Introduction
Invasive species are organisms that overcome biogeographical barriers as a result of human actions, subsequently becoming established widely from their points of introduction (Pysek et al. Reference Pysek, Hulme, Simberloff, Bacher, Blackburn and Carlton2020). Invasive species negatively impact the novel ecosystem they are introduced into (Tye Reference Tye2018) and may also cause severe economic losses for numerous stakeholders (Hoffmann & Broadhurst Reference Hoffmann and Broadhurst2016). Introductions of these species can occur intentionally or accidentally from various sources, such as from the ballast water of shipping vessels (Hallegraeff & Bolch Reference Hallegraeff and Bolch1992), the aquarium trade (Gertzen et al. Reference Gertzen, Familiar and Leung2008) or from firewood transport (Muirhead et al. Reference Muirhead, Leung, van Overdijk, Kelly, Nandakumar and Marchant2006). Effective removal can be difficult once invasive species are introduced (Zavaleta et al. Reference Zavaleta, Hobbs and Mooney2001, Lampert et al. Reference Lampert, Hastings, Grosholz, Jardine and Sanchirico2014). This emphasizes the importance of early detection and rapid response measures, which are more effective than control or eradication (Reaser et al. Reference Reaser, Burgiel, Kirkey, Brantley, Veatch and Burgos-Rodríguez2020). Invasive species are as costly as natural disasters (Turbelin et al. Reference Turbelin, Cuthbert, Essl, Haubrock, Ricciardi and Courchamp2023).
Whether invasive species are introduced intentionally or accidentally, public awareness is thought to play a role in determining their geographical spread through anthropogenic vectors (Eiswerth et al. Reference Eiswerth, Yen and van Kooten2011). Given the ease with which invasive species can be introduced by members of the public who may be unaware of their associated impacts, policymakers and environmental managers often spend time and resources on increasing awareness using public awareness campaigns (Bremner & Park Reference Bremner and Park2007, Eiswerth et al. Reference Eiswerth, Yen and van Kooten2011, Novoa et al. Reference Novoa, Dehnen-Schmutz, Fried and Vimercati2017). Changing the way people think and behave may be essential for the management of invasive species because individual-scale actions (e.g., washing boots and boat propellers when moving a boat from one lake to another; verifying that plants purchased for a home garden are native) can be effective in limiting their spread (Eiswerth et al. Reference Eiswerth, Yen and van Kooten2011, Hands et al. Reference Hands, Shaw, Gibson and Miller2018, Cordeiro et al. Reference Cordeiro, Marchante, Castro and Marchante2020). Moreover, garnering support and improving public perception of conservation efforts are important for governing bodies, given that the outcome of control or eradication efforts is largely dependent upon the acceptance of these efforts by citizens (Olszańska et al. Reference Olszańska, Solarz and Najberek2016, Cordeiro et al. Reference Cordeiro, Marchante, Castro and Marchante2020). An informed public can generate political pressure and funding, increase the number of volunteers to aid in mitigation at local scales and create more observers for early detection efforts (Witmer et al. Reference Witmer, Keirn, Hawley, Martin, Reaser and JR2009).
Although public awareness campaigns are often assumed to be ‘good’ activities, the negative outcomes that may arise from a campaign must also be considered. For instance, if awareness campaigns are implemented poorly or reach the wrong audience, they can become counterproductive, wasting resources. For example, they can lead to individual behavioural changes that make the problem worse (Hiom Reference Hiom2006) or elicit backlash (e.g., individuals turn against the planned action or act against recommendations; Kahan Reference Kahan2013). Some awareness campaigns may also be designed using top-down communication processes, which can be inefficient compared to two-way engagement and participation with the public to improve outcomes (Weingart et al. Reference Weingart, Joubert and Connoway2021). Thus, the decision to perform a public awareness campaign should be made after a process of thoughtful consideration of potential gains and adverse outcomes.
Specific to the management of invasive species, raising awareness is often one of the first recommendations (Eiswerth et al. Reference Eiswerth, Yen and van Kooten2011, Olszańska et al. Reference Olszańska, Solarz and Najberek2016). It is assumed that the increased knowledge acquired through invasive species awareness campaigns will translate into changes in individual behaviour, increased support for conservation efforts and/or a tangible benefit to native biodiversity (Eiswerth et al. Reference Eiswerth, Yen and van Kooten2011, Olszańska et al. Reference Olszańska, Solarz and Najberek2016). While awareness campaigns intuitively seem like they could lead to productive outcomes, the efficacy of different campaign types (or even awareness campaigns in general) is poorly understood and rarely assessed (Seekamp et al. Reference Seekamp, McCreary, Mayer, Zack, Charlebois and Pasternak2016, Wallen & Kyle Reference Wallen and Kyle2018). Developing a deeper understanding of how and to what extent awareness campaigns contribute to tangible conservation efforts can facilitate the development and implementation of future campaigns that are more effective. The objectives of this paper are to: (1) evaluate the effectiveness of public awareness campaigns in meeting the goals of awareness campaigns for the management of invasive species of gaining support for managing invasive species and changing behaviours in a way that benefits conservation (Maibach Reference Maibach1993); (2) identify best practices for the evaluation of the efficacy of these campaigns; and (3) identify means by which the evidence base can be advanced, highlighting knowledge gaps that may be hindering the creation of effective public awareness campaigns focused on issues related to invasive species.
