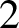Introduction
The notions of dual and trace in symmetric monoidal categories were introduced by Dold and Puppe [Reference Dold and PuppeDP]. They have been extended to higher categories and have found important applications in algebraic geometry and other contexts (see [Reference Ben-Zvi and NadlerBZN] by Ben-Zvi and Nadler and the references therein).
The goal of the present article is to record several applications of the formalism of duals and traces to the symmetric monoidal
![]() $2$
-category of cohomological correspondences in étale cohomology. One of our main results is the following relative Lefschetz–Verdier theorem.
$2$
-category of cohomological correspondences in étale cohomology. One of our main results is the following relative Lefschetz–Verdier theorem.
Theorem 0.1. Let S be a Noetherian scheme and let
![]() $\Lambda $
be a Noetherian commutative ring with
$\Lambda $
be a Noetherian commutative ring with
![]() $m\Lambda =0$
for some m invertible on S. Let
$m\Lambda =0$
for some m invertible on S. Let

be a commutative diagram of schemes separated of finite type over S, with p and
![]() $D\to D'\times _{Y'} Y$
proper. Let
$D\to D'\times _{Y'} Y$
proper. Let
![]() $L\in D_{{c\mathrm {ft}}}(X,\Lambda )$
such that L and
$L\in D_{{c\mathrm {ft}}}(X,\Lambda )$
such that L and
![]() $f_!L$
are locally acyclic over S. Let
$f_!L$
are locally acyclic over S. Let
![]() $M\in D(Y,\Lambda )$
,
$M\in D(Y,\Lambda )$
,
![]() $u\colon \overleftarrow {c}^*L\to \overrightarrow {c}^! M$
,
$u\colon \overleftarrow {c}^*L\to \overrightarrow {c}^! M$
,
![]() $v\colon \overleftarrow {d}^*M\to \overrightarrow {d}^! L$
. Then
$v\colon \overleftarrow {d}^*M\to \overrightarrow {d}^! L$
. Then
![]() $s\colon C\times _{X\times _S Y} D\to C'\times _{X'\times _S Y'} D'$
is proper and
$s\colon C\times _{X\times _S Y} D\to C'\times _{X'\times _S Y'} D'$
is proper and
Here
![]() $D_{c\mathrm {ft}}(X,\Lambda )\subseteq D(X,\Lambda )$
denotes the full subcategory spanned by objects of finite tor-dimension and of constructible cohomology sheaves, and
$D_{c\mathrm {ft}}(X,\Lambda )\subseteq D(X,\Lambda )$
denotes the full subcategory spanned by objects of finite tor-dimension and of constructible cohomology sheaves, and
![]() $\langle u,v\rangle $
is the relative Lefschetz–Verdier pairing.
$\langle u,v\rangle $
is the relative Lefschetz–Verdier pairing.
Remark 0.2. In the case where S is the spectrum of a field, local acyclicity is trivial and the theorem generalises [Reference GrothendieckSGA5, III Corollaire 4.5] and (the scheme case of) [Reference VarshavskyV1, Proposition 1.2.5]. For S smooth over a perfect field and under additional assumptions of smoothness and transversality, Theorem 0.1 was proved by Yang and Zhao [Reference Yang and ZhaoYZ, Corollary 3.10]. The original proof in [Reference GrothendieckSGA5] and its adaptation in [Reference Yang and ZhaoYZ] require the verification of a large amount of commutative diagrams. The categorical interpretation we adopt makes our proof arguably more conceptual.
It was observed by Lurie that Grothendieck’s cohomological operations can be encoded by a (pseudo) functor
![]() $\mathcal {B}\to \mathcal {C}\mathit {at}$
, where
$\mathcal {B}\to \mathcal {C}\mathit {at}$
, where
![]() $\mathcal {B}$
denotes the category of correspondences and
$\mathcal {B}$
denotes the category of correspondences and
![]() $\mathcal {C}\mathit {at}$
denotes the
$\mathcal {C}\mathit {at}$
denotes the
![]() $2$
-category of categories. Contrary to the situation of [Reference Ben-Zvi and NadlerBZN, Definition 2.15], in the context of étale cohomology, the functor has a right-lax symmetric monoidal structure that is not expected to be symmetric monoidal even after enhancement to higher categories. Instead, we apply the formalism of traces to the corresponding cofibred category produced by the Grothendieck construction, which is the category
$2$
-category of categories. Contrary to the situation of [Reference Ben-Zvi and NadlerBZN, Definition 2.15], in the context of étale cohomology, the functor has a right-lax symmetric monoidal structure that is not expected to be symmetric monoidal even after enhancement to higher categories. Instead, we apply the formalism of traces to the corresponding cofibred category produced by the Grothendieck construction, which is the category
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
of cohomological correspondences. The relative Lefschetz–Verdier formula follows from the functoriality of traces for dualisable objects
$\mathcal {C}$
of cohomological correspondences. The relative Lefschetz–Verdier formula follows from the functoriality of traces for dualisable objects
![]() $(X,L)$
of
$(X,L)$
of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
.
$\mathcal {C}$
.
To complete the proof, we show that under the assumption
![]() $L\in D_{{c\mathrm {ft}}}(X,\Lambda )$
, dualisability is equivalent to local acyclicity (Theorem 2.16). As a byproduct of this equivalence, we deduce immediately that local acyclicity is preserved by duality (Corollary 2.18). Note that this last statement does not involve cohomological correspondences.
$L\in D_{{c\mathrm {ft}}}(X,\Lambda )$
, dualisability is equivalent to local acyclicity (Theorem 2.16). As a byproduct of this equivalence, we deduce immediately that local acyclicity is preserved by duality (Corollary 2.18). Note that this last statement does not involve cohomological correspondences.
We also give applications to the nearby cycle functor
![]() $\Psi $
over a Henselian valuation ring. The functor
$\Psi $
over a Henselian valuation ring. The functor
![]() $\Psi $
extends the usual nearby cycle functor over a Henselian discrete valuation ring and was studied by Huber [Reference HuberH, Section 4.2]. By studying specialisation of cohomological correspondences, we generalise Gabber’s theorem that
$\Psi $
extends the usual nearby cycle functor over a Henselian discrete valuation ring and was studied by Huber [Reference HuberH, Section 4.2]. By studying specialisation of cohomological correspondences, we generalise Gabber’s theorem that
![]() $\Psi $
preserves duals and a fixed point theorem of Vidal to Henselian valuation rings (Corollaries 3.8 and 3.13). We hope that the latter can be used to study ramification over higher-dimensional bases.
$\Psi $
preserves duals and a fixed point theorem of Vidal to Henselian valuation rings (Corollaries 3.8 and 3.13). We hope that the latter can be used to study ramification over higher-dimensional bases.
Scholze remarked that our arguments also apply in the étale cohomology of diamonds and imply the equivalence between dualisability and universal local acyclicity in this situation. This fact and applications are discussed in his work with Fargues on the geometrisation of the Langlands correspondence [Reference Fargues and ScholzeFS].
Let us briefly mention some other categorical approaches to Lefschetz type theorems. In [Reference Dold and PuppeDP, Section 4], the Lefschetz fixed point theorem is deduced from the functoriality of traces by passing to suspension spectra. In [Reference PetitP], a categorical framework is set up for Lefschetz–Lunts type formulas. In May 2019, as a first draft of this article was being written, Varshavsky informed us that he had a different strategy to deduce the Lefschetz–Verdier formula, using categorical traces in
![]() $(\infty ,2)$
-categories.
$(\infty ,2)$
-categories.
This article is organised as follows. In Section 1, we review duals and traces in symmetric monoidal
![]() $2$
-categories and the Grothendieck construction. In Section 2, we define the symmetric monoidal
$2$
-categories and the Grothendieck construction. In Section 2, we define the symmetric monoidal
![]() $2$
-category of cohomological correspondences and prove the relative Lefschetz–Verdier theorem. In Section 3, we discuss applications to the nearby cycle functor over a Henselian valuation ring.
$2$
-category of cohomological correspondences and prove the relative Lefschetz–Verdier theorem. In Section 3, we discuss applications to the nearby cycle functor over a Henselian valuation ring.
1 Pairings in symmetric monoidal
 $2$
-categories
$2$
-categories
We review duals, traces and pairings in symmetric monoidal
![]() $2$
-categories. We give the definitions in Subsection 1.1 and discuss the functoriality of pairings in Subsection 1.2. These two subsections are mostly standard (see [Reference Ben-Zvi and NadlerBZN] and [Reference Hoyois, Scherotzke and SibillaHSS] for generalisations to higher categories). In Subsection 1.3 we review the Grothendieck construction in the symmetric monoidal context, which will be used to interpret the category of cohomological correspondences later.
$2$
-categories. We give the definitions in Subsection 1.1 and discuss the functoriality of pairings in Subsection 1.2. These two subsections are mostly standard (see [Reference Ben-Zvi and NadlerBZN] and [Reference Hoyois, Scherotzke and SibillaHSS] for generalisations to higher categories). In Subsection 1.3 we review the Grothendieck construction in the symmetric monoidal context, which will be used to interpret the category of cohomological correspondences later.
By a
![]() $2$
-category, we mean a weak
$2$
-category, we mean a weak
![]() $2$
-category (also known as a bicategory in the literature).
$2$
-category (also known as a bicategory in the literature).
1.1 Pairings
Let
![]() $(\mathcal {C},\otimes ,1_{\mathcal {C}})$
be a symmetric monoidal
$(\mathcal {C},\otimes ,1_{\mathcal {C}})$
be a symmetric monoidal
![]() $2$
-category.
$2$
-category.
Definition 1.1 dual
An object X of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
is dualisable if there exist an object
$\mathcal {C}$
is dualisable if there exist an object
of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
, called the dual of X, and morphisms
$\mathcal {C}$
, called the dual of X, and morphisms
,
, called evaluation and coevaluation, respectively, such that the composites

