Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Lange, H.
and
Teismann, H.
2007.
Controllability of the nonlinear Schrödinger equation in the vicinity of the ground state.
Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 13,
p.
1483.
Beauchard, Karine
2008.
Controllablity of a quantum particle in a 1D variable domain.
ESAIM: Control, Optimisation and Calculus of Variations,
Vol. 14,
Issue. 1,
p.
105.
Rosier, Lionel
and
Zhang, Bing-Yu
2009.
Local Exact Controllability and Stabilizability of the Nonlinear Schrödinger Equation on a Bounded Interval.
SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization,
Vol. 48,
Issue. 2,
p.
972.
Rosier, Lionel
and
Zhang, Bing-Yu
2009.
Exact boundary controllability of the nonlinear Schrödinger equation.
Journal of Differential Equations,
Vol. 246,
Issue. 10,
p.
4129.
Beauchard, Karine
and
Laurent, Camille
2010.
Local controllability of 1D linear and nonlinear Schrödinger equations with bilinear control.
Journal de Mathématiques Pures et Appliquées,
Vol. 94,
Issue. 5,
p.
520.
ROSIER, LIONEL
and
ZHANG, BING-YU
2010.
CONTROL AND STABILIZATION OF THE NONLINEAR SCHRÖDINGER EQUATION ON RECTANGLES.
Mathematical Models and Methods in Applied Sciences,
Vol. 20,
Issue. 12,
p.
2293.
Bloch, Anthony M.
Brockett, Roger W.
and
Rangan, Chitra
2010.
Finite Controllability of Infinite-Dimensional Quantum Systems.
IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control,
Vol. 55,
Issue. 8,
p.
1797.
Beauchard, Karine
2011.
Local controllability and non-controllability for a 1D wave equation with bilinear control.
Journal of Differential Equations,
Vol. 250,
Issue. 4,
p.
2064.
Mendes, R Vilela
and
Man'ko, Vladimir I
2011.
On the problem of quantum control in infinite dimensions.
Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical,
Vol. 44,
Issue. 13,
p.
135302.
Boussaid, N.
Caponigro, M.
and
Chambrion, T.
2012.
Implementation of logical gates on infinite dimensional quantum oscillators.
p.
5825.
Sarychev, Andrey
2012.
Controllability of the cubic Schroedinger equation via a low-dimensional source term.
Mathematical Control & Related Fields,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 3,
p.
247.
Boussaid, Nabile
Caponigro, Marco
and
Chambrion, Thomas
2013.
Weakly Coupled Systems in Quantum Control.
IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control,
Vol. 58,
Issue. 9,
p.
2205.
Beauchard, Karine
and
Morancey, Morgan
2014.
Local controllability of 1D Schrödinger equations with bilinear control and minimal time.
Mathematical Control & Related Fields,
Vol. 4,
Issue. 2,
p.
125.
De Leo, Mariano
Sánchez Fernández de la Vega, Constanza
and
Rial, Diego
2014.
Controllability of Schrödinger equation with a nonlocal term.
ESAIM: Control, Optimisation and Calculus of Variations,
Vol. 20,
Issue. 1,
p.
23.
Boscain, Ugo
Gauthier, Jean-Paul
Rossi, Francesco
and
Sigalotti, Mario
2015.
Approximate Controllability, Exact Controllability, and Conical Eigenvalue Intersections for Quantum Mechanical Systems.
Communications in Mathematical Physics,
Vol. 333,
Issue. 3,
p.
1225.
Beauchard, Karine
Lange, Horst
and
Teismann, Holger
2015.
Local Exact Controllability of a One-Dimensional Nonlinear Schrödinger Equation.
SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization,
Vol. 53,
Issue. 5,
p.
2781.
Boussaid, Nabile
Caponigro, Marco
and
Chambrion, Thomas
2019.
On the Ball-Marsden-Slemrod obstruction for bilinear control systems.
p.
4971.
Boussaïd, Nabile
Caponigro, Marco
and
Chambrion, Thomas
2020.
Regular propagators of bilinear quantum systems.
Journal of Functional Analysis,
Vol. 278,
Issue. 6,
p.
108412.
Chambrion, Thomas
and
Thomann, Laurent
2020.
On the bilinear control of the Gross-Pitaevskii equation.
Annales de l'Institut Henri Poincaré C, Analyse non linéaire,
Vol. 37,
Issue. 3,
p.
605.
Devillanova, G.
Florio, G.
and
Maddalena, F.
2021.
Variational functionals for the driven quantum harmonic oscillator.
Complex Variables and Elliptic Equations,
Vol. 66,
Issue. 2,
p.
312.
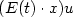 is not controllable in finite or infinite time. Finally, in Section 3, we give criteria for additive controllability of linear Schrödinger equations, andwe give a distributed additive controllability result for the nonlinear Schrödinger equation if the data are small.
is not controllable in finite or infinite time. Finally, in Section 3, we give criteria for additive controllability of linear Schrödinger equations, andwe give a distributed additive controllability result for the nonlinear Schrödinger equation if the data are small. 