Methods
Using Web of Science (Clarivate Analytics), we employed a semi-systematic approach to find literature that measured the efficacy of invasive species awareness campaigns (Snyder Reference Snyder2019). The search string aimed to retain publications that included taxonomic groups from both aquatic and terrestrial environments across the globe. We recognize that this approach largely excludes theses, technical reports and other grey literature. Nonetheless, our preliminary searches suggested that the evidence base was small. While focusing solely on peer-reviewed papers identified via the use of academic databases could impart biases, it also enables a level of reproducibility.
The data extraction was performed on 14 November 2022. Our search string included the terms: ((invasive species or non-native species or exotic species or alien species or introduced species) AND (social marketing or awareness or educat* or outreach or campaign*) NOT (Language or Speech)) (Fig. S1). This search string included synonyms for invasive species and awareness campaigns and excluded educational terms unrelated to invasive species (Table 1). We limited our scope to publications in English. We recognize that this may have limited the number of publications captured in the search string as other languages will have been missed. The following inclusion criteria were used to standardize publication retention: (1) the publication referenced at least one invasive species occurring outside its native range in a novel, natural ecosystem (e.g., not within human infrastructure such as with termites; not in relation to disease as with mosquitoes); (2) the publication referenced public awareness, outreach or educational programmes concerning invasive species; and (3) the publication provided either an empirical evaluation or description of a public awareness campaign.
Table 1. Articles included in the evidence synthesis.
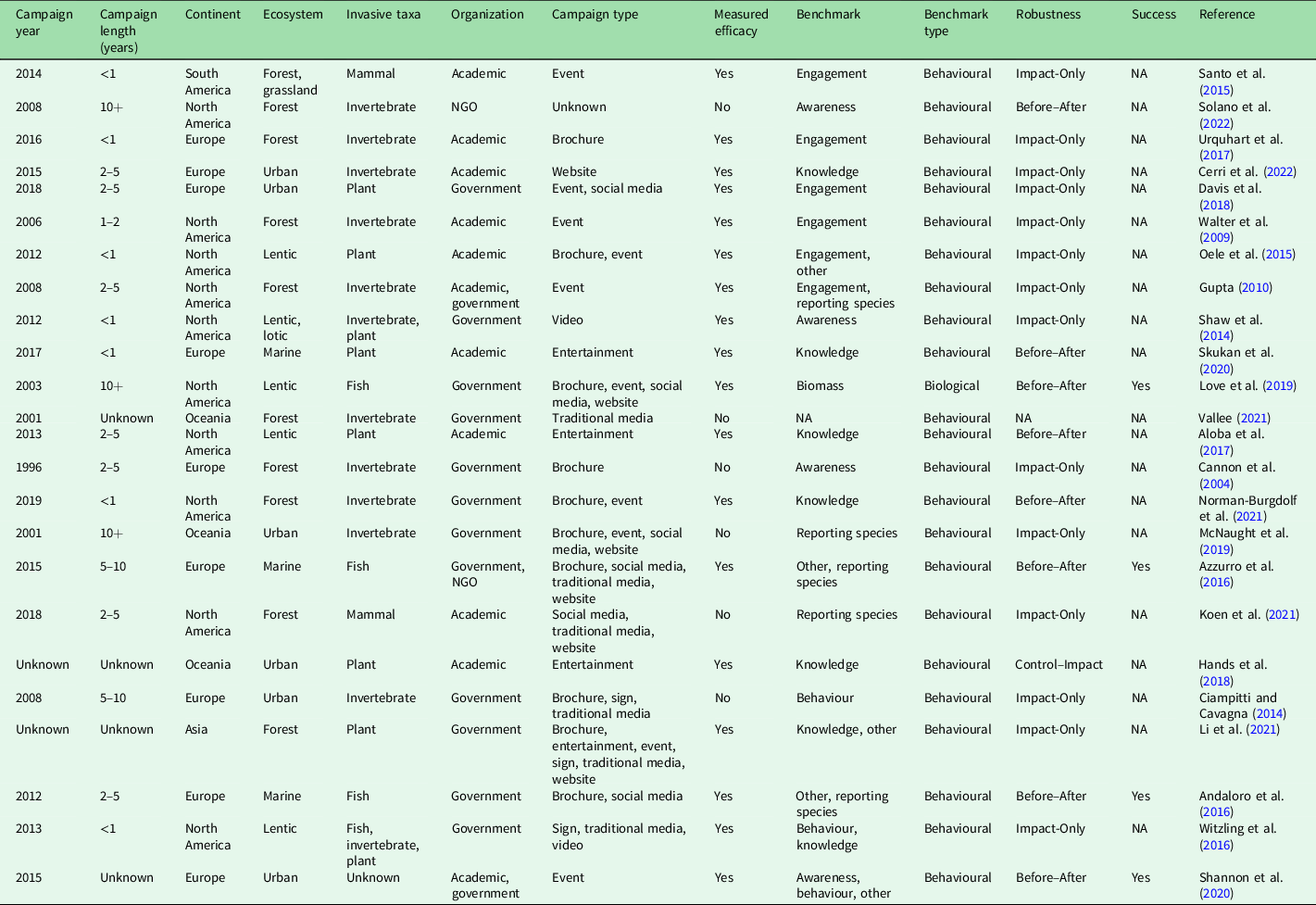
NA = not applicable; NGO = non-governmental organization.