are isomorphic to identities.
Remark 1.2. For X dualisable,
![]() is dualisable of dual X. For X and Y dualisable,
is dualisable of dual X. For X and Y dualisable,
![]() $X\otimes Y$
is dualisable of dual
$X\otimes Y$
is dualisable of dual
![]() .
.
For X and Y in
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
, we let
$\mathcal {C}$
, we let
![]() $\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,Y)$
denote the internal mapping object if it exists.
$\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,Y)$
denote the internal mapping object if it exists.
Remark 1.3. Assume that X is dualisable of dual
![]() .
.
-
(a) The morphisms
 $\mathrm {coev}_X$
and
$\mathrm {coev}_X$
and
 $\mathrm {ev}_X$
exhibit
$\mathrm {ev}_X$
exhibit
 as right (and left) adjoint to
as right (and left) adjoint to
 $-\otimes X$
. Thus, for every object Y,
$-\otimes X$
. Thus, for every object Y,
 $\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,Y)$
exists and is equivalent to
$\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,Y)$
exists and is equivalent to
 . In particular,
. In particular,
 $\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,1_{\mathcal {C}})$
exists and is equivalent to
$\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,1_{\mathcal {C}})$
exists and is equivalent to
 .
. -
(b) If, moreover,
 $\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(Y,1_{\mathcal {C}})$
exists, then we have equivalences
$\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(Y,1_{\mathcal {C}})$
exists, then we have equivalences 
Lemma 1.4. An object X is dualisable if and only if
![]() $\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,1_{\mathcal {C}})$
and
$\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,1_{\mathcal {C}})$
and
![]() $\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,X)$
exist and the morphism
$\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,X)$
exist and the morphism
![]() $m\colon X\otimes \mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,1_{\mathcal {C}})\to \mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,X)$
adjoint to
$m\colon X\otimes \mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,1_{\mathcal {C}})\to \mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,X)$
adjoint to
 $$ \begin{align*} X\otimes \mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(X,1_{\mathcal{C}})\otimes X\xrightarrow{\mathrm{id}_X\otimes \mathrm{ev}_X} X \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} X\otimes \mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(X,1_{\mathcal{C}})\otimes X\xrightarrow{\mathrm{id}_X\otimes \mathrm{ev}_X} X \end{align*} $$
is a split epimorphism. Here
![]() $\mathrm {ev}_X\colon \mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,1_{\mathcal {C}})\otimes X\to 1_{\mathcal {C}}$
denotes the co-unit.
$\mathrm {ev}_X\colon \mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,1_{\mathcal {C}})\otimes X\to 1_{\mathcal {C}}$
denotes the co-unit.
Proof. The ‘only if’ part is a special case of Remark 1.3. For the ‘if’ part, we define
![]() $\mathrm {coev}_X\colon 1_{\mathcal {C}}\to X\otimes \mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,1_{\mathcal {C}})$
to be the composite of a section of m and the morphism
$\mathrm {coev}_X\colon 1_{\mathcal {C}}\to X\otimes \mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,1_{\mathcal {C}})$
to be the composite of a section of m and the morphism
![]() $1_{\mathcal {C}}\to \mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,X)$
corresponding to
$1_{\mathcal {C}}\to \mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,X)$
corresponding to
![]() $\mathrm {id}_X$
. It is easy to see that
$\mathrm {id}_X$
. It is easy to see that
![]() $\mathrm {ev}_X$
and
$\mathrm {ev}_X$
and
![]() $\mathrm {coev}_X$
exhibit
$\mathrm {coev}_X$
exhibit
![]() $\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,1_{\mathcal {C}})$
as a dual of X.
$\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(X,1_{\mathcal {C}})$
as a dual of X.
For X and Y dualisable, the dual of a morphism
![]() $u\colon X\to Y$
is the composite
$u\colon X\to Y$
is the composite

This construction gives rise to a functor
. We have commutative squares with invertible
![]() $2$
-morphisms
$2$
-morphisms

Moreover, for
![]() $X\xrightarrow {u} Y\xrightarrow {v} Z$
with X, Y, Z dualisable, we have
$X\xrightarrow {u} Y\xrightarrow {v} Z$
with X, Y, Z dualisable, we have
.
Notation 1.5. We let
![]() $\Omega \mathcal {C}$
denote the category
$\Omega \mathcal {C}$
denote the category
![]() $\mathrm {End}(1_{\mathcal {C}})$
.
$\mathrm {End}(1_{\mathcal {C}})$
.
Construction 1.6 dimension, trace and pairing
Let X be a dualisable object of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
and let
$\mathcal {C}$
and let
![]() $e\colon X\to X$
be an endomorphism. We define the trace
$e\colon X\to X$
be an endomorphism. We define the trace
![]() $\mathrm {tr}(e)$
to be the object of
$\mathrm {tr}(e)$
to be the object of
![]() $\Omega \mathcal {C}$
given by the composite
$\Omega \mathcal {C}$
given by the composite

where in the last arrow we used the commutativity constraint.
Let
![]() $u\colon X\to Y$
and
$u\colon X\to Y$
and
![]() $v\colon Y\to X$
be morphisms with X dualisable. We define the pairing by
$v\colon Y\to X$
be morphisms with X dualisable. We define the pairing by
![]() $\langle u,v\rangle =\mathrm {tr}(v\circ u)$
.
$\langle u,v\rangle =\mathrm {tr}(v\circ u)$
.
We define the dimension of a dualisable object X to be
![]() $\dim (X):= \langle \mathrm {id}_X,\mathrm {id}_X\rangle $
, which is the composite
$\dim (X):= \langle \mathrm {id}_X,\mathrm {id}_X\rangle $
, which is the composite
 .
.
If X and Y are both dualisable, then
![]() $\langle u,v\rangle $
is isomorphic to the composite
$\langle u,v\rangle $
is isomorphic to the composite

In this case, we have an isomorphism
![]() $\langle u,v\rangle \simeq \langle v,u\rangle $
. In fact, by (1.1), we have commutative squares with invertible
$\langle u,v\rangle \simeq \langle v,u\rangle $
. In fact, by (1.1), we have commutative squares with invertible
![]() $2$
-morphisms
$2$
-morphisms

The definition and construction above hold in particular for symmetric monoidal
![]() $1$
-categories. In the next subsection,
$1$
-categories. In the next subsection,
![]() $2$
-morphisms will play an important role.
$2$
-morphisms will play an important role.
1.2 Functoriality of pairings
A morphism
![]() $f\colon X\to X'$
in a
$f\colon X\to X'$
in a
![]() $2$
-category is said to be right adjointable if there exist a morphism
$2$
-category is said to be right adjointable if there exist a morphism
![]() $f^!\colon X'\to X$
, called the right adjoint of f, and
$f^!\colon X'\to X$
, called the right adjoint of f, and
![]() $2$
-morphisms
$2$
-morphisms
![]() $\eta \colon \mathrm {id}_X\to f^!\circ f$
and
$\eta \colon \mathrm {id}_X\to f^!\circ f$
and
![]() $\epsilon \colon f\circ f^!\to \mathrm {id}_{X'}$
such that the composites
$\epsilon \colon f\circ f^!\to \mathrm {id}_{X'}$
such that the composites
 $$ \begin{align*}f\xrightarrow{\mathrm{id} \circ \eta} f\circ f^!\circ f \xrightarrow{\epsilon\circ \mathrm{id}} f,\quad f^!\xrightarrow{\eta\circ \mathrm{id}} f^!\circ f\circ f^!\xrightarrow{\mathrm{id}\circ \epsilon} f^!\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}f\xrightarrow{\mathrm{id} \circ \eta} f\circ f^!\circ f \xrightarrow{\epsilon\circ \mathrm{id}} f,\quad f^!\xrightarrow{\eta\circ \mathrm{id}} f^!\circ f\circ f^!\xrightarrow{\mathrm{id}\circ \epsilon} f^!\end{align*} $$
are identities.
Let
![]() $(\mathcal {C},\otimes ,1_{\mathcal {C}})$
be a symmetric monoidal
$(\mathcal {C},\otimes ,1_{\mathcal {C}})$
be a symmetric monoidal
![]() $2$
-category.
$2$
-category.
Construction 1.7. Consider a diagram in
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
$\mathcal {C}$

