Natural disasters, biological terrorism, nuclear leakage, public health emergencies, epidemic diseases, and other disasters directly threaten the survival and development of mankind. Currently, a major disaster occurs almost daily in some part of the world.Reference Tavakoli, Jahanbakhsh and Fooladvand 1 Most population centers are concentrated in high-risk locales like metropolitan cities, which feature very frequent and multiple person-to-person contacts. High-risk occupations, international trade, and housing construction all increase the possibility of human exposure to disasters, leading to increased casualties after each disaster. The ever-increasing spiral of human populations, the rapid growth of technology, swift world-wide travel by millions of persons, and the exponential expansion of at-risk industries and residences combine to increase human exposure to disasters.Reference Pepe, Rinnert and Wigginton 2
In particular, the major casualties caused by the Wenchuan earthquake, the Nepal earthquake, and the Indian Ocean tsunami pose great challenges to disaster medicine.Reference Bibo and Jingchen 3 The 2008 Wenchuan earthquake was one of the most devastating disasters in the past 10 years and caused more than 370,000 casualties; the main causes of death were trauma and crush syndrome. In addition, there was a significant increase in the number of respiratory infections, enteritis, and skin diseases in the week after the earthquake. Even a full year after the earthquake, some survivors began to suffer from posttraumatic stress disorder.Reference Zhang, Liu and Li 4
Disaster medicine has attracted global attention gradually by implementing emergency medical treatment, disease prevention, and health care science under the conditions of disastrous damage. After the September 11 attacks, the United States made two major adjustments to the National Disaster Medical System (NDMS) to form a high-efficiency operating mechanism called the national disaster medical rescue system.Reference Morhard and Franco 5 Japan has also established a national rescue medical center in Tachikawa City, Tokyo. As a data transmission and command center for disaster medical care, it features a disaster medical information system used to determine damage for medical institutions. In addition, Japan has enhanced its disaster emergency medical rescues by launching civil and community organizations.Reference Homma 6 After the outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in 2003, China likewise began to attach importance to the establishment of an emergency medical system. Then, after experiencing the Wenchuan, Lushan, and Yushu earthquakes, and observing the actual rescue experience, it built an emergency medical rescue system, including a rescue command center and a medical rescue scene and rescue information platform.Reference Zhu, Ji and Junxing 7
Disaster medicine scholars have published a substantial amount of original research based on care during disaster rescues, emergency medical treatment, and disease prevention. However, the bibliometric profile of disaster medicine in the literature is still unknown. Therefore, in this study, a scientometric analysis was conducted on disaster medicine to estimate the productivity of specific journals, countries, institutions, authors, and research areas, and to identify research hotspots and trends in this field.
METHODS