Publications were screened by title, abstract and, finally, by the contents of their full text (Fig. S1). Publications that were found to have met all three criteria were included in our analysis. Publications that only included two out of three criteria were set aside as possible sources of discussion but were not included in the final data synthesis. Publications were not excluded based on the date of publication. Review papers were excluded unless they presented new information.
For data extraction, we collected information regarding the ecosystem, taxa, common name, Latin binomial and target vector of introduction. If one study evaluated multiple things (i.e., more than one species), we listed each item separately. We further checked each publication for an indication that the efficacy of an awareness campaign was measured, making note of those that did. The robustness of each publication was then assessed based on its experimental design and was categorized as either Impact-Only (I), Control–Impact (CI), Before–After Impact (BAI) or Before–After Control–Impact (BACI) based on when and how efficacy measurements were performed. Finally, awareness campaigns were categorized by year, duration, location, organization, campaign type, method of delivery and target audience.
For those publications that did measure efficacy, the biological and/or behavioural benchmarks of efficacy used were identified as relative indicators of the effectiveness of each campaign. This evaluation was based on public awareness campaigns’ goals for managing invasive species: to gain support for species management and to benefit conservation through changed behaviours (Maibach Reference Maibach1993). A measured improvement of a biological benchmark was considered a direct indication of conservation success. The behaviour benchmark was considered indicative of achieving the goal of changing people’s behaviours towards invasive species in a way that benefits conservation. For example, engagement was considered indicative of achieving the goal of garnering support for conservation and thus as a measured improvement in a behavioural benchmark. Lastly, we considered an improvement of either biological or behavioural benchmarks as success.
Publications and campaigns
A total of 24 publications described the use of public awareness campaigns for the management of invasive species (Table 1). There were 14 countries represented in the publications, the most frequent being the USA and Italy. The earliest campaign started in 1996 (Cannon et al. Reference Cannon, Koerper, Ashby, Baker, Bartlett and Brookes2004) and the latest started in 2019 (Norman-Burgdolf & Rieske Reference Norman-Burgdolf and Rieske2021; Fig. S2a). The earliest publication was from 2004 (Cannon et al. Reference Cannon, Koerper, Ashby, Baker, Bartlett and Brookes2004) and the latest were from 2022 (Cerri et al. Reference Cerri, Lioy, Porporato and Bertolino2022, Solano et al. Reference Solano, Rodriguez, Greenwood, Rosopa and Coyle2022), and there was an increasing trend in the number of publications on this topic over time (Fig. S2b). The campaigns varied in duration from being less than 1 year long (e.g., Santo et al. Reference Santo, Sorice, Donlan, Franck and Anderson2015) to more than 10 years long (e.g., Love & Genovese Reference Love and Genovese2019), with most being under 1 year or between 2 and 5 years long (Fig. S3). There were at least six different ecosystems (Fig. 1a), four taxonomic groups (Fig. 1b) and 22 species studied across the 24 publications (for additional details on each publication, see Table 1). A large proportion of publications focused on forest ecosystems (42%; Fig. 1a; e.g., Walter et al. Reference Walter, Ellis and Sadof2009). The species studied were primarily terrestrial (61%; e.g., Davis et al. Reference Davis, Caffrey, Coughlan, Dick and Lucy2018), and, of the aquatic species studied, 21% were freshwater (e.g., Oele et al. Reference Oele, Wagner, Mikulyuk, Seeley-Schreck and Hauxwell2015) and 14% were marine (e.g., Skukan et al. Reference Skukan, Borrell, Ordás and Miralles2020). Invertebrates were the most common taxonomic group, followed by plants, fish, mammals and unknown (i.e., not specified).

Figure 1. (a) The number of times each ecosystem was included in a publication and (b) the number of times each taxonomic group was included in a publication.
