 11
- Cited by