All of the data for this study were obtained from the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) of Thomson Reuters on March 27, 2017 (incomplete data existed in 2017).Reference Chen, Hu and Liu 8 The WoSCC, which includes the Social Sciences Citation Index, Current Chemical Reactions, and Index Chemicus, is the most frequently used source of scientific information.Reference Li, Zhang, Wang and Ho 9 The search term “disaster medicine” was used to retrieve titles, keywords, author information, abstracts, and references published from 2008 to 2017. The following search string was used: (TS=(disaster medicine)) AND Languages: (English) AND document type: (Article OR Review). The impact factor of each journal was obtained from the 2016 Journal Citation Reports Science Edition, accessed on March 27, 2017.Reference Huang 10 CiteSpace III (64 bits)Reference Chen, Hu and Liu 8 was used to analyze publication outputs and construct knowledge maps, to analyze the extracted records for citation characteristics, and to visualize the patterns and trends in disaster medicine.Reference Yin, Chen and Li 11 – 15
RESULTS
General Data
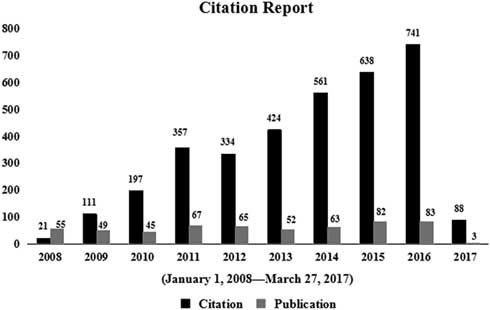
A total of 564 studies on disaster medicine, published from 2008 to 2017, were retrieved from the WoSCC (incomplete data existed in 2017). Of these, 497 (88.12%) were original articles. Although the number of publications increased only mildly from 2008 (n=55) to 2016 (n=83), the number of citations increased substantially from 2008 (n=21) to 2016 (n=741) (Figure 1). Of 564 studies, 403 (71.45%) were cited at least once, with an average of 6.12 citations per article for 3,452 total citations. Table 1 shows the 10 most frequently cited articles.Reference Devereaux, Dichter and Christian 16 – Reference Gordon, Staples and Blyta 25 Among these 10 articles, the most common topic was disaster rescue and post-disaster health effects (9 of 10 [90%]). The top-ranking paper (73 citations) was published in CHEST and involved critical care treatment: “Definitive care for the critically ill during a disaster: A framework for allocation of scarce resources in mass critical care – From a Task Force for Mass Critical Care summit meeting, January 26-27, 2007, Chicago, IL.”Reference Devereaux, Dichter and Christian 16 The article provided 4 suggestions to perform triage while allocating scarce critical care resources during a disaster.
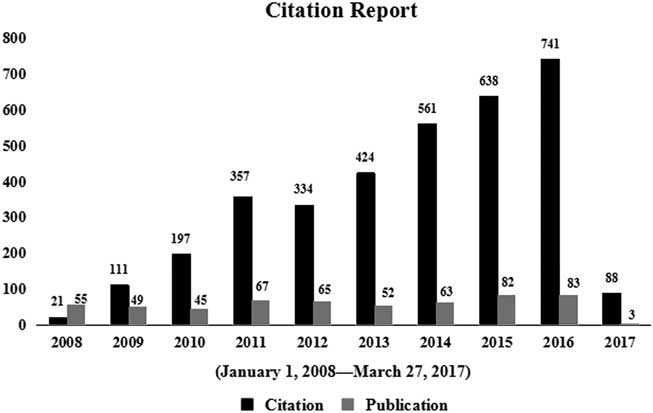
Figure 1 The Number of Publications and Citations From 2008 to 2017.
Table 1 Top 10 Most Cited Articles in Disaster Medicine Field

Journal Analysis
The studies were published in 102 different journals. The top-ranked journal, which published 65 papers, was Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness, followed by two other journals with more than 10 papers each: Academic Emergency Medicine (n=19) and American Journal of Preventive Medicine (n=15). Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness also had the greatest number of total citations (n=151), again followed by Academic Emergency Medicine (n=134) and American Journal of Preventive Medicine (n=127) (Table 1 in the online data supplement).
Country and Institution Analysis
These research studies were published by 54 countries. The top 10 countries published 484 of the 564 studies, accounting for 85.82% of the total number of publications. The country with the greatest number of publications was the United States (n=278), followed by Japan (n=46) and China (n=33) (Table 2 in the online data supplement). Similarly, among the 100 sponsoring institutions, the top 10 institutions published 142 literatures, accounting for 25.18% of the total number of publications. New York University had the most publications (n=20), followed by the University of Washington (n=17) and Johns Hopkins University (n=16) (Table 2S).
Author and Research Area Analysis
A total of 103 authors contributed to these 564 studies; the top 10 authors accounted for 67 studies, 11.88% of the total. Three authors tied for first place, each with 9 publications: M. D. Christian, F. Della Corte, and P. L. Ingrassia (Table 3 in the online data supplement). A total of 73 research areas were represented, with the majority of articles focusing on public environmental/occupational health (n=148), general internal medicine (n=113), and emergency medicine (n=98) (Table 3S).
