Article contents
Équivalence motivique des groupes algébriques semisimples
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 July 2017
Abstract
We prove that the standard motives of a semisimple algebraic group 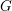 $G$ with coefficients in a field of order
$G$ with coefficients in a field of order 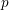 $p$ are determined by the upper motives of the group
$p$ are determined by the upper motives of the group 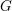 $G$ . As a consequence of this result, we obtain a partial version of the motivic rigidity conjecture of special linear groups. The result is then used to construct the higher indexes which characterize the motivic equivalence of semisimple algebraic groups. The criteria of motivic equivalence derived from the expressions of these indexes produce a dictionary between motives, algebraic structures and the birational geometry of twisted flag varieties. This correspondence is then described for special linear groups and orthogonal groups (the criteria associated with other groups being obtained in De Clercq and Garibaldi [Tits
$G$ . As a consequence of this result, we obtain a partial version of the motivic rigidity conjecture of special linear groups. The result is then used to construct the higher indexes which characterize the motivic equivalence of semisimple algebraic groups. The criteria of motivic equivalence derived from the expressions of these indexes produce a dictionary between motives, algebraic structures and the birational geometry of twisted flag varieties. This correspondence is then described for special linear groups and orthogonal groups (the criteria associated with other groups being obtained in De Clercq and Garibaldi [Tits  $p$ -indexes of semisimple algebraic groups, J. Lond. Math. Soc. (2) 95 (2017) 567–585]). The proofs rely on the Levi-type motivic decompositions of isotropic twisted flag varieties due to Chernousov, Gille and Merkurjev, and on the notion of pondered field extensions.
$p$ -indexes of semisimple algebraic groups, J. Lond. Math. Soc. (2) 95 (2017) 567–585]). The proofs rely on the Levi-type motivic decompositions of isotropic twisted flag varieties due to Chernousov, Gille and Merkurjev, and on the notion of pondered field extensions.
On prouve dans cet article que l’ensemble des motifs standards d’un groupe semisimple  $G$ à coefficients dans un corps à
$G$ à coefficients dans un corps à 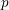 $p$ éléments est déterminé par l’ensemble des motifs supérieurs du groupe
$p$ éléments est déterminé par l’ensemble des motifs supérieurs du groupe  $G$ . En conséquence de ce résultat, on obtient une version partielle de la conjecture de rigidité motivique des groupes spéciaux linéaires. Ce résultat est ensuite utilisé pour construire les indices supérieurs qui caractérisent l’équivalence motivique des groupes semisimples. Les critères d’équivalence motivique dérivés de l’expression de ces indices fournissent un dictionnaire mêlant motifs, structures algébriques et géométrie birationnelle des variétés de drapeaux généralisées. Cette correspondance est ensuite décrite pour les groupes spéciaux linéaires et les groupes orthogonaux (les critères afférents pour les autres groupes faisant l’objet de De Clercq and Garibaldi [Tits
$G$ . En conséquence de ce résultat, on obtient une version partielle de la conjecture de rigidité motivique des groupes spéciaux linéaires. Ce résultat est ensuite utilisé pour construire les indices supérieurs qui caractérisent l’équivalence motivique des groupes semisimples. Les critères d’équivalence motivique dérivés de l’expression de ces indices fournissent un dictionnaire mêlant motifs, structures algébriques et géométrie birationnelle des variétés de drapeaux généralisées. Cette correspondance est ensuite décrite pour les groupes spéciaux linéaires et les groupes orthogonaux (les critères afférents pour les autres groupes faisant l’objet de De Clercq and Garibaldi [Tits  $p$ -indexes of semisimple algebraic groups, J. Lond. Math. Soc. (2) 95 (2017) 567–585]). Les preuves de ces résultats reposent principalement sur les décompositions motiviques de type Levi de Chernousov, Gille et Merkurjev des variétés de drapeaux isotropes, ainsi que sur la notion d’extension pondérée.
$p$ -indexes of semisimple algebraic groups, J. Lond. Math. Soc. (2) 95 (2017) 567–585]). Les preuves de ces résultats reposent principalement sur les décompositions motiviques de type Levi de Chernousov, Gille et Merkurjev des variétés de drapeaux isotropes, ainsi que sur la notion d’extension pondérée.
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author 2017
References
- 3
- Cited by