The publications also varied in terms of how their campaigns were implemented. Seven of the campaigns focused on a specific vector such as firewood transport (Solano et al. Reference Solano, Rodriguez, Greenwood, Rosopa and Coyle2022), economic trade (Oele et al. Reference Oele, Wagner, Mikulyuk, Seeley-Schreck and Hauxwell2015, Urquhart et al. Reference Urquhart, Potter, Barnett, Fellenor, Mumford and Quine2017, Cerri et al. Reference Cerri, Lioy, Porporato and Bertolino2022), solid wood packing materials (Walter et al. Reference Walter, Ellis and Sadof2009), boats (Shaw et al. Reference Shaw, Howell and Genskow2014, Witzling et al. Reference Witzling, Shaw and Seiler2016) and bait buckets (Witzling et al. Reference Witzling, Shaw and Seiler2016). Most of the campaigns were organized by either governments (46%; e.g., Love & Genovese Reference Love and Genovese2019) or academics (38%; e.g., Aloba et al. Reference Aloba, Coleman, Ong, Yan, Albrecht and Suvajdzic2017), whereas only one was organized by a non-governmental organization (NGO; Solano et al. Reference Solano, Rodriguez, Greenwood, Rosopa and Coyle2022). One was a collaboration between a government and an NGO (Azzurro et al. Reference Azzurro, Castriota, Falautano, Bariche, Broglio and Andaloro2016), while two were collaborations between academics and governments (Gupta Reference Gupta2010, Shannon et al. Reference Shannon, Stebbing, Quinn, Warren and Dunn2020). Brochures were the most common campaign type (e.g., Li et al. Reference Li, Liu, Zeng, Zhang and Zhang2021) along with events (e.g., McNaught et al. Reference McNaught, Wylie and Bell2019), followed by websites (e.g., Cerri et al. Reference Cerri, Lioy, Porporato and Bertolino2022), traditional media (e.g., Vallée Reference Vallée2021) and social media (e.g., Andaloro et al. Reference Andaloro, Castriota, Falautano, Azzurro, Deidun and Fenech-Farrugia2016; Fig. 2). Most campaign types were delivered in person (58%; e.g., Azzurro et al. Reference Azzurro, Castriota, Falautano, Bariche, Broglio and Andaloro2016) as opposed to online (32%; e.g., Shannon et al. Reference Shannon, Stebbing, Quinn, Warren and Dunn2020). Most campaign types were targeted towards a specific audience (55%; e.g., Hands et al. Reference Hands, Shaw, Gibson and Miller2018) rather than directed at the general public (37%; e.g., Norman-Burgdolf & Rieske Reference Norman-Burgdolf and Rieske2021). Furthermore, targeted audiences included anglers (e.g., Azzurro et al. Reference Azzurro, Castriota, Falautano, Bariche, Broglio and Andaloro2016), beekeepers (Cerri et al. Reference Cerri, Lioy, Porporato and Bertolino2022), boaters (e.g., Shaw et al. Reference Shaw, Howell and Genskow2014), children (e.g., Skukan et al. Reference Skukan, Borrell, Ordás and Miralles2020), farmers (Li et al. Reference Li, Liu, Zeng, Zhang and Zhang2021), field workers (Shannon et al. Reference Shannon, Stebbing, Quinn, Warren and Dunn2020), landowners (Santo et al. Reference Santo, Sorice, Donlan, Franck and Anderson2015), pest control operators (Walter et al. Reference Walter, Ellis and Sadof2009), professionals (e.g., Gupta Reference Gupta2010), policymakers (e.g., Davis et al. Reference Davis, Caffrey, Coughlan, Dick and Lucy2018), residential gardeners (Hands et al. Reference Hands, Shaw, Gibson and Miller2018) and store owners (Oele et al. Reference Oele, Wagner, Mikulyuk, Seeley-Schreck and Hauxwell2015). The most targeted audience was anglers (25%).

Figure 2. The number of times each campaign type was used. Brochures include brochures, pamphlets, factsheets, bulletins and guides. Events include fairs, conferences, informational sessions, workshops, demonstrations and courses. Traditional media include TV, radio, newspapers and press releases. Entertainment includes personal/fun items (e.g., comics, wall calendars and games). Signs include signs and posters. Videos include videos and public service announcements.
Campaign effectiveness
Of the 24 publications, 23 (96%) measured the public awareness campaign’s effectiveness using biological or behavioural benchmarks. Of those that measured effectiveness, one included both biological and behavioural measurements, and all 24 included behavioural measurements (Fig. 3). The benchmark used to measure biological efficacy was a change in the biological mass of the invasive species (Love & Genovese Reference Love and Genovese2019), whereas the behavioural benchmarks included awareness (10%; e.g., Shaw et al. Reference Shaw, Howell and Genskow2014), behaviour (19%; e.g., Koen & Newton Reference Koen and Newton2021), knowledge retention (33%; e.g., Aloba et al. Reference Aloba, Coleman, Ong, Yan, Albrecht and Suvajdzic2017), engagement (29%; i.e., level of compliance, number of volunteers, level of interaction; e.g., Walter et al. Reference Walter, Ellis and Sadof2009), reporting species (19%; e.g., McNaught et al. Reference McNaught, Wylie and Bell2019) and other (24%; Fig. 3; e.g., risk perception, Shannon et al. Reference Shannon, Stebbing, Quinn, Warren and Dunn2020). According to our analyses, 4 (17%) of the 24 public awareness campaigns were successful. The success of the other campaigns was indeterminable either because before-and-after measurements were not taken, the benchmark that was measured was unrelated to one of the two main goals of public awareness campaigns or efficacy was not measured in any way. In terms of robustness of efficacy evaluations, eight articles completed Before–After evaluations (33%), one completed a Control–Impact evaluation (4%), 14 completed Impact-Only evaluations (53%), one article conducted no analyses and no articles implemented BACI designs.