with X and
![]() $X'$
dualisable and f right adjointable. We will construct a morphism
$X'$
dualisable and f right adjointable. We will construct a morphism
![]() $\langle u,v\rangle \to \langle u',v'\rangle $
in
$\langle u,v\rangle \to \langle u',v'\rangle $
in
![]() $\Omega \mathcal {C}$
.
$\Omega \mathcal {C}$
.
In the case where Y and
![]() $Y'$
are also dualisable and g is also right adjointable, we define
$Y'$
are also dualisable and g is also right adjointable, we define
![]() $\langle u,v\rangle \to \langle u',v'\rangle $
by the diagram
$\langle u,v\rangle \to \langle u',v'\rangle $
by the diagram

where
![]() $\beta ^!$
is the composite
$\beta ^!$
is the composite
 $$ \begin{align*}v\circ g^!\xrightarrow{\eta_f} f^!\circ f\circ v\circ g^!\xrightarrow{\mathrm{id}\circ \beta\circ \mathrm{id}} f^!\circ v'\circ g\circ g^!\xrightarrow{\epsilon_g} f^!\circ v' \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}v\circ g^!\xrightarrow{\eta_f} f^!\circ f\circ v\circ g^!\xrightarrow{\mathrm{id}\circ \beta\circ \mathrm{id}} f^!\circ v'\circ g\circ g^!\xrightarrow{\epsilon_g} f^!\circ v' \end{align*} $$
and the
![]() $2$
-morphisms in the triangles are
$2$
-morphisms in the triangles are


In particular, a morphism
![]() $\mathrm {tr}(e)\to \mathrm {tr}(e')$
is defined for every diagram in
$\mathrm {tr}(e)\to \mathrm {tr}(e')$
is defined for every diagram in
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
of the form
$\mathcal {C}$
of the form

with X and
![]() $X'$
dualisable and f right adjointable.
$X'$
dualisable and f right adjointable.
In general, we define
![]() $\langle u,v\rangle \to \langle u',v'\rangle $
as the morphism
$\langle u,v\rangle \to \langle u',v'\rangle $
as the morphism
![]() $\mathrm {tr}(v\circ u)\to \mathrm {tr}(v'\circ u')$
associated to the composite down-square of (1.2).
$\mathrm {tr}(v\circ u)\to \mathrm {tr}(v'\circ u')$
associated to the composite down-square of (1.2).
Trace can be made into a functor
![]() $\mathrm {End}(\mathcal {C})\to \Omega \mathcal {C}$
, where
$\mathrm {End}(\mathcal {C})\to \Omega \mathcal {C}$
, where
![]() $\mathrm {End}(\mathcal {C})$
is a
$\mathrm {End}(\mathcal {C})$
is a
![]() $(2,1)$
-category whose objects are pairs
$(2,1)$
-category whose objects are pairs
![]() $(X,e\colon X\to X)$
with X dualisable and morphisms are diagrams (1.5) with f right adjointable [Reference Hoyois, Scherotzke and SibillaHSS, Section 2.1]. Composition in
$(X,e\colon X\to X)$
with X dualisable and morphisms are diagrams (1.5) with f right adjointable [Reference Hoyois, Scherotzke and SibillaHSS, Section 2.1]. Composition in
![]() $\mathrm {End}(\mathcal {C})$
is given by vertical composition of diagrams.
$\mathrm {End}(\mathcal {C})$
is given by vertical composition of diagrams.
For the case of Theorem 0.1 where f is not proper, we will need to relax the adjointability condition in Construction 1.7 as follows. In a
![]() $2$
-category, a down-square equipped with a splitting is a diagram
$2$
-category, a down-square equipped with a splitting is a diagram

Note that the composition of (1.6) with a down-square on the left or on the right is a down-square equipped with a splitting. Moreover, a down-square with one vertical arrow f right adjointable is equipped with a splitting induced by the diagram

Construction 1.8. Consider a diagram in
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
$\mathcal {C}$

with X and
![]() $X'$
dualisable. We will construct a morphism
$X'$
dualisable. We will construct a morphism
![]() $\langle u,v\rangle \to \langle u',v'\rangle $
in
$\langle u,v\rangle \to \langle u',v'\rangle $
in
![]() $\Omega \mathcal {C}$
.
$\Omega \mathcal {C}$
.
In the case where Y is also dualisable, we decompose (1.7) into

and take the composite
Here the two arrows are given by the case
![]() $f=\mathrm {id}$
of Construction 1.7. In particular, a morphism
$f=\mathrm {id}$
of Construction 1.7. In particular, a morphism
![]() $\mathrm {tr}(e)\to \mathrm {tr}(e')$
is defined for every diagram in
$\mathrm {tr}(e)\to \mathrm {tr}(e')$
is defined for every diagram in
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
of the form
$\mathcal {C}$
of the form

with X and
![]() $X'$
dualisable.
$X'$
dualisable.
In general, we define
![]() $\langle u,v\rangle \to \langle u',v'\rangle $
as the morphism
$\langle u,v\rangle \to \langle u',v'\rangle $
as the morphism
![]() $\mathrm {tr}(v\circ u)\to \mathrm {tr}(v'\circ u')$
associated to the horizontal composition of (1.7).
$\mathrm {tr}(v\circ u)\to \mathrm {tr}(v'\circ u')$
associated to the horizontal composition of (1.7).
Remark 1.9. Let
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
and
$\mathcal {C}$
and
![]() $\mathcal {D}$
be symmetric monoidal
$\mathcal {D}$
be symmetric monoidal
![]() $2$
-categories and let
$2$
-categories and let
![]() $F\colon \mathcal {C}\to \mathcal {D}$
be a symmetric monoidal functor. Then F preserves duals, pairings and functoriality of pairings.
$F\colon \mathcal {C}\to \mathcal {D}$
be a symmetric monoidal functor. Then F preserves duals, pairings and functoriality of pairings.
1.3 The Grothendieck construction
Given a category B and a (pseudo) functor
![]() $F\colon B\to \mathcal {C}\mathit {at}$
, Grothendieck constructed a category cofibred over B whose strict fibre at an object X of B is
$F\colon B\to \mathcal {C}\mathit {at}$
, Grothendieck constructed a category cofibred over B whose strict fibre at an object X of B is
![]() $F(X)$
[Reference GrothendieckSGA1, Exposé VI]. We review Grothendieck’s construction in the context of symmetric monoidal
$F(X)$
[Reference GrothendieckSGA1, Exposé VI]. We review Grothendieck’s construction in the context of symmetric monoidal
![]() $2$
-categories. Our convention on
$2$
-categories. Our convention on
![]() $2$
-morphisms is made with applications to categorical correspondences in mind.
$2$
-morphisms is made with applications to categorical correspondences in mind.
Let
![]() $(\mathcal {B},\otimes ,1_{\mathcal {B}})$
be a symmetric monoidal
$(\mathcal {B},\otimes ,1_{\mathcal {B}})$
be a symmetric monoidal
![]() $2$
-category. We consider the symmetric monoidal
$2$
-category. We consider the symmetric monoidal
![]() $2$
-category
$2$
-category
![]() $(\mathcal {C}\mathit {at}^{\mathrm {co}},\times ,*)$
, where
$(\mathcal {C}\mathit {at}^{\mathrm {co}},\times ,*)$
, where
![]() $\mathcal {C}\mathit {at}^{\mathrm {co}}$
denotes the
$\mathcal {C}\mathit {at}^{\mathrm {co}}$
denotes the
![]() $2$
-category obtained from the 2-category
$2$
-category obtained from the 2-category
![]() $\mathcal {C}\mathit {at}$
of categories by reversing the
$\mathcal {C}\mathit {at}$
of categories by reversing the
![]() $2$
-morphisms,
$2$
-morphisms,
![]() $\times $
denotes the strict product and
$\times $
denotes the strict product and
![]() $*$
denotes the category with a unique object and a unique morphism.
$*$
denotes the category with a unique object and a unique morphism.
Construction 1.10. Let
![]() $F\colon (\mathcal {B},\otimes ,1_{\mathcal {B}})\to (\mathcal {C}\mathit {at}^{\mathrm {co}},\times ,*)$
be a right-lax symmetric monoidal functor. We have an object
$F\colon (\mathcal {B},\otimes ,1_{\mathcal {B}})\to (\mathcal {C}\mathit {at}^{\mathrm {co}},\times ,*)$
be a right-lax symmetric monoidal functor. We have an object
![]() $e_{F}$
of
$e_{F}$
of
![]() $F(1_{\mathcal {B}})$
and functors
$F(1_{\mathcal {B}})$
and functors
 $F(X)\times F(X')\xrightarrow {\boxtimes } F(X\otimes X')$
for objects X and
$F(X)\times F(X')\xrightarrow {\boxtimes } F(X\otimes X')$
for objects X and
![]() $X'$
of
$X'$
of
![]() $\mathcal {B}$
. Given morphisms
$\mathcal {B}$
. Given morphisms
![]() $c\colon X\to Y$
and
$c\colon X\to Y$
and
![]() $c'\colon X'\to Y'$
in
$c'\colon X'\to Y'$
in
![]() $\mathcal {B}$
, we have a natural transformation
$\mathcal {B}$
, we have a natural transformation