Co-Citation Analysis
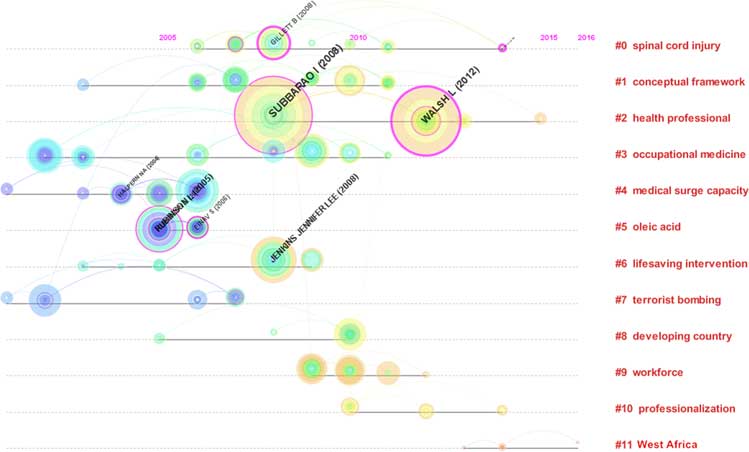
The visualization analysis for reference citations was conducted by CiteSpace III. The parameters in CiteSpace were as follows: time span=10 years (2008–2017); time slicing=1; term type=burst terms; selection criteria (c, cc, ccv)=(2, 2, 20) (4, 3, 20) (4, 3, 20). The top 50 most cited or occurring items from each slice were selected. The Pathfinder network method was used to streamline the network and to map the visualization analysis. The network revealed 244 nodes and 517 lines. In Figure 2, the thicker circle indicates a higher level of between-study centrality. In general, a study with a centrality value equal to or greater than 0.10 can be considered a key study; therefore, the key studies were [Subbarao I, 2008]Reference Subbarao, Lyznicki and Hsu 26 (0.22), followed by [Einav S, 2006]Reference Einav, Aharonson-Daniel and Weissman 27 (0.19) and [Gillett B, 2008]Reference Gillett, Peckler and Sinert 28 (0.16). In addition, the red circles represent burst studies which represent the frontier of a periodReference Xiaodan Zhou 29 ; Among them, the key burst studies were [Subbarao I, 2008]Reference Subbarao, Lyznicki and Hsu 26 and [Walsh L, 2012],Reference Walsh, Subbarao and Gebbie 30 which had the highest citation rates between 2014 and 2017.