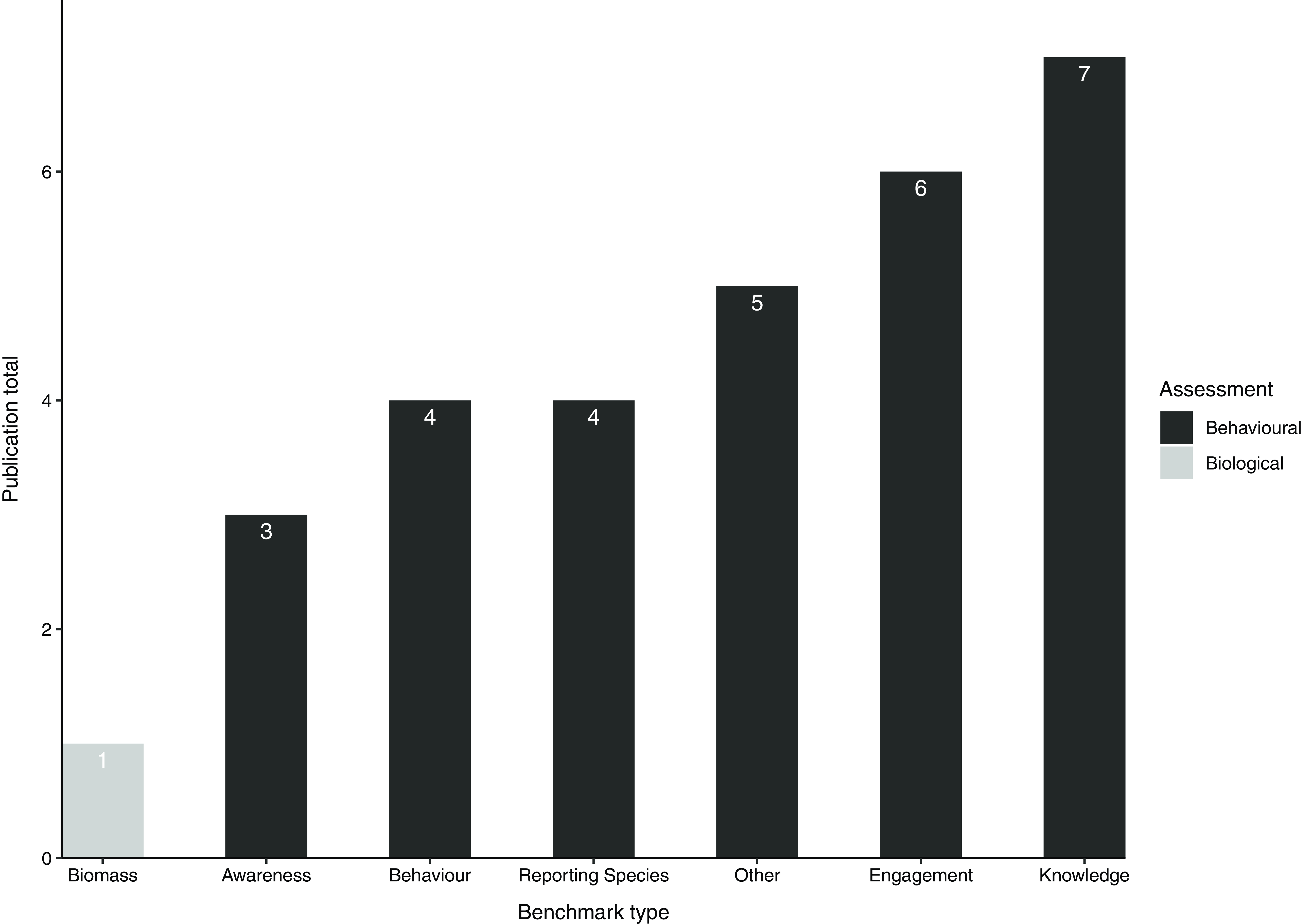
Figure 3. Number of publications according to the benchmark used to evaluate the efficacy of the awareness campaigns. Behaviour includes self-reported and actual. Engagement includes compliance, the number of volunteers and interaction. Reporting species includes individuals reporting presence and/or turning in species. Other includes benchmarks that were only used on one occasion, including media reports, online information, number of invasive species sold, management and risk perception.
Showcasing successful campaigns: case studies
Among the 24 papers that used awareness campaigns targeting invasive species and conducted evaluations of efficacy, we focus on three case studies to further examine the scientific rigour associated with both behavioural and biological benchmarks and the use of comparators (i.e., controls) or a temporal component in the experimental design (e.g., Before–After). For example, directly comparing a campaign to a group that did not receive the same material is imperative for understanding the standalone impact that awareness campaigns can have.
Control–Impact of behavioural benchmarks: the effect of an educational comic on urban gardeners’ knowledge and intentions for invasive plant species management in Australia
Invasive plants are a serious economic and ecological problem in Australia, as they were responsible for an estimated AU$3.5–4.5 billion in damages and management costs in 2005 alone (Sinden et al. Reference Sinden, Jones, Hester, Odom, Kalish and James2005), and they have various negative biological impacts on native species (Schirmel et al. Reference Schirmel, Bundschuh, Entling, Kowarik and Buchholz2016). To assess the impacts of different educational tools on combating these invasive plants, Hands et al. (Reference Hands, Shaw, Gibson and Miller2018) developed and distributed an educational comic and social survey designed to explore respondents’ current gardening choices, future gardening intentions, knowledge of environmental weeds and attitudes towards plant choice and control in the city of Knox (Australia). Random sampling was used for the distribution of the survey. Two versions of this survey were developed: one with a short educational comic designed to warn about the potential for invasive plants to escape from gardens at the beginning of the survey (i.e., the treatment) and one without (i.e., the control; both versions of the survey included the same questions).
The comic was found to have a positive influence on self-reported intentions. When asked how likely they were to purchase native plants over non-native plants in the future, the group that received the comic was significantly more likely to buy native plants than the control group who had not received the comic. In addition, the majority of respondents from this survey (from both the comic and no-comic group) strongly agreed that urban gardeners had a responsibility for the environment, were aware that invasive plants were an issue in Australia and would go out of their way to remove invasive species. Despite these attitudes, however, it was clear that most respondents were unaware that their gardening behaviours could impact the environment negatively regardless of their group. For example, to the question ‘My garden choices do not affect the environment’, 33% of those in the comic group still agreed, another 31% were unsure and only 36% disagreed.