The Grothendieck construction provides a symmetric monoidal
![]() $2$
-category
$2$
-category
![]() $(\mathcal {C},\otimes ,1_{\mathcal {C}})$
as follows.
$(\mathcal {C},\otimes ,1_{\mathcal {C}})$
as follows.
An object of
![]() $\mathcal {C}=\mathcal {C}_F$
is a pair
$\mathcal {C}=\mathcal {C}_F$
is a pair
![]() $(X,L)$
, where
$(X,L)$
, where
![]() $X\in \mathcal {B}$
and
$X\in \mathcal {B}$
and
![]() $L\in F(X)$
. A morphism
$L\in F(X)$
. A morphism
![]() $(X,L)\to (Y,M)$
in
$(X,L)\to (Y,M)$
in
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
is a pair
$\mathcal {C}$
is a pair
![]() $(c,u)$
, where
$(c,u)$
, where
![]() $c\colon X\to Y$
is a morphism in
$c\colon X\to Y$
is a morphism in
![]() $\mathcal {B}$
and
$\mathcal {B}$
and
![]() $u\colon F(c)(L)\to M$
is a morphism in
$u\colon F(c)(L)\to M$
is a morphism in
![]() $F(Y)$
. A
$F(Y)$
. A
![]() $2$
-morphism
$2$
-morphism
![]() $(c,u)\to (d,v)$
is a
$(c,u)\to (d,v)$
is a
![]() $2$
-morphism
$2$
-morphism
![]() $p\colon c\to d$
such that the following diagram commutes:
$p\colon c\to d$
such that the following diagram commutes:

We take
![]() $1_{\mathcal {C}}=(1_{\mathcal {B}},e_{F})$
. We put
$1_{\mathcal {C}}=(1_{\mathcal {B}},e_{F})$
. We put
![]() $(X,L)\otimes (X',l’):= (X\otimes X',L\boxtimes l’)$
. For morphisms
$(X,L)\otimes (X',l’):= (X\otimes X',L\boxtimes l’)$
. For morphisms
![]() $(c,u)\colon (X,L)\to (Y,M)$
and
$(c,u)\colon (X,L)\to (Y,M)$
and
![]() $(c',u')\colon (X',l’)\to (Y',M')$
, we put
$(c',u')\colon (X',l’)\to (Y',M')$
, we put
![]() $(c,u)\otimes (c',u'):= (c\otimes c',v)$
, where
$(c,u)\otimes (c',u'):= (c\otimes c',v)$
, where
 $$ \begin{align*}v\colon F(c\otimes c')(L\boxtimes l’)\xrightarrow{F_{c,c'}} F(c)L\boxtimes F(c')l’\xrightarrow{u\boxtimes u'} M\boxtimes M'.\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}v\colon F(c\otimes c')(L\boxtimes l’)\xrightarrow{F_{c,c'}} F(c)L\boxtimes F(c')l’\xrightarrow{u\boxtimes u'} M\boxtimes M'.\end{align*} $$
In applications in later sections,
![]() $F_{c,c'}$
will be a natural isomorphism.
$F_{c,c'}$
will be a natural isomorphism.
Given a morphism
![]() $f\colon X\to X'$
in
$f\colon X\to X'$
in
![]() $\mathcal {B}$
and an object L of
$\mathcal {B}$
and an object L of
![]() $F(X)$
, we write
$F(X)$
, we write
![]() $f_\natural =(f,\mathrm {id}_{F(f)L})\colon (X,L)\to (X',F(f)L)$
.
$f_\natural =(f,\mathrm {id}_{F(f)L})\colon (X,L)\to (X',F(f)L)$
.
Lemma 1.11. Given a
![]() $2$
-morphism
$2$
-morphism

in
![]() $\mathcal {B}$
and a morphism
$\mathcal {B}$
and a morphism
![]() $(c,u)\colon (X,L)\to (Y,M)$
in
$(c,u)\colon (X,L)\to (Y,M)$
in
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
above c, there exists a unique morphism
$\mathcal {C}$
above c, there exists a unique morphism
![]() $(c',u')\colon (X',F(f)L)\to (Y',F(g)M)$
in
$(c',u')\colon (X',F(f)L)\to (Y',F(g)M)$
in
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
above
$\mathcal {C}$
above
![]() $c'$
such that p defines a
$c'$
such that p defines a
![]() $2$
-morphism in
$2$
-morphism in
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
:
$\mathcal {C}$
:

Proof. By definition,
![]() $u'$
is the morphism
$u'$
is the morphism
 $F(c')F(f)L\simeq F(c'f)L\xrightarrow {F(p)}F(gc)L\simeq F(g)F(c)L\xrightarrow {u} F(g)M$
.
$F(c')F(f)L\simeq F(c'f)L\xrightarrow {F(p)}F(gc)L\simeq F(g)F(c)L\xrightarrow {u} F(g)M$
.
Remark 1.12. Let
![]() $f\colon X\to X'$
be a morphism in
$f\colon X\to X'$
be a morphism in
![]() $\mathcal {B}$
admitting a right adjoint
$\mathcal {B}$
admitting a right adjoint
![]() $f^!\colon X'\to X$
. Let
$f^!\colon X'\to X$
. Let
![]() $\eta \colon \mathrm {id}_X\to f^!\circ f$
and
$\eta \colon \mathrm {id}_X\to f^!\circ f$
and
![]() $\epsilon \colon f\circ f^!\to \mathrm {id}_{X'}$
denote the unit and the co-unit. Let L be an object of
$\epsilon \colon f\circ f^!\to \mathrm {id}_{X'}$
denote the unit and the co-unit. Let L be an object of
![]() $F(X)$
.
$F(X)$
.
-
(a)
 $f_\natural \colon (X,L)\to (X',F(f)L)$
admits the right adjoint with unit and co-unit given by
$f_\natural \colon (X,L)\to (X',F(f)L)$
admits the right adjoint with unit and co-unit given by $$ \begin{align*}f^\natural=(f^!,F(\eta)(L))\colon (X',F(f)L)\to (X,L),\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}f^\natural=(f^!,F(\eta)(L))\colon (X',F(f)L)\to (X,L),\end{align*} $$
 $\eta $
and
$\eta $
and
 $\epsilon $
.
$\epsilon $
.
-
(b) Assume that
 $F_{c,c'}$
is an isomorphism for all c and
$F_{c,c'}$
is an isomorphism for all c and
 $c'$
,
$c'$
,
 $(X,L)$
is dualisable in
$(X,L)$
is dualisable in
 $\mathcal {C}$
of dual
$\mathcal {C}$
of dual
 and
and
 $X'$
is dualisable in
$X'$
is dualisable in
 $\mathcal {B}$
of dual
$\mathcal {B}$
of dual
 . Then
. Then
 $(X',F(f)(L))$
is dualisable in
$(X',F(f)(L))$
is dualisable in
 $\mathcal {C}$
of dual
$\mathcal {C}$
of dual
 . The coevaluation and evaluation are given by where
. The coevaluation and evaluation are given by where
 $\bar \epsilon $
is (1.3),
$\bar \epsilon $
is (1.3),
 $\bar \eta $
is (1.4) (with
$\bar \eta $
is (1.4) (with
 $g=f$
) and
$g=f$
) and
 $\mathrm {coev}_L$
and
$\mathrm {coev}_L$
and
 $\mathrm {ev}_L$
denote the second components of
$\mathrm {ev}_L$
denote the second components of
 $\mathrm {coev}_{(X,L)}$
and
$\mathrm {coev}_{(X,L)}$
and
 $\mathrm {ev}_{(X,L)}$
, respectively.
$\mathrm {ev}_{(X,L)}$
, respectively.
Construction 1.13. Let
![]() $F,G\colon (\mathcal {B},\otimes ,1_{\mathcal {B}})\to (\mathcal {C}\mathit {at}^{\mathrm {co}},\times ,*)$
be right-lax symmetric monoidal functors. Let
$F,G\colon (\mathcal {B},\otimes ,1_{\mathcal {B}})\to (\mathcal {C}\mathit {at}^{\mathrm {co}},\times ,*)$
be right-lax symmetric monoidal functors. Let
![]() $\alpha \colon F\to G$
be a right-lax symmetric monoidal natural transformation, which consists of the following data:
$\alpha \colon F\to G$
be a right-lax symmetric monoidal natural transformation, which consists of the following data:
-
• for every object X of
 $\mathcal {B}$
, a functor
$\mathcal {B}$
, a functor
 $\alpha _X\colon F(X)\to G(X)$
;
$\alpha _X\colon F(X)\to G(X)$
; -
• for every morphism
 $c\colon X\to Y$
, a natural transformation
$c\colon X\to Y$
, a natural transformation 
-
• a morphism
 $e_\alpha \colon e_{G}\to \alpha _{1_{\mathcal {B}}}(e_{F})$
in
$e_\alpha \colon e_{G}\to \alpha _{1_{\mathcal {B}}}(e_{F})$
in
 $F(1_{\mathcal {B}})$
;
$F(1_{\mathcal {B}})$
; -
• for objects X and
 $X'$
of
$X'$
of
 $\mathcal {B}$
, a natural transformation
$\mathcal {B}$
, a natural transformation 
subject to various compatibilities. We construct a right-lax symmetric monoidal functor
![]() $\psi \colon (\mathcal {C}_F,\otimes ,1)\to (\mathcal {C}_G,\otimes ,1)$
as follows.
$\psi \colon (\mathcal {C}_F,\otimes ,1)\to (\mathcal {C}_G,\otimes ,1)$
as follows.
We take
![]() $\psi (X,L)=(X,\alpha _X(L))$
and
$\psi (X,L)=(X,\alpha _X(L))$
and
![]() $\psi (c,u)=(c,\psi u)$
, where
$\psi (c,u)=(c,\psi u)$
, where
 $$ \begin{align*}\psi u\colon G(c)(\alpha_X(L))\xrightarrow{\alpha_c} \alpha_Y(F(c) L)\xrightarrow{u}\alpha_Y(M) \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\psi u\colon G(c)(\alpha_X(L))\xrightarrow{\alpha_c} \alpha_Y(F(c) L)\xrightarrow{u}\alpha_Y(M) \end{align*} $$
for
![]() $(c,u)\colon (X,L)\to (Y,M)$
. We let
$(c,u)\colon (X,L)\to (Y,M)$
. We let
![]() $\psi $
send every
$\psi $
send every
![]() $2$
-morphism p to p. The right-lax symmetric monoidal structure on
$2$
-morphism p to p. The right-lax symmetric monoidal structure on
![]() $\psi $
is given by
$\psi $
is given by