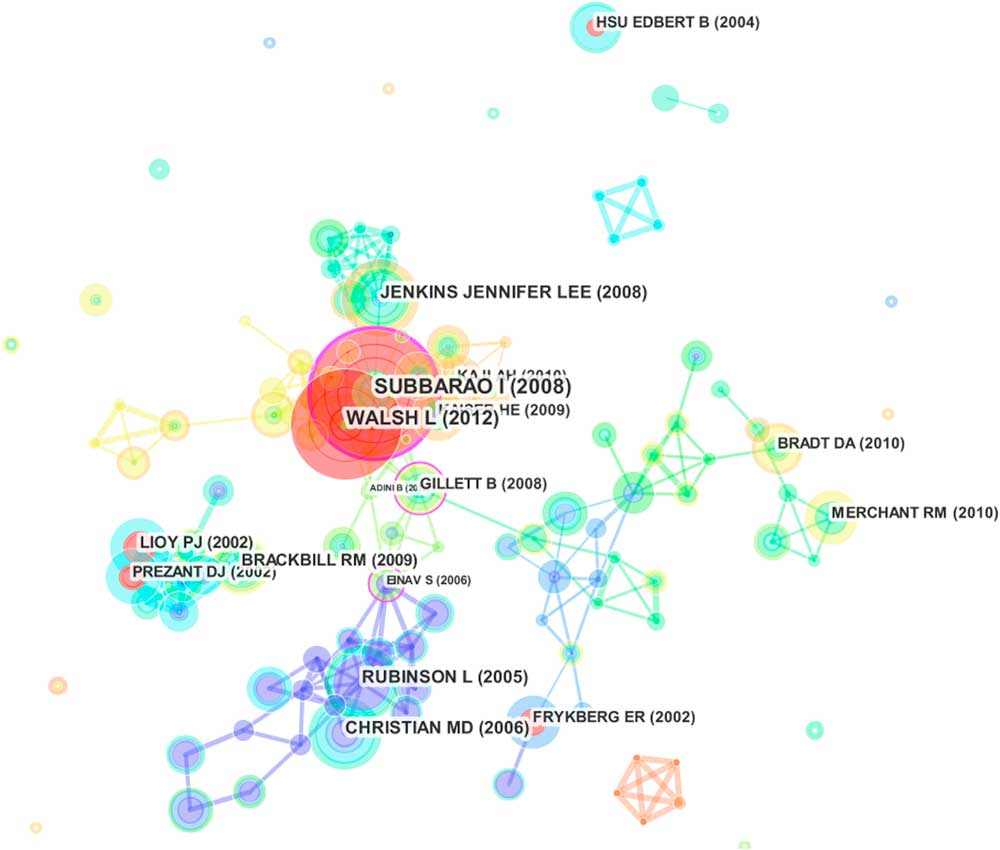
Figure 2 Reference Co-Citation Map of Papers Related to Disaster Medicine Research.
Figure 3 presents the timeline view for hot keywords. The results show that the hotspots of disaster medicine during this period were spinal cord injury, conceptual framework, health professional, occupational medicine, medical surge capacity, oleic acid, lifesaving intervention, terrorist bombing, developing country, workforce, professionalization and West Africa (Figure 3). In addition, the research papers published in journals represent the frontiers of certain subjects, and the references cited in these papers provide the knowledge base of the papers.Reference Li, Ma and Qu 31 In Figure 3, The nodes of clusters #3, #4, #5, #6, and #7 were mainly distributed before 2008 (the knowledge base), while the nodes of clusters #0, #1, #2, #8, #9, #10, and #11 were mainly distributed between 2008 and 2016 (the frontiers).
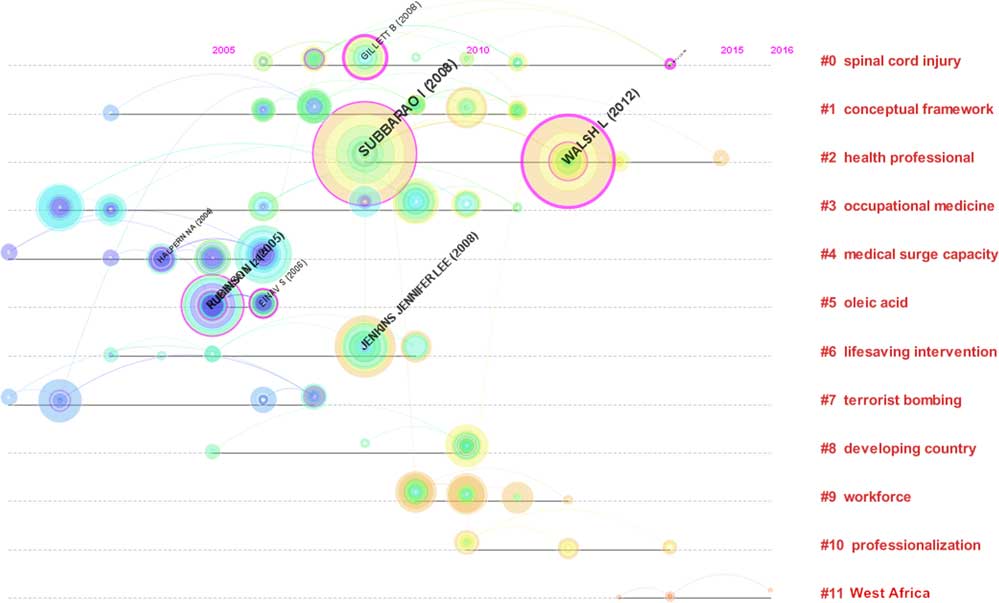
Figure 3 Reference Co-Citation Time-View Map of Papers Related to Disaster Medicine Research Published from 2008 to 2017.