This research illustrates the ease with which knowledge gaps and misinterpretations surrounding invasive species can occur among members of the public. Even among individuals who were conscious of the impacts of invasive species and supportive of control efforts (i.e., those we would expect to know the most), there was a lack of understanding regarding how invasive plants spread and how people’s choices can impact this spread. This publication was scientifically robust in that it included an experimental design that permitted a comparison across treatment (comic) and control (no-comic) groups to detect trends. Therefore, this publication can be used as a basis for additional studies on the topic, as it highlights how even simple messaging campaigns can go a long way towards increasing knowledge and changing individuals’ behaviours surrounding invasive species in at least the short term.
Before–After for behaviour benchmarks: awareness campaigns increased sightings of invasive wild pigs in Ontario
Wild pigs (Sus scrofa), like other invasive species, are responsible for a wide range of negative environmental and economic impacts on the ecosystems they invade (Keiter & Beasley Reference Keiter and Beasley2017). To mitigate these impacts in Ontario, Canada, members of the public were asked to submit reports of wild pig sightings to crowdsource (via citizen science) an early detection network (Koen & Newton Reference Koen and Newton2021). Beginning in October 2018, this project solicited individuals to report sightings of wild pigs online, submitting details regarding pig behaviour and the number of pigs observed. The researchers released a mixture of media messages (via print, radio, online news and social networks) describing the impacts of wild pigs and advertising the existence of the reporting framework to examine the influence that media campaigns could have on stimulating interest in the online reporting and monitoring tool.
Overall, this awareness campaign was effective at changing behaviour. Over the first 27 months of the campaign, 277 sightings were reported, compared to just 18 reports submitted between the pre-campaign period of 2012–October 2018. Moreover, these researchers found that the number of reported sightings significantly increased in the weeks when media statements occurred. Because this publication incorporated a temporal aspect within the experimental design and analyses (with the use of a Before–After comparison), its results illustrate that public awareness campaigns can be a useful tool for increasing public engagement.
Using biological benchmarks to evaluate the efficacy of multiple awareness campaigns on the northern snakehead in Maryland
The northern snakehead (Channa argus) was first introduced to the USA from Asia for food and ritualistic and spiritual reasons, but the fish has since spread into numerous waterways (Love & Genovese Reference Love and Genovese2019). This fish is problematic because it is a top predator that threatens native fish populations (Love & Genovese Reference Love and Genovese2019). As outlined by Love and Genovese (Reference Love and Genovese2019), the Maryland Department of Natural Resources (MDDNR) developed awareness campaigns targeting anglers to manage this invasive species. The MDDNR developed seven different campaigns: regulation, an agency-to-agency information network, an MDDNR-to-public information network, social media initiatives, tournaments, fishing awards promoting recreational harvest and seafood marketing initiatives to encourage commercial harvest.
Basic biological benchmarks were used to evaluate the levels of success of the MDDNR’s public awareness campaign. The number of euthanized northern snakeheads was used to determine the effectiveness of campaigns to increase the recreational harvest. It was found that the number of fish euthanized increased both after the social media campaign and after implementing the incentive campaign. Biological mass harvested from tournaments was measured annually in the 3 years following the initial release of awareness campaigns (the years in which the first tournament was held), although no pre-campaign measurement was provided. The mass of northern snakeheads sold annually over time was used to determine the effectiveness of the seafood awareness campaign for increasing commercial harvest, and this substantially increased in the years following the release of the awareness campaign. This was the only campaign that attempted to use any type of biological benchmark. Because biological measurements are necessary for evaluating conservation benefits, we chose to highlight this article as a stepping-stone that future campaigns could draw upon for achieving the second goal of awareness campaigns: changing people’s behaviours towards invasive species in a way that benefits conservation.
On campaign efficacy and looking forward
Across the 24 publications that measured the efficacy of awareness campaigns for managing invasive species, the benchmarks measured, type and duration of campaigns were highly variable. The combination of a relatively small sample size and high variability/lack of consistency across published works makes it difficult to generalize trends and outline guidelines for undertaking successful awareness campaigns. Furthermore, the types of campaigns used in the case studies were very different (e.g., educational comics, fishing tournaments, mailed brochures). It remains unclear which campaign type is most effective at increasing awareness of invasive species and/or decreasing associated biological impacts on native ecosystems. We also found that the degree of scientific rigour was highly variable across publications, with no examples including a true BACI design and few providing any temporal component (e.g., Before–After). Thus, the evidence base needed to determine the effectiveness of public awareness campaigns for the management of invasive species is currently insufficient, although this study was limited to published scientific literature. However, unpublished public awareness campaigns that might have the degree of rigour required were probably completed in the government sector and NGO realm but were beyond the scope of this paper.