This is a symmetric monoidal structure if
![]() $e_\alpha $
and
$e_\alpha $
and
![]() $\alpha _{X,X'}$
are isomorphisms (which will be the case in our applications).
$\alpha _{X,X'}$
are isomorphisms (which will be the case in our applications).
Lemma 1.14. Consider a
![]() $2$
-morphism (1.9) in
$2$
-morphism (1.9) in
![]() $\mathcal {B}$
and a morphism
$\mathcal {B}$
and a morphism
![]() $(c,u)\colon (X,L)\to (Y,M)$
in
$(c,u)\colon (X,L)\to (Y,M)$
in
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
above c. Let
$\mathcal {C}$
above c. Let
![]() $(c',u')\colon (X',F(f)L)\to (Y',G(g)M)$
be the morphism associated to
$(c',u')\colon (X',F(f)L)\to (Y',G(g)M)$
be the morphism associated to
![]() $(c,u)$
and let
$(c,u)$
and let
![]() $(c',(\psi u)')\colon (X',G(f)\alpha _X L)\to (Y',G(g)\alpha _Y M)$
be the morphism associated to
$(c',(\psi u)')\colon (X',G(f)\alpha _X L)\to (Y',G(g)\alpha _Y M)$
be the morphism associated to
![]() $(c,\psi u)$
. Then the following square commutes:
$(c,\psi u)$
. Then the following square commutes:

Proof. The square decomposes into

where the inner cells commute.
Construction 1.15. Let
 $(\mathcal {B},\otimes ,1_{\mathcal {B}})\xrightarrow {H} (\mathcal {B}',\otimes ,1_{\mathcal {B}'})\xrightarrow {G}(\mathcal {C}\mathit {at}^{\mathrm {co}},\times ,*)$
be right-lax symmetric monoidal functors. Then we have an obvious right-lax symmetric monoidal functor
$(\mathcal {B},\otimes ,1_{\mathcal {B}})\xrightarrow {H} (\mathcal {B}',\otimes ,1_{\mathcal {B}'})\xrightarrow {G}(\mathcal {C}\mathit {at}^{\mathrm {co}},\times ,*)$
be right-lax symmetric monoidal functors. Then we have an obvious right-lax symmetric monoidal functor
![]() $\mathcal {C}_{GH}\to \mathcal {C}_G$
sending
$\mathcal {C}_{GH}\to \mathcal {C}_G$
sending
![]() $(X,L)$
to
$(X,L)$
to
![]() $(HX,L)$
,
$(HX,L)$
,
![]() $(c,u)$
to
$(c,u)$
to
![]() $(Hc,u)$
and every
$(Hc,u)$
and every
![]() $2$
-morphism p to
$2$
-morphism p to
![]() $Hp$
. This is a symmetric monoidal functor if H is.
$Hp$
. This is a symmetric monoidal functor if H is.
Construction 1.16. Let