Terms Analysis
A total of 564 papers on disaster medicine research were included in this analysis. The visualization was generated by the Carrot system based on the first 100 results of a search on regenerative medicine. There were 69 results from the Lingo Clustering Algorithm; the first ranked cluster was Practices in Disaster (n=112), followed by Hospital Disaster (n=107), Disaster Events (n=102), Disaster Setting (n=92), and Earthquake Disaster (n=78) (Figure 4). In addition, the time interval is depicted as a blue line, whereas the time period that represents a burst cited journal is depicted as a red line, indicating the beginning and the end of the time interval of each burst.Reference Xiaodan Zhou 29 The top 3 burst references were public health preparedness (7.35), Hurricane Katrina (4.72), and European journal (3.75) (Table 2).
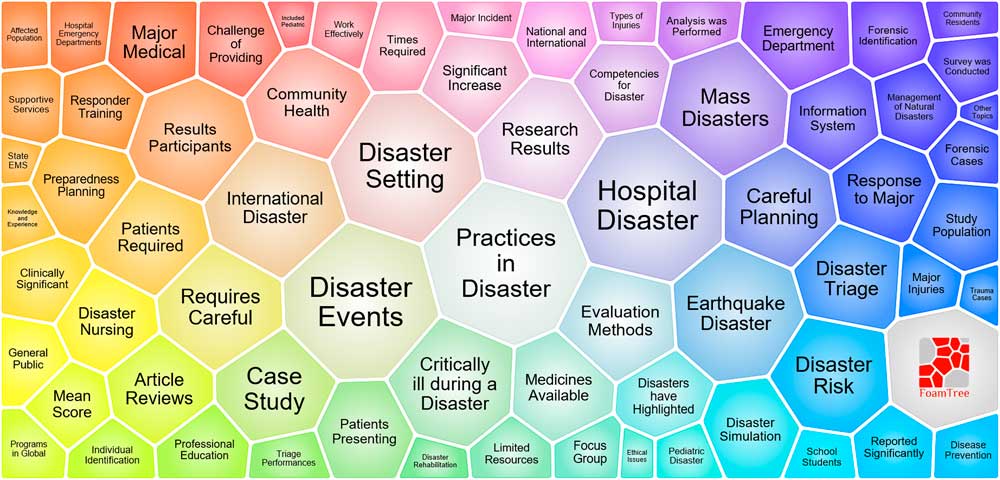
Figure 4 A Lightweight Map of Major Terms on Disaster Medicine.
Table 2 Top 12 Terms With Strongest Citation Bursts
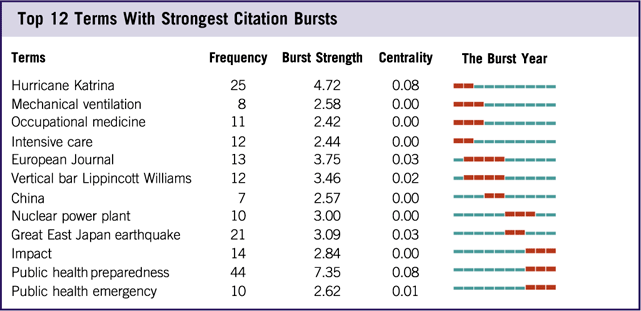
Burst strength: representing the intensity of the frequency of a key word suddenly increasing over a short period of time. The burst-detection algorithm can be adapted for detecting sharp increases of interest in a specialty. In CiteSpace III, a current research front is identified based on such burst terms extracted from titles, abstracts, descriptors, and identifiers of bibliographic records. Burst-detection algorithms can identify emergent terms; Centrality: evaluating the parameter of the number of lines on a certain node, the larger the value, the more the number of lines, that is, the importance of the node in the whole network.
![]() : 2008-2017.
: 2008-2017.
![]() : the burst year.
: the burst year.
