Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
BRODERICK, RYAN
FISHMAN, LIOR
KLEINBOCK, DMITRY
REICH, ASAF
and
WEISS, BARAK
2012.
The set of badly approximable vectors is strongly C1 incompressible.
Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society,
Vol. 153,
Issue. 2,
p.
319.
Mayeda, Dustin
and
Merrill, Keith
2013.
Limit points badly approximable by horoballs.
Geometriae Dedicata,
Vol. 163,
Issue. 1,
p.
127.
Broderick, Ryan
Fishman, Lior
and
Simmons, David
2013.
Badly approximable systems of affine forms and incompressibility on fractals.
Journal of Number Theory,
Vol. 133,
Issue. 7,
p.
2186.
Hu, Hui
and
Yu, Yueli
2014.
On Schmidt's game and the set of points with non-dense orbits under a class of expanding maps.
Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications,
Vol. 418,
Issue. 2,
p.
906.
Weil, Steffen
2015.
Jarník-type inequalities.
Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society,
Vol. 110,
Issue. 1,
p.
172.
Wu, Weisheng
2015.
Modified Schmidt games and non-dense forward orbits of partially hyperbolic systems.
Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems,
Vol. 36,
Issue. 6,
p.
3463.
Bergelson, Vitaly
Einsiedler, Manfred
and
Tseng, Jimmy
2015.
Simultaneous dense and nondense orbits for commuting maps.
Israel Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 210,
Issue. 1,
p.
23.
Shi, Ronggang
and
Tseng, Jimmy
2015.
Simultaneous Dense and Nondense Orbits and the Space of Lattices.
International Mathematics Research Notices,
Vol. 2015,
Issue. 21,
p.
11276.
An, Jinpeng
Guan, Lifan
and
Kleinbock, Dmitry
2015.
Bounded Orbits of Diagonalizable Flows on SL3(ℝ)/SL3(ℤ).
International Mathematics Research Notices,
Vol. 2015,
Issue. 24,
p.
13623.
WU, WEISHENG
2016.
Schmidt games and non-dense forward orbits of certain partially hyperbolic systems.
Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems,
Vol. 36,
Issue. 5,
p.
1656.
TSENG, JIMMY
2017.
Simultaneous dense and non-dense orbits for toral diffeomorphisms.
Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems,
Vol. 37,
Issue. 4,
p.
1308.
Lytle, Beverly
and
Maier, Alex
2018.
Simultaneous dense and nondense orbits for noncommuting toral endomorphisms.
Monatshefte für Mathematik,
Vol. 185,
Issue. 3,
p.
473.
Wu, Weisheng
2018.
On Non-dense Orbits of Certain Non-algebraic Dynamical Systems.
Journal of Dynamics and Differential Equations,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 2,
p.
501.
WU, WEISHENG
2019.
The topological entropy of non-dense orbits and generalized Schmidt games.
Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems,
Vol. 39,
Issue. 2,
p.
500.
Dyakova, Natalia
2019.
Sets of inhomogeneous linear forms can be not isotropically winning.
Moscow Journal of Combinatorics and Number Theory,
Vol. 8,
Issue. 1,
p.
3.
Dani, S. G.
2020.
Elements of Dynamical Systems.
Vol. 79,
Issue. ,
p.
169.
Duvall, Jason
2020.
Schmidt’s game and nonuniformly expanding interval maps.
Nonlinearity,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 11,
p.
5611.
WU, WEISHENG
2020.
Simultaneous dense and non-dense orbits for certain partially hyperbolic diffeomorphisms.
Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems,
Vol. 40,
Issue. 4,
p.
1083.
EINSIEDLER, MANFRED
and
MAIER, ALEX
2020.
Simultaneous equidistributing and non-dense points for non-commuting toral automorphisms.
Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems,
Vol. 40,
Issue. 1,
p.
175.
AN, JINPENG
GUAN, LIFAN
and
KLEINBOCK, DMITRY
2022.
Non-dense orbits on homogeneous spaces and applications to geometry and number theory.
Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems,
Vol. 42,
Issue. 4,
p.
1327.
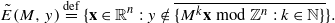 S. G. Dani showed in 1988 that whenever M is semisimple and y∈ℚn/ℤn, the set
S. G. Dani showed in 1988 that whenever M is semisimple and y∈ℚn/ℤn, the set 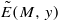 has full Hausdorff dimension. In this paper we strengthen this result, extending it to arbitrary M∈GLn(ℝ)∩Mn×n(ℤ) and y∈ℝn/ℤn, and in fact replacing the sequence of powers of M by any lacunary sequence of (not necessarily integer) m×n matrices. Furthermore, we show that sets of the form
has full Hausdorff dimension. In this paper we strengthen this result, extending it to arbitrary M∈GLn(ℝ)∩Mn×n(ℤ) and y∈ℝn/ℤn, and in fact replacing the sequence of powers of M by any lacunary sequence of (not necessarily integer) m×n matrices. Furthermore, we show that sets of the form 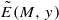 and their generalizations always intersect with ‘sufficiently regular’ fractal subsets of ℝn. As an application, we give an alternative proof of a recent result [M. Einsiedler and J. Tseng. Badly approximable systems of affine forms, fractals, and Schmidt games. Preprint, arXiv:0912.2445] on badly approximable systems of affine forms.
and their generalizations always intersect with ‘sufficiently regular’ fractal subsets of ℝn. As an application, we give an alternative proof of a recent result [M. Einsiedler and J. Tseng. Badly approximable systems of affine forms, fractals, and Schmidt games. Preprint, arXiv:0912.2445] on badly approximable systems of affine forms.