be a diagram of right-lax symmetric monoidal functors and right-lax symmetric monoidal transformation. Combining the two preceding constructions, we obtain right-lax symmetric monoidal functors
![]() $\mathcal {C}_{F}\to \mathcal {C}_{GH}\to \mathcal {C}_G$
.
$\mathcal {C}_{F}\to \mathcal {C}_{GH}\to \mathcal {C}_G$
.
2 A relative Lefschetz–Verdier formula
We apply the formalism of duals and pairings to the symmetric monoidal
![]() $2$
-category of cohomological correspondences, which we define in Subsection 2.2. We prove relative Künneth formulas in Subsection 2.1 and use them to show the equivalence of dualisability and local acyclicity (Theorem 2.16) in Subsection 2.3. We prove the relative Lefschetz–Verdier theorem for dualisable objects (Theorem 2.21) in Subsection 2.4. Together, the two theorems imply Theorem 0.1. In Subsection 2.5, we prove that base change preserves duals (Proposition 2.26).
$2$
-category of cohomological correspondences, which we define in Subsection 2.2. We prove relative Künneth formulas in Subsection 2.1 and use them to show the equivalence of dualisability and local acyclicity (Theorem 2.16) in Subsection 2.3. We prove the relative Lefschetz–Verdier theorem for dualisable objects (Theorem 2.21) in Subsection 2.4. Together, the two theorems imply Theorem 0.1. In Subsection 2.5, we prove that base change preserves duals (Proposition 2.26).
We will often drop the letters L and R from the notation of derived functors.
2.1 Relative Künneth formulas
We extend some Künneth formulas over fields [Reference GrothendieckSGA5, III 1.6, Proposition 1.7.4, (3.1.1)] to Noetherian base schemes under the assumption of universal local acyclicity. Some special cases over a smooth scheme over a perfect field were previously known [Reference Yang and ZhaoYZ, Corollary 3.3, Proposition 3.5].
Let S be a coherent scheme and let
![]() $\Lambda $
be a torsion commutative ring. Let X be a scheme over S. We let
$\Lambda $
be a torsion commutative ring. Let X be a scheme over S. We let
![]() $D(X,\Lambda )$
denote the unbounded derived category of the category of étale sheaves of
$D(X,\Lambda )$
denote the unbounded derived category of the category of étale sheaves of
![]() $\Lambda $
-modules on X. Following [Reference DeligneD, Th. finitude, Définition 2.12], we say that
$\Lambda $
-modules on X. Following [Reference DeligneD, Th. finitude, Définition 2.12], we say that
![]() $L\in D(X,\Lambda )$
is locally acyclic over S if the canonical map
$L\in D(X,\Lambda )$
is locally acyclic over S if the canonical map
![]() $L_x\to R\Gamma (X_{(x)t},L)$
is an isomorphism for every geometric point
$L_x\to R\Gamma (X_{(x)t},L)$
is an isomorphism for every geometric point
![]() $x\to X$
and every algebraic geometric point
$x\to X$
and every algebraic geometric point
![]() $t\to S_{(x)}$
. Here
$t\to S_{(x)}$
. Here
![]() $X_{(x)t}:= X_{(x)}\times _{S_{(x)}} t$
denotes the Milnor fibre. For X of finite type over S, local acyclicity coincides with strong local acyclicity [Reference Lu and ZhengLZ, Lemma 4.7].
$X_{(x)t}:= X_{(x)}\times _{S_{(x)}} t$
denotes the Milnor fibre. For X of finite type over S, local acyclicity coincides with strong local acyclicity [Reference Lu and ZhengLZ, Lemma 4.7].
Notation 2.1. For
![]() $a_X\colon X\to S$
separated of finite type, we write
$a_X\colon X\to S$
separated of finite type, we write
 $K_{X/S}=a_X^!\Lambda _S$
and
$K_{X/S}=a_X^!\Lambda _S$
and
![]() $D_{X/S}=R\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(-,K_X)$
. Note that
$D_{X/S}=R\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(-,K_X)$
. Note that
![]() $K_{S/S}=\Lambda _S$
is in general not an (absolute) dualising complex.
$K_{S/S}=\Lambda _S$
is in general not an (absolute) dualising complex.
Assume in the rest of Subsection 2.1 that S and
![]() $\Lambda $
are Noetherian. We let
$\Lambda $
are Noetherian. We let
![]() $D_{{\mathrm {ft}}}(X,\Lambda )$
denote the full subcategory of
$D_{{\mathrm {ft}}}(X,\Lambda )$
denote the full subcategory of
![]() $D(X,\Lambda )$
consisting of complexes of finite tor-amplitude.
$D(X,\Lambda )$
consisting of complexes of finite tor-amplitude.
Proposition 2.2. Let
![]() $X',X,Y$
be schemes of finite type over S and let
$X',X,Y$
be schemes of finite type over S and let
![]() $f\colon X\to X'$
be a morphism over S. Let
$f\colon X\to X'$
be a morphism over S. Let
![]() $M\in D_{{\mathrm {ft}}}(Y,\Lambda )$
universally locally acyclic over S,
$M\in D_{{\mathrm {ft}}}(Y,\Lambda )$
universally locally acyclic over S,
![]() $L\in D^+(X,\Lambda )$
. Then the canonical morphism
$L\in D^+(X,\Lambda )$
. Then the canonical morphism
![]() $f_*L\boxtimes _S M\to (f\times _S \mathrm {id}_Y)_*(L\boxtimes _S M)$
is an isomorphism.
$f_*L\boxtimes _S M\to (f\times _S \mathrm {id}_Y)_*(L\boxtimes _S M)$
is an isomorphism.
This follows from [Reference FuF, Theorem 7.6.9]. We recall the proof for completeness.
Proof. By cohomological descent for a Zariski open cover, we may assume f separated. By Nagata compactification, we are reduced to two cases: either f is proper, in which case we apply proper base change, or f is an open immersion, in which case we apply [Reference DeligneD, Th. finitude, App., Proposition 2.10] (with
![]() $i=\mathrm {id}_{X'}$
).
$i=\mathrm {id}_{X'}$
).
In the rest of Subsection 2.1, assume that
![]() $m\Lambda =0$
for some integer m invertible on S.
$m\Lambda =0$
for some integer m invertible on S.
Proposition 2.3. Let
![]() $X',X,Y$
be schemes of finite type over S and let
$X',X,Y$
be schemes of finite type over S and let
![]() $f\colon X\to X'$
be a separated morphism over S. Let
$f\colon X\to X'$
be a separated morphism over S. Let
![]() $M\in D_{{\mathrm {ft}}}(Y,\Lambda )$
universally locally acyclic over S,
$M\in D_{{\mathrm {ft}}}(Y,\Lambda )$
universally locally acyclic over S,
![]() $L\in D^+(X',\Lambda )$
. Then the canonical morphism
$L\in D^+(X',\Lambda )$
. Then the canonical morphism
![]() $f^!L\boxtimes _S M\to (f\times _S \mathrm {id}_Y)^!(L\boxtimes _S M)$
is an isomorphism.
$f^!L\boxtimes _S M\to (f\times _S \mathrm {id}_Y)^!(L\boxtimes _S M)$
is an isomorphism.
The morphism is adjoint to
 $$ \begin{align*}(f\times_S \mathrm{id}_Y)_! (f^!L\boxtimes_S M)\simeq f_!f^!L\boxtimes_S M\xrightarrow{\mathrm{adj} \boxtimes_S \mathrm{id}_M} L\boxtimes_S M, \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}(f\times_S \mathrm{id}_Y)_! (f^!L\boxtimes_S M)\simeq f_!f^!L\boxtimes_S M\xrightarrow{\mathrm{adj} \boxtimes_S \mathrm{id}_M} L\boxtimes_S M, \end{align*} $$
where
![]() $\mathrm {adj}\colon f_!f^!L\to L$
denotes the adjunction.
$\mathrm {adj}\colon f_!f^!L\to L$
denotes the adjunction.
Proof. We may assume that f is smooth or a closed immersion. For f smooth of dimension d,
![]() $f^*(d)[2d]\simeq f^!$
and the assertion is clear. Assume that f is a closed immersion and let j be the complementary open immersion. Let
$f^*(d)[2d]\simeq f^!$
and the assertion is clear. Assume that f is a closed immersion and let j be the complementary open immersion. Let
![]() $f_Y=f\times _S \mathrm {id}_Y$
and
$f_Y=f\times _S \mathrm {id}_Y$
and
![]() $j_Y=j\times _S \mathrm {id}_Y$
. Then we have a morphism of distinguished triangles
$j_Y=j\times _S \mathrm {id}_Y$
. Then we have a morphism of distinguished triangles

where
![]() $\beta $
is an isomorphism by Proposition 2.2. It follows that
$\beta $
is an isomorphism by Proposition 2.2. It follows that
![]() $\alpha $
is an isomorphism.
$\alpha $
is an isomorphism.
The following is a variant of [Reference SaitoS, Corollary 8.10] and [Reference Lu and ZhengLZ, Theorem 6.8]. Here we do not require smoothness or regularity.
Corollary 2.4. Let X and Y be schemes of finite type over S, with X separated over S. Let
![]() $M\in D_{{\mathrm {ft}}}(Y,\Lambda )$
universally locally acyclic over S. Then the canonical morphism
$M\in D_{{\mathrm {ft}}}(Y,\Lambda )$
universally locally acyclic over S. Then the canonical morphism
 $K_{X/S}\boxtimes _S M \to p_Y^! M$
is an isomorphism, where
$K_{X/S}\boxtimes _S M \to p_Y^! M$
is an isomorphism, where
![]() $p_Y\colon X\times _S Y\to Y$
is the projection.
$p_Y\colon X\times _S Y\to Y$
is the projection.
Proof. This is Proposition 2.3 applied to
![]() $X'=S$
and
$X'=S$
and
![]() $L=\Lambda _S$
.
$L=\Lambda _S$
.
Proposition 2.5. Let X and Y be schemes of finite type over S, with X separated over S. Let
![]() $M\in D_{{\mathrm {ft}}}(Y,\Lambda )$
universally locally acyclic over S,
$M\in D_{{\mathrm {ft}}}(Y,\Lambda )$
universally locally acyclic over S,
![]() $L\in D^-_c(X,\Lambda )$
. Then the canonical morphism
$L\in D^-_c(X,\Lambda )$
. Then the canonical morphism
 $D_{X/S}L\boxtimes _S M\to R\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(p_X^*L,p_Y^!M)$
is an isomorphism. Here
$D_{X/S}L\boxtimes _S M\to R\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(p_X^*L,p_Y^!M)$
is an isomorphism. Here
![]() $p_X\colon X\times _S Y\to X$
and
$p_X\colon X\times _S Y\to X$
and
![]() $p_Y\colon X\times _S Y\to Y$
are the projections.
$p_Y\colon X\times _S Y\to Y$
are the projections.
The morphism is adjoint to
 $(D_{X/S}L\otimes L)\boxtimes _S M\to K_{X/S}\boxtimes _S M\to p_Y^!M$
.
$(D_{X/S}L\otimes L)\boxtimes _S M\to K_{X/S}\boxtimes _S M\to p_Y^!M$
.
Proof. By [Reference Artin, Grothendieck and VerdierSGA4, IX Proposition 2.7], we may assume
![]() $L=j_!\Lambda $
for
$L=j_!\Lambda $
for
![]() $j\colon U\to X$
étale with U affine. Then the morphism can be identified with
$j\colon U\to X$
étale with U affine. Then the morphism can be identified with
 $$ \begin{align*} & j_*D_{U/S} \Lambda_U\boxtimes_S M\to j_{Y*}(D_{U/S}\Lambda_U\boxtimes M)\to j_{Y*}R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(\Lambda_{U\times_S Y},j_Y^! p_Y^!M) \\ &\quad \simeq R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(j_{Y!}\Lambda_{U\times_S Y},p_Y^!M), \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} & j_*D_{U/S} \Lambda_U\boxtimes_S M\to j_{Y*}(D_{U/S}\Lambda_U\boxtimes M)\to j_{Y*}R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(\Lambda_{U\times_S Y},j_Y^! p_Y^!M) \\ &\quad \simeq R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(j_{Y!}\Lambda_{U\times_S Y},p_Y^!M), \end{align*} $$
where
![]() $j_Y=j\times _S \mathrm {id}_Y\colon U\times _S Y\to X\times _S Y$
. The first arrow is an isomorphism by Proposition 2.2. The second arrow is an isomorphism by Corollary 2.4.
$j_Y=j\times _S \mathrm {id}_Y\colon U\times _S Y\to X\times _S Y$
. The first arrow is an isomorphism by Proposition 2.2. The second arrow is an isomorphism by Corollary 2.4.
2.2 The category of cohomological correspondences
Let S be a coherent scheme and let
![]() $\Lambda $
be a torsion commutative ring.
$\Lambda $
be a torsion commutative ring.
Construction 2.6. We define the
![]() $2$
-category of cohomological correspondences
$2$
-category of cohomological correspondences
![]() $\mathcal {C}=\mathcal {C}_{S,\Lambda }$
as follows. An object of
$\mathcal {C}=\mathcal {C}_{S,\Lambda }$
as follows. An object of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
is a pair
$\mathcal {C}$
is a pair
![]() $(X,L)$
, where X is a scheme separated of finite type over S and
$(X,L)$
, where X is a scheme separated of finite type over S and
![]() $L\in D(X,\Lambda )$
. A correspondence over S is a pair of morphisms
$L\in D(X,\Lambda )$
. A correspondence over S is a pair of morphisms
 $X\xleftarrow {\overleftarrow {c}} C\xrightarrow {\overrightarrow {c}} Y$
of schemes over S, where X, Y and C are separated and of finite type over S. A morphism
$X\xleftarrow {\overleftarrow {c}} C\xrightarrow {\overrightarrow {c}} Y$
of schemes over S, where X, Y and C are separated and of finite type over S. A morphism
![]() $(X,L)\to (Y,M)$
in
$(X,L)\to (Y,M)$
in
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
is a cohomological correspondence over S, namely, a pair
$\mathcal {C}$
is a cohomological correspondence over S, namely, a pair
![]() $(c,u)$
, where
$(c,u)$
, where
![]() $c=(\overleftarrow {c},\overrightarrow {c})$
is a correspondence over S and
$c=(\overleftarrow {c},\overrightarrow {c})$
is a correspondence over S and
![]() $u\colon \overleftarrow {c}^*L\to \overrightarrow {c}^!M$
is a morphism in
$u\colon \overleftarrow {c}^*L\to \overrightarrow {c}^!M$
is a morphism in
![]() $D(C,\Lambda )$
. Given cohomological correspondences
$D(C,\Lambda )$
. Given cohomological correspondences
 $(X,L)\xrightarrow {(c,u)} (Y,M)\xrightarrow {(d,v)}(Z,N)$
, the composite is
$(X,L)\xrightarrow {(c,u)} (Y,M)\xrightarrow {(d,v)}(Z,N)$
, the composite is
![]() $(e,w)$
, where e is the composite correspondence given by the diagram
$(e,w)$
, where e is the composite correspondence given by the diagram