DISCUSSION
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first scientometric analysis on the topic of disaster medicine. The results indicated a significant increase in the number of publications worldwide on this topic; the publications and citations in 2011 (67 and 357) were significantly higher than in 2010 (45 and 197). This increase may be due to several major disasters. The year 2011 was the first year after the Haiti earthquake, and much of the related research focused on the implementation and development of international medical rescue.Reference Jobe 32 – Reference Farfel, Assa and Amir 33 It was also the third year after the Wenchuan earthquake, research on which mainly focused on disease classification and patient management of the patients.Reference Nie, Tang and Lau 34 – Reference Zhang, Liu and Liu 35 Finally, 2011 was the 10th anniversary of the 9/11 attacks; the relevant research mainly focused on post-disaster effects, including respiratory and mental health problems, among survivors and rescuers.Reference Weakley, Webber and Gustave 36 – Reference Dunlop, Logue and Beltran 37 The United States, Japan, and China published the most research on disaster medicine. This may be because the frequent occurrence of disasters in these countries has caused serious casualties and property losses.Reference Zhang, Liu and Liu 35 , Reference Webber, Glaser and Weakley 38 – Reference Ishigaki, Higashi and Sakamoto 40 Likewise, these countries have participated in international humanitarian relief efforts many times, so they have a wealth of medical rescue experience.Reference Babcock, Theodosis and Bills 41 – Reference Ling, Ye and Cai 43 The top 10 studies (by number of citations) all emphasized 2 categories of disaster medicine, except for [Leaning J, 2007],Reference Leaning and Guhasapir 17 which summarizes the challenges and pressures posed by natural disasters to public health. These categories are disaster rescueReference Devereaux, Dichter and Christian 16 , Reference Weinberg, Auerbach and Shah 20 – Reference Devereaux, Christian and Dichter 23 and post-disaster health effects.Reference Webber, Gustave and Lee 18 – Reference North and Pfefferbaum 19 , Reference de la Hoz, Shohet and Chasan 24 – Reference Gordon, Staples and Blyta 25
Overall, the most cited article was “Definitive care for the critically ill during a disaster: A framework for allocation of scarce resources in mass critical care – From a Task Force for Mass Critical Care summit meeting, January 26-27, 2007, Chicago, IL,” which offers guidance for allocating scarce critical care resources, drawn from a task force on mass critical care. This task force provided several suggestions for managing the triage process when medical systems are overwhelmed.Reference Devereaux, Dichter and Christian 16 In addition, [Devereaux AV, 2008]Reference Devereaux, Dichter and Christian 16 was sponsored by New York University, which sponsored the greatest number of disaster medicine publications from 2008 to 2017. Among the authors, F. Della Corte, M. D. Christian, and P. L. Ingrassia were the most productive. In their papers, the most cited articles were all associated with the “Task Force for Mass Critical Care.” Reference Devereaux, Dichter and Christian 16 , Reference Devereaux, Christian and Dichter 44 – Reference Rubinson, Hick and Hanfling 45 Among the studies of post-disaster health effects, the most cited article was “Trends in respiratory symptoms of firefighters exposed to the World Trade Center disaster: 2001-2005,” which described trends in post-911 respiratory and gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms in WTC-exposed fire fighters.Reference Webber, Gustave and Lee 46 This study also contributed to the literature on public environmental/occupational health, the discipline that produced the most disaster medicine studies from 2008 to 2017.
Based on the co-citation analysis, “A consensus-based educational framework and competency set for the discipline of disaster medicine and public health preparedness” had the highest centrality; it developed a new educational framework for disaster medicine and public health preparedness, based on consensus identification from an expert working group in the American Medical Association.Reference Einav, Aharonson-Daniel and Weissman 27 A time-view map of the co-citation activities appears to the left of the column with the clusters’ labels.Reference Rubinson, Hick and Hanfling 45 New clusters include cluster #0 on spinal cord injury, #1 on conceptual framework, and #2 on health professionals; the landmark publications include [Subbarao I, 2008]Reference Subbarao, Lyznicki and Hsu 26 and [Walsh L, 2012].Reference Walsh, Subbarao and Gebbie 30 They were also the newest burst strength publications, which suggests that “public health preparedness” will become a hot topic in disaster medicine.
