Article contents
Range-renewal structure in continued fractions
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 08 March 2016
Abstract
Let 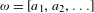 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D714}=[a_{1},a_{2},\ldots ]$ be the infinite expansion of a continued fraction for an irrational number
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D714}=[a_{1},a_{2},\ldots ]$ be the infinite expansion of a continued fraction for an irrational number 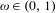 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D714}\in (0,1)$ , and let
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D714}\in (0,1)$ , and let 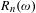 $R_{n}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D714})$ (respectively,
$R_{n}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D714})$ (respectively, 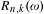 $R_{n,k}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D714})$ ,
$R_{n,k}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D714})$ , 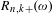 $R_{n,k+}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D714})$ ) be the number of distinct partial quotients, each of which appears at least once (respectively, exactly
$R_{n,k+}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D714})$ ) be the number of distinct partial quotients, each of which appears at least once (respectively, exactly 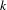 $k$ times, at least
$k$ times, at least 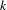 $k$ times) in the sequence
$k$ times) in the sequence 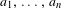 $a_{1},\ldots ,a_{n}$ . In this paper, it is proved that, for Lebesgue almost all
$a_{1},\ldots ,a_{n}$ . In this paper, it is proved that, for Lebesgue almost all 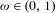 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D714}\in (0,1)$ and all
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D714}\in (0,1)$ and all 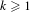 $k\geq 1$ ,
$k\geq 1$ , 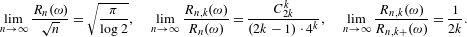 $$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle \lim _{n\rightarrow \infty }\frac{R_{n}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D714})}{\sqrt{n}}=\sqrt{\frac{\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}}{\log 2}},\quad \lim _{n\rightarrow \infty }\frac{R_{n,k}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D714})}{R_{n}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D714})}=\frac{C_{2k}^{k}}{(2k-1)\cdot 4^{k}},\quad \lim _{n\rightarrow \infty }\frac{R_{n,k}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D714})}{R_{n,k+}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D714})}=\frac{1}{2k}.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle \lim _{n\rightarrow \infty }\frac{R_{n}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D714})}{\sqrt{n}}=\sqrt{\frac{\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}}{\log 2}},\quad \lim _{n\rightarrow \infty }\frac{R_{n,k}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D714})}{R_{n}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D714})}=\frac{C_{2k}^{k}}{(2k-1)\cdot 4^{k}},\quad \lim _{n\rightarrow \infty }\frac{R_{n,k}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D714})}{R_{n,k+}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D714})}=\frac{1}{2k}.\end{eqnarray}$$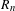 $R_{n}$ are discussed.
$R_{n}$ are discussed.
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press, 2016
References
- 2
- Cited by