and w is given by the composite
 $$ \begin{align*}\overleftarrow{d}^{\prime}*\overleftarrow{c}^*L\xrightarrow{u} \overleftarrow{d}^{\prime}*\overrightarrow{c}^!M\xrightarrow{\alpha} \overrightarrow{c}^{\prime}!\overleftarrow{d}^*M\xrightarrow{v}\overrightarrow{c}^{\prime}!\overrightarrow{d}^!N,\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\overleftarrow{d}^{\prime}*\overleftarrow{c}^*L\xrightarrow{u} \overleftarrow{d}^{\prime}*\overrightarrow{c}^!M\xrightarrow{\alpha} \overrightarrow{c}^{\prime}!\overleftarrow{d}^*M\xrightarrow{v}\overrightarrow{c}^{\prime}!\overrightarrow{d}^!N,\end{align*} $$
where
![]() $\alpha $
is adjoint to the base change isomorphism
$\alpha $
is adjoint to the base change isomorphism
 $\overrightarrow {c}^{\prime }_!\overleftarrow {d}^{\prime }*\simeq \overleftarrow {d}^*\overrightarrow {c}_!$
. Given
$\overrightarrow {c}^{\prime }_!\overleftarrow {d}^{\prime }*\simeq \overleftarrow {d}^*\overrightarrow {c}_!$
. Given
![]() $(c,u)$
and
$(c,u)$
and
![]() $(d,v)$
from
$(d,v)$
from
![]() $(X,L)$
to
$(X,L)$
to
![]() $(Y,M)$
, a
$(Y,M)$
, a
![]() $2$
-morphism
$2$
-morphism
![]() $(c,u)\to (d,v)$
is a proper morphism of schemes
$(c,u)\to (d,v)$
is a proper morphism of schemes
![]() $p\colon C\to D$
satisfying
$p\colon C\to D$
satisfying
 $\overleftarrow {d}p=\overleftarrow {c}$
and
$\overleftarrow {d}p=\overleftarrow {c}$
and
 $\overrightarrow {d}p=\overrightarrow {c}$
and such that v is equal to
$\overrightarrow {d}p=\overrightarrow {c}$
and such that v is equal to
 $$ \begin{align*}\overleftarrow{d}^*L\xrightarrow{\mathrm{adj}} p_*p^*\overleftarrow{d}^*L\simeq p_!\overleftarrow{c}^*L \xrightarrow{u}p_!\overrightarrow{c}^!M\simeq p_!p^!\overrightarrow{d}^!M\xrightarrow{\mathrm{adj}} \overrightarrow{d}^!M. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\overleftarrow{d}^*L\xrightarrow{\mathrm{adj}} p_*p^*\overleftarrow{d}^*L\simeq p_!\overleftarrow{c}^*L \xrightarrow{u}p_!\overrightarrow{c}^!M\simeq p_!p^!\overrightarrow{d}^!M\xrightarrow{\mathrm{adj}} \overrightarrow{d}^!M. \end{align*} $$
Here we used the canonical isomorphism
![]() $p_!\simeq p_*$
. Composition of
$p_!\simeq p_*$
. Composition of
![]() $2$
-morphisms is given by composition of morphisms of schemes.
$2$
-morphisms is given by composition of morphisms of schemes.
The
![]() $2$
-category admits a symmetric monoidal structure. We put
$2$
-category admits a symmetric monoidal structure. We put
Given
![]() $(c,u)\colon (X,L)\to (Y,M)$
and
$(c,u)\colon (X,L)\to (Y,M)$
and
![]() $(c',u')\colon (X',l’)\to (Y',M')$
, we define
$(c',u')\colon (X',l’)\to (Y',M')$
, we define
![]() $(c,u)\otimes (c',u')$
to be
$(c,u)\otimes (c',u')$
to be
![]() $(d,v)$
, where
$(d,v)$
, where
 $d=(\overleftarrow {c}\times _S \overleftarrow {c'},\overrightarrow {c}\times _S \overrightarrow {c'})$
and v is the composite
$d=(\overleftarrow {c}\times _S \overleftarrow {c'},\overrightarrow {c}\times _S \overrightarrow {c'})$
and v is the composite
 $$ \begin{align*}\overleftarrow{d}^* (L\boxtimes_S l’)\simeq \overleftarrow{c}^*L\boxtimes_S\overleftarrow{c'}^*l’\xrightarrow{u\boxtimes_S u'}\overrightarrow{c}^!M\boxtimes_S\overrightarrow{c'}^!M'\xrightarrow{\alpha} \overrightarrow{d}^!(M\boxtimes_S M'), \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\overleftarrow{d}^* (L\boxtimes_S l’)\simeq \overleftarrow{c}^*L\boxtimes_S\overleftarrow{c'}^*l’\xrightarrow{u\boxtimes_S u'}\overrightarrow{c}^!M\boxtimes_S\overrightarrow{c'}^!M'\xrightarrow{\alpha} \overrightarrow{d}^!(M\boxtimes_S M'), \end{align*} $$
where
![]() $\alpha $
is adjoint to the Künneth formula
$\alpha $
is adjoint to the Künneth formula
 $\overrightarrow {d}_!(-\boxtimes _S -)\simeq \overrightarrow {c}_!-\boxtimes _S \overrightarrow {c'}_!-$
. Tensor product of
$\overrightarrow {d}_!(-\boxtimes _S -)\simeq \overrightarrow {c}_!-\boxtimes _S \overrightarrow {c'}_!-$
. Tensor product of
![]() $2$
-morphisms is given by product of morphisms of schemes over S. The monoidal unit of
$2$
-morphisms is given by product of morphisms of schemes over S. The monoidal unit of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
is
$\mathcal {C}$
is
![]() $(S,\Lambda _S)$
.
$(S,\Lambda _S)$
.
Remark 2.7. Let
![]() $\mathcal {B}_S$
be the symmetric monoidal
$\mathcal {B}_S$
be the symmetric monoidal
![]() $2$
-category of correspondences obtained by omitting L from the above construction. The symmetric monoidal structure on
$2$
-category of correspondences obtained by omitting L from the above construction. The symmetric monoidal structure on
![]() $\mathcal {B}_S$
is given by fibre product of schemes over S (which is not the product in
$\mathcal {B}_S$
is given by fibre product of schemes over S (which is not the product in
![]() $\mathcal {B}_S$
for S nonempty). Consider the functor
$\mathcal {B}_S$
for S nonempty). Consider the functor
![]() $F\colon \mathcal {B}_S\to \mathcal {C}\mathit {at}^{\mathrm {co}}$
carrying X to
$F\colon \mathcal {B}_S\to \mathcal {C}\mathit {at}^{\mathrm {co}}$
carrying X to
![]() $D(X,\Lambda )$
and
$D(X,\Lambda )$
and
![]() $c=(\overleftarrow {c},\overrightarrow {c})$
to
$c=(\overleftarrow {c},\overrightarrow {c})$
to
![]() $\overrightarrow {c}_!\overleftarrow {c}^*$
and a
$\overrightarrow {c}_!\overleftarrow {c}^*$
and a
![]() $2$
-morphism
$2$
-morphism
![]() $p\colon c\to d$
to the natural transformation
$p\colon c\to d$
to the natural transformation
 $\overrightarrow {d}_!\overleftarrow {d}^*\xrightarrow {\mathrm {adj}} \overrightarrow {d}_!p_*p^*\overleftarrow {d}^*\simeq \overrightarrow {c}_!\overleftarrow {c}^*$
. The compatibility of F with composition (2.1) is given by the base change isomorphism
$\overrightarrow {d}_!\overleftarrow {d}^*\xrightarrow {\mathrm {adj}} \overrightarrow {d}_!p_*p^*\overleftarrow {d}^*\simeq \overrightarrow {c}_!\overleftarrow {c}^*$
. The compatibility of F with composition (2.1) is given by the base change isomorphism
 $\overleftarrow {d}^*\overrightarrow {c}_!\simeq \overrightarrow {c}^{\prime }_!\overleftarrow {d}^{\prime }*$
. The functor F admits a right-lax symmetric monoidal structure given by
$\overleftarrow {d}^*\overrightarrow {c}_!\simeq \overrightarrow {c}^{\prime }_!\overleftarrow {d}^{\prime }*$