Terms analysis provides a reasonable description of research hotspots (areas of focused attention by a number of scientific researchers, addressing a set of related research problems and concepts), whereas burst words represent new research frontiers (emerging trends and abrupt changes that occur in a timely manner).Reference Chen and CiteSpace 47 As shown in Figure 4, The top 5 hotspots of disaster medicine research were:
(1) “Practices in disasters.” These papers focus on the practical elements of disaster medicine, including the treatment of wounded, effect evaluation, first aid, and disaster medical education.Reference Webber, Gustave and Lee 48 – Reference Nidaa, Ahmadreza and Luigi 52
(2) “Hospital disasters.” These papers also focus on practical elements of disaster medicine, including modular management, humanitarian relief, first aid management processes, and disaster emergency departments.Reference Song, Yang and Zhang 53 – Reference Aleksanin 55 , Reference Caspers, Smith and Seth 56
(3) “Disaster events.” These papers summarize the casualties of disasters and their impact on public health.Reference Cecchi, Bottoni and Cappelletti 57 – Reference Kraushar and Rosenberg 60
(4) “Disaster settings.” These papers focus on the medical needs of the disaster, including medical personnel, medical equipment, and medical technology.Reference Khorram-Manesh, Lupesco and Friedl 61 – Reference Gowan, Sloan and Kirk 64
(5) “Earthquake disasters.” These papers focus on medical rescues during an earthquake, including the medical decision-making, the rescue process, and the treatment of the special population.Reference Yong and Wei 65 – Reference Shinichi, Nobuo and Fuji 68
In addition, several burst terms were detected by CiteSpace III and are considered indicators of research frontiers over time. In the results, the time interval is shown as a blue line, and the time period that represents a burst term category is shown as a red line, indicating the beginning and the end of the time interval of each burst. Therefore, the three newest frontiers were:
(1) “Impact.” These papers focus on post-disaster effects on the physiology and mental health of survivors, including their daily behaviors, physiological indicators, and mental states.Reference Tsuboya, Aida and Hikichi 69 – Reference Ohira, Hosoya and Yasumura 70 , Reference Loo, DiMaggio and Gershon 63
(2) “Public health preparedness.” These papers focus on the establishment, evaluation, and management of medical rescue systems.Reference Al Thobaity, Plummer and Williams 71 – Reference Kuntz, Frable and Qureshi 75
(3) “Public health emergencies.” These papers focus on the training of emergency personnel, the promotion of emergency technology, and the management of emergency procedures.Reference Su, Han and Chen 72 , Reference King, Larkin and Fowler 76 – Reference Love, Karp and Delgado 77
LIMITATION
In this study, although the noise data can be reduced by setting up the requisite statistical parameters in CiteSpace III, the source of data is limited by a generic search term strategy, which is likely to lead to some noise in the selection of articles.
CONCLUSION
The major findings of the present scientometric study are helpful for all those involved in worldwide disaster medicine research. Indeed, this study can help researchers better understand disaster medicine research worldwide and be useful, for example, in choosing appropriate journals for publication and collaborations. Fellows choosing an institution for advanced work may also be interested in such an analysis. Journals can determine where they stand in relation to other journals in publishing articles related to disaster medicine. Governments and policy-makers can also ascertain the most effective countries and institutions in the world in this field, and this analysis may assist them to apprehend and predict the hotspots and dynamic directions of disaster medicine research and to target resources so that further developments can be encouraged, supported, and monitored.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Third Military Medical University Military Doctoral Program (No. JSKT201607).
LZ and PZ conceived and designed the paper. LZ, NX, and SL wrote the article. ZZ, LF, ST, KH, LZ, and PZ collected and analyzed the data. SL provided critical revisions. All authors approved the final version of the paper.
Supplementary Material
To view supplementary material for this article, please visit https://doi.org/10.1017/dmp.2018.11