To advance this evidence base, organizations running awareness campaigns must strengthen the implementation of evaluation practices as a part of their campaign programmes. Specifically, we recommend the use of experimental designs that include comparators with controls: treatment groups (e.g., groups of individuals or study sites that received the awareness campaign versus those that did not) and/or a temporal comparator (e.g., comparison of the same group of individuals or sites before the campaign was administered and then after (Before–After; Goodacre Reference Goodacre2015). A BACI design would be ideal because it would help to account for other activities (Green Reference Green1979). However, other approaches are equally valid (e.g., Bayesian network analyses or socio-ecological networks, as in Robbins Reference Robbins2004) in contexts where there are many sources of uncertainties, varying types of data and conceptual frameworks are already employed for invasive species decision-making and risk analysis (Andersen et al. Reference Andersen, Adams, Hope and Powell2004, Kumschick et al. Reference Kumschick, Bacher, Dawson, Heikkilä, Sendek, Sendek and Pluess2012).
It is also important to ensure that studies are replicable. This will allow for any developed practices to be independently verified by other researchers and further enable them to be adapted and used in the study of other invasive species (Cardoso et al. Reference Cardoso, Tsiamis, Gervasini, Schade, Taucer and Adriaens2017). To ensure reproducibility, data need to be collected in a consistent and transparent manner that adequately considers the many factors involved in invasive species’ establishment. Moreover, to further allow for replication of results by third parties, it is encouraged that all generated data or data summaries going forward are openly accessible and searchable to all who may wish to consult them. Beyond this, researchers should also strive to perform comprehensive, long-term studies. Biological invasions often take place over the span of many years, and hence understanding how the retention of messages by those who viewed a campaign or how the effectiveness of a campaign varies as time from delivery increases is essential for the long-term management of invasive species (Larson et al. Reference Larson, Phillips-Mao, Quiram, Sharpe, Stark and Sugita2011). Finally, researchers should develop and measure benchmarks of success quantitatively in a consistent and comparable manner. Ensuring that results are reported consistently not only allows for the rigorous comparison of results between publications, but also minimizes the risk of introducing unconscious bias or sources of error into the evidence base (Frampton et al. Reference Frampton, Livoreil and Petrokofsky2017).
The majority of publications found in our review only measured behavioural benchmarks (e.g., knowledge); however, the goal of most awareness campaigns on invasive species is to elicit a positive change in biological factors, such as biodiversity, rate of spread or population trends of the invasive species (Novoa et al. Reference Novoa, Dehnen-Schmutz, Fried and Vimercati2017). Therefore, in addition to behavioural benchmarks, we advocate for increased use of suitable biological benchmarks to evaluate the success of campaigns in order to advance the knowledge base. For example, the paper highlighted in our case studies on invasive northern snakeheads in Maryland measured commercial harvest as its benchmark, which, while biological, may not be accurate, as an increase in commercial harvest numbers could be related to an increased abundance of the invasive species, but this is likely to be affected by other factors, such as fishing effort (Love & Genovese Reference Love and Genovese2019). Ideally, research would include both benchmarks: demonstrating how the campaign altered human variables (e.g., behaviour, knowledge, attitudes) as well as a measured biological link to human behaviour, such as a reduction in the rate of spread of the invasive species or measurement of public attitudes towards novel removal methods.
Given that invasive species awareness campaigns aim to link the ecological and social aspects of a problem in order to arrive at a simple solution (Kemp et al. Reference Kemp, van Riper, BouFajreldin, Stewart, Scheunemann and van den Born2017), methods and findings from the social science should be increasingly considered for assessing and evaluating invasive species campaigns. Such work has already revealed that public opinion, risk perception and conflict transformation will continue to impact invasive species management (García-Llorente et al. Reference Garcia-Llorente, Martín-López, González, Alcorlo and Montes2008, Estévez et al. Reference Estevez, Anderson, Cristobal Pizarro and Burgman2015, MacDonald et al. Reference MacDonald, Balanovic, Edwards, Abrahamse, Frame and Greenaway2020). Furthermore, a review of the social perception of invasive species highlights challenges and opportunities that could improve invasive species awareness campaigns and the assessment of their efficacy, such as accounting for inconsistent and value-laden definitions of invasives species and, in a context where quantitative research is overrepresented, needing qualitative research that considers the social, cultural and political context in which invasives species are embedded (Kapitza et al. Reference Kapitza, Zimmermann, Martin-Lopez and von Wehrden2019). Gaining a better understanding of these social dimensions could inform the design of awareness campaigns and their assessments to align with the local context.
A rigorous application of social sciences could also help to facilitate social impact assessments of invasive species management (Crowley et al. Reference Crowley, Hinchcliffe and McDonald2017) and, by extension, awareness campaigns (García-Llorente et al. Reference Garcia-Llorente, Martín-López, González, Alcorlo and Montes2008). Integrating social science assessments into public engagement strategies has already proven successful in enabling conditions for management action (Glen & Hoshino Reference Glen and Hoshino2020, Liang Reference Liang2023). For example, invasive species eradication programmes on islands (e.g., New Zealand, Lord Howe Island, Stewart Island) have employed this framework to successfully initiate control or eradication programmes and maintain biosecurity (Oppel et al. Reference Oppel, Beaven, Bolton, Vickery and Bodey2011, Russel et al. Reference Russel, Taylor and Aley2018). Owing to the diverse methods of introduction, the number of species and the myriad ways by which invasive species negatively impact ecosystems, commodities and economies, decision-makers cannot rely on a simple solution to raise awareness (Ostrom Reference Ostrom2007, Fischer et al. Reference Fischer, Gardner, Bennett, Balvanera, Biggs and Carpenter2015). This is especially key in a context where there is a push for invasive species management and decision-making to be increasingly democratic and participatory, in part to reduce conflict (Crowley et al. Reference Crowley, Hinchcliffe and McDonald2017, Kapitza et al. Reference Kapitza, Zimmermann, Martin-Lopez and von Wehrden2019). Social-ecological approaches thus provide a useful perspective for addressing the number of variables and spatiotemporal scales that, combined, lead to campaign success or failure (Léger et al. Reference Léger, Lambraki, Graells, Cousins, Henriksson and Harbarth2021).