. The functor F admits a right-lax symmetric monoidal structure given by
![]() $e_F=\Lambda _S$
and
$e_F=\Lambda _S$
and
![]() $\boxtimes _S$
, with Künneth formula for
$\boxtimes _S$
, with Künneth formula for
![]() $!$
-pushforward providing a natural isomorphism
$!$
-pushforward providing a natural isomorphism
![]() $F_{c,c'}$
(1.8). The Grothendieck construction (Construction 1.10) then produces
$F_{c,c'}$
(1.8). The Grothendieck construction (Construction 1.10) then produces
![]() $\mathcal {C}_{S,\Lambda }$
.
$\mathcal {C}_{S,\Lambda }$
.
The category
![]() $\Omega \mathcal {C}$
consists of pairs
$\Omega \mathcal {C}$
consists of pairs
![]() $(X,\alpha )$
, where X is a scheme separated of finite type over S and
$(X,\alpha )$
, where X is a scheme separated of finite type over S and
![]() $\alpha \in H^0(X,K_{X/S})$
. A morphism
$\alpha \in H^0(X,K_{X/S})$
. A morphism
![]() $(X,\alpha )\to (Y,\beta )$
is a proper morphism
$(X,\alpha )\to (Y,\beta )$
is a proper morphism
![]() $X\to Y$
of schemes over S such that
$X\to Y$
of schemes over S such that
![]() $\beta =p_*\alpha $
, where
$\beta =p_*\alpha $
, where
 $$ \begin{align} p_*\colon H^0(X,K_{X/S})\to H^0(Y,K_{Y/S}) \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} p_*\colon H^0(X,K_{X/S})\to H^0(Y,K_{Y/S}) \end{align} $$
is given by adjunction
![]() $p_*p^!\simeq p_!p^!\to \mathrm {id}$
.
$p_*p^!\simeq p_!p^!\to \mathrm {id}$
.
Lemma 2.8. The symmetric monoidal structure
![]() $\otimes $
on
$\otimes $
on
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
is closed, with internal mapping object
$\mathcal {C}$
is closed, with internal mapping object
 $\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}((X,L),(Y,M))=(X\times _S Y,R\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(p_X^*L,p_Y^!M))$
.
$\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}((X,L),(Y,M))=(X\times _S Y,R\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(p_X^*L,p_Y^!M))$
.
Proof. We construct an isomorphism of categories
as follows. An object of the source (respectively target) is a pair
 $(C\xrightarrow {c} X\times _S Y\times _S Z,u)$
, where u belongs to
$(C\xrightarrow {c} X\times _S Y\times _S Z,u)$
, where u belongs to
![]() $H^0(C,c^!-)$
applied to the left-hand (respectively right-hand) side of the isomorphism
$H^0(C,c^!-)$
applied to the left-hand (respectively right-hand) side of the isomorphism
 $$ \begin{align*}\alpha\colon R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_X^*L\otimes p_Y^*M,p_Z^!N)\simeq R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_X^*L, R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_Y^*M,p_Z^!N)).\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\alpha\colon R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_X^*L\otimes p_Y^*M,p_Z^!N)\simeq R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_X^*L, R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_Y^*M,p_Z^!N)).\end{align*} $$
Here
![]() $p_X,p_Y,p_Z$
denote the projections from
$p_X,p_Y,p_Z$
denote the projections from
![]() $X\times _S Y\times _S Z$
. We define F by
$X\times _S Y\times _S Z$
. We define F by
![]() $F(c,u)=(c,u')$
, where
$F(c,u)=(c,u')$
, where
![]() $u'$
is the image of u under the map induced by
$u'$
is the image of u under the map induced by
![]() $\alpha $
and
$\alpha $
and
![]() $F(p)=p$
for every morphism p in the source of F.
$F(p)=p$
for every morphism p in the source of F.
For an object
![]() $(X,L)$
of
$(X,L)$
of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
and a morphism
$\mathcal {C}$
and a morphism
![]() $f\colon X\to X'$
of schemes separated of finite type over S, we let
$f\colon X\to X'$
of schemes separated of finite type over S, we let
 $$ \begin{align*}f_\natural=(\mathrm{id}_X,f)_\natural=((\mathrm{id}_X,f),L\xrightarrow{\mathrm{adj}} f^!f_!L)\colon (X,L)\to (X',f_!L).\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}f_\natural=(\mathrm{id}_X,f)_\natural=((\mathrm{id}_X,f),L\xrightarrow{\mathrm{adj}} f^!f_!L)\colon (X,L)\to (X',f_!L).\end{align*} $$
Lemma 2.9. Let
![]() $(X,L)$
be an object of
$(X,L)$
be an object of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
and let
$\mathcal {C}$
and let
![]() $f\colon X\to X'$
be a proper morphism of schemes separated of finite type over S. Then
$f\colon X\to X'$
be a proper morphism of schemes separated of finite type over S. Then
![]() $f_\natural \colon (X,L)\to (X',f_*L)$
admits the right adjoint
$f_\natural \colon (X,L)\to (X',f_*L)$
admits the right adjoint
 $$ \begin{align*}f^\natural=((f,\mathrm{id}_{X}),f^*f_*L\xrightarrow{\mathrm{adj}} L)\colon (X',f_*L)\to (X,L).\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}f^\natural=((f,\mathrm{id}_{X}),f^*f_*L\xrightarrow{\mathrm{adj}} L)\colon (X',f_*L)\to (X,L).\end{align*} $$
Proof. The co-unit
 $f_\natural f^\natural \to \mathrm {id}_{(X',f_*L)}$
is given by f and the unit
$f_\natural f^\natural \to \mathrm {id}_{(X',f_*L)}$
is given by f and the unit
 $\mathrm {id}_{(X,L)}\to f^\natural f_\natural $
is given by the diagonal
$\mathrm {id}_{(X,L)}\to f^\natural f_\natural $
is given by the diagonal
![]() $X\to X\times _{X'} X$
. (This is an example of Remark 1.12 (a).)
$X\to X\times _{X'} X$
. (This is an example of Remark 1.12 (a).)
Construction 2.10
 $!$
-pushforward
$!$
-pushforward
Consider a commutative diagram of schemes separated of finite type over S

such that
![]() $q\colon C\to X\times _{X'} C'$
is proper. Let
$q\colon C\to X\times _{X'} C'$
is proper. Let
![]() $(c,u)\colon (X,L)\to (Y,M)$
be a cohomological correspondence above c. Let
$(c,u)\colon (X,L)\to (Y,M)$
be a cohomological correspondence above c. Let
![]() $p^\sharp =(f,p,g)$
. By Lemma 1.11, we have a unique cohomological correspondence
$p^\sharp =(f,p,g)$
. By Lemma 1.11, we have a unique cohomological correspondence
 $(c',p^\sharp _!u)\colon (X',f_!l’)\to (Y',g_!M')$
above
$(c',p^\sharp _!u)\colon (X',f_!l’)\to (Y',g_!M')$
above
![]() $c'$
such that q defines a
$c'$
such that q defines a
![]() $2$
-morphism in
$2$
-morphism in
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
:
$\mathcal {C}$
:
