Article contents
The weak Bernoulli property for matrix Gibbs states
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 18 December 2018
Abstract
We study the ergodic properties of a class of measures on 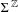 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6F4}^{\mathbb{Z}}$ for which
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6F4}^{\mathbb{Z}}$ for which 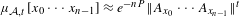 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}_{{\mathcal{A}},t}[x_{0}\cdots x_{n-1}]\approx e^{-nP}\Vert A_{x_{0}}\cdots A_{x_{n-1}}\Vert ^{t}$, where
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}_{{\mathcal{A}},t}[x_{0}\cdots x_{n-1}]\approx e^{-nP}\Vert A_{x_{0}}\cdots A_{x_{n-1}}\Vert ^{t}$, where  ${\mathcal{A}}=(A_{0},\ldots ,A_{M-1})$ is a collection of matrices. The measure
${\mathcal{A}}=(A_{0},\ldots ,A_{M-1})$ is a collection of matrices. The measure  $\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}_{{\mathcal{A}},t}$ is called a matrix Gibbs state. In particular, we give a sufficient condition for a matrix Gibbs state to have the weak Bernoulli property. We employ a number of techniques to understand these measures, including a novel approach based on Perron–Frobenius theory. We find that when
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}_{{\mathcal{A}},t}$ is called a matrix Gibbs state. In particular, we give a sufficient condition for a matrix Gibbs state to have the weak Bernoulli property. We employ a number of techniques to understand these measures, including a novel approach based on Perron–Frobenius theory. We find that when  $t$ is an even integer the ergodic properties of
$t$ is an even integer the ergodic properties of 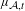 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}_{{\mathcal{A}},t}$ are readily deduced from finite-dimensional Perron–Frobenius theory. We then consider an extension of this method to
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}_{{\mathcal{A}},t}$ are readily deduced from finite-dimensional Perron–Frobenius theory. We then consider an extension of this method to  $t>0$ using operators on an infinite- dimensional space. Finally, we use a general result of Bradley to prove the main theorem.
$t>0$ using operators on an infinite- dimensional space. Finally, we use a general result of Bradley to prove the main theorem.
MSC classification
Information
- Type
- Original Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press, 2018
References
- 10
- Cited by