Lastly, although we recognize that changes in biological and human impacts are difficult to assess, future studies should design methods that measure these social-ecological benchmarks in a rigorous fashion, creating a standardized set of core benchmarks that will enable meta-analyses of future public awareness campaigns. Logical benchmarks could include the abundance of the invasive species (as an example of a biological indicator) or the number of reports of invasive species (as a behavioural example).
We found no examples of occurrences where publications declared that their public awareness campaigns failed to achieve associated goals. Failures could stem from any number of aspects within campaigns, but without reliable benchmarks of effectiveness or the ability to evaluate failures with which to compare successful campaigns, there is currently no way of determining which types of campaigns work and which do not. A lack of failures found within our review may be attributed to frequency bias, such as in cases of commercial harvest to control invasive species. There is also very likely a ‘file drawer problem’, whereby studies do not reach publication without significant results (i.e., ‘failure’; Rosenthal Reference Rosenthal1979). This is particularly concerning for environmental studies, given that these cases could still have immense value through vicarious learning, leading to more productive campaigns and studies in the future. Furthermore, learning from failure can promote reflection on what worked (or did not) and why (Cooke et al. Reference Cooke, Rytwinski, Taylor, Nyboer, Nguyen and Bennett2020). As such, sharing public awareness campaign failures is also needed and should be encouraged.
We did not capture the full extent of the literature through our search. Specifically, we acknowledge that our search string probably did not capture campaigns that were not published in peer-reviewed papers. Thus, we could have missed important work stemming from ‘boots on the ground’ groups such as the public, communities and institutions, including governments or NGOs. For example, it is common for governments or NGOs to publish primarily grey literature (i.e., not in peer-reviewed publications; Lawrence Reference Lawrence, Chan and Loizides2017). Indeed, of our 24 publications, very few were undertaken by NGOs. Therefore, it is possible that there are other occurrences of awareness campaigns for the management of invasive species that were not included in our analysis. Lower numbers of publications by governments or NGOs could be a result of a variety of reasons, such as limited resources/capacity (i.e., time, money) or lack of incentive to publish (Ferraro & Pattanayak Reference Ferraro and Pattanayak2006). Additionally, it is likely that many awareness campaigns have been undertaken but not assessed for efficacy. Finally, our literature review was only of articles in English, which could have limited the number of publications captured in the search string, and we acknowledge that the search string probably missed non-English literature that plays an important role in conservation (see Amano et al. Reference Amano, Berdejo-Espinola, Akasaka, de Andrade Junior, Blaise and Checco2023, Konno et al. Reference Konno, Akasaka, Koshida, Katayama, Osada, Spake and Amano2020). Thus, future research should include grey literature, either through published reports of the outcomes from government or NGO agencies or from qualitative work including surveys, ethnographies or interviews that could yield important knowledge to improve our understanding of and the efficacy of public awareness campaigns and/or expand the literature search beyond the English language.
Conclusion
Despite the small evidence base, we highlight some indications that public awareness campaigns can be effective for the management of invasive species; however, the evidence base must be advanced in order to perform a proper evaluation. Based on our review, we recommend that: (1) public awareness campaigns use biological outcomes, human behavioural benchmarks and a BACI design or Bayesian analysis to evaluate the campaign’s effectiveness; (2) studies should be replicable, long term and measure consistency; and (3) failed public awareness campaigns are published and evaluated to improve campaign design and prevent the file drawer effect, whereby only positive outcomes are shared.
Our review highlights a lack of evidence about the efficacy of public awareness campaign publications on invasive species. Although we found some cases of success, consistent data across publications were difficult to extract and analyse. It was also unclear which type of campaign was most successful as there were various campaign types, along with many invasive species exploiting multiple ecosystems. Furthermore, biological benchmarks were lacking. A social-ecological framework may aid in clarifying not only the ecological dimensions of invasive species, but also who is involved and how levels of governance influence each player, facilitating the communication of results across multiple disciplines (Fleischman et al. Reference Fleischman, Ban, Evans, Epstein, Garcia-Lopez and Villamayor-Tomas2014). Taken together, these results clearly show that rigorous studies employing consistent methods and measuring biological and behavioural benchmarks are needed to properly assess the efficacy of awareness campaigns on invasive species. Only then will effective mitigation of the introduction and spread of invasive species and promotion of the conservation of natural biodiversity be possible on the basis of good evidence.
Supplementary material
For supplementary material accompanying this paper, visit https://doi.org/10.1017/S037689292300019X.
Acknowledgements
We thank Parks Canada and Corina Brdar, who were instrumental in creating and implementing this study, and two anonymous reviewers, who greatly improved the quality of the manuscript.
Financial support
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests
The authors declare none.
Ethical standards
None.







