Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Rossi, Giuseppe
Smith, David C.
Ungaretti, Luciano
and
Domeneghetti, M. Chiara
1983.
Crystal-chemistry and cation ordering in the system diopside-jadeite: A detailed study by crystal structure refinement.
Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,
Vol. 83,
Issue. 3-4,
p.
247.
Smith, David C.
1984.
Coesite in clinopyroxene in the Caledonides and its implications for geodynamics.
Nature,
Vol. 310,
Issue. 5979,
p.
641.
Agrinier, Pierre
Javoy, Marc
Smith, David C.
and
Pineau, Françoise
1985.
Carbon and oxygen isotopes in eclogites, amphibolites, veins and marbles from the Western Gneiss region, Norway.
Chemical Geology: Isotope Geoscience section,
Vol. 52,
Issue. 2,
p.
145.
Pinet, Michèle
and
Smith, David C.
1985.
Petrochemistry of opaque minerals in eclogites from the Western Gneiss Region, Norway.
Chemical Geology,
Vol. 50,
Issue. 1-3,
p.
225.
Gebauer, Dieter
Lappin, Michael A.
Grünenfelder, Marc
and
Wyttenbach, Armin
1985.
The age and origin of some Norwegian eclogites: A UPb zircon and REE study.
Chemical Geology: Isotope Geoscience section,
Vol. 52,
Issue. 2,
p.
227.
Koons, Peter O.
and
Thompson, Alan B.
1985.
Non-mafic rocks in the greenschist, blueschist and eclogite facies.
Chemical Geology,
Vol. 50,
Issue. 1-3,
p.
3.
Griffin, William L.
and
Brueckner, Hannes K.
1985.
REE, RbSr and SmNd studies of Norwegian eclogites.
Chemical Geology: Isotope Geoscience section,
Vol. 52,
Issue. 2,
p.
249.
Franz, G.
Thomas, S.
and
Smith, D. C.
1986.
High-pressure phengite decomposition in the Weissenstein eclogite, M�nchberger Gneiss Massif, Germany.
Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,
Vol. 92,
Issue. 1,
p.
71.
Griffin, W. L.
1987.
‘On the eclogites of Norway’—65 years later.
Mineralogical Magazine,
Vol. 51,
Issue. 361,
p.
333.
Andersen, T.
Burke, E. A. J.
and
Austrheim, H.
1989.
Nitrogen-bearing, aqueous fluid inclusions in some eclogites from the Western Gneiss Region of the Norwegian Caledonides.
Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,
Vol. 103,
Issue. 2,
p.
153.
O'Brien, P.J
1989.
The petrology of retrograded eclogites of the Oberpfalz Forest, northeastern Bavaria, West Germany.
Tectonophysics,
Vol. 157,
Issue. 1-3,
p.
195.
Smith, David C.
and
Lappin, Michael A.
1989.
Coesite in the Straumen kyanite‐eclogite pod, Norway.
Terra Nova,
Vol. 1,
Issue. 1,
p.
47.
Philippot, Pascal
and
Kienast, Jean-Robert
1989.
Chemical-microstructural changes in eclogite-facies shear zones (Monviso, Western Alps, north Italy) as indicators of strain history and the mechanism and scale of mass transfer.
Lithos,
Vol. 23,
Issue. 3,
p.
179.
Andersen, T.
Austrheim, H.
and
Burke, E. A. J.
1990.
Fluid inclusions in granulites and eclogites from the Bergen Arcs, Caledonides of W. Norway.
Mineralogical Magazine,
Vol. 54,
Issue. 375,
p.
145.
Agrinier, Pierre
1991.
The natural calibration of 18O16O geothermometers: application to the quartz-rutile mineral pair.
Chemical Geology,
Vol. 91,
Issue. 1,
p.
49.
Hirajima, T.
Zhang, R.
Li, J.
and
Cong, B.
1992.
Petrology of the nyböite-bearing eclogite in the Donghai area, Jiangsu Province, eastern China.
Mineralogical Magazine,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 382,
p.
37.
ENAMI, MASAKI
ZANG, QUIJA
and
YIN, YUJUN
1993.
High‐pressure eclogites in northern Jiangsu – southern Shandong province, eastern China.
Journal of Metamorphic Geology,
Vol. 11,
Issue. 4,
p.
589.
Miller, Christine
and
Thöni, Martin
1995.
Origin of eclogites from the Austroalpine Ötztal basement (Tirol, Austria): geochemistry and SmNd vs. RbSr isotope systematics.
Chemical Geology,
Vol. 122,
Issue. 1-4,
p.
199.
Van Wyck, N.
Valley, J.w.
and
Austrheim, H.
1996.
Oxygen and carbon isotopic constraints on the development of eclogites, Holsnøy, Norway.
Lithos,
Vol. 38,
Issue. 3-4,
p.
129.
Van Roermund
and
Drury
1998.
Ultra‐high pressure (P > 6 GPa) garnet peridotites in Western Norway: exhumation of mantle rocks from > 185 km depth.
Terra Nova,
Vol. 10,
Issue. 6,
p.
295.
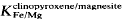 is provisionally calibrated. It yields T estimates for given P very similar to those given by the
is provisionally calibrated. It yields T estimates for given P very similar to those given by the 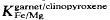 geothermobarometer, e.g. 759–829°C at 20 kb and 803–894°C at 40 kb. P is tentatively estimated at 30±10, 23±6 and 10 ± 3 kb respectively for the three metamorphic stages.
geothermobarometer, e.g. 759–829°C at 20 kb and 803–894°C at 40 kb. P is tentatively estimated at 30±10, 23±6 and 10 ± 3 kb respectively for the three metamorphic stages.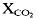 or fluid-absent, but not low
or fluid-absent, but not low 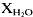 . A unique quartz-magnesite-dolomite vein represents an influx of CO2 in the P-T regime of instability of CO2 + pyroxene. Tectonic emplacement by deep-level obduction of diverse foreign source materials remains the petrogenetic model which best fits the data for these eclogites.
. A unique quartz-magnesite-dolomite vein represents an influx of CO2 in the P-T regime of instability of CO2 + pyroxene. Tectonic emplacement by deep-level obduction of diverse foreign source materials remains the petrogenetic model which best fits the data for these eclogites.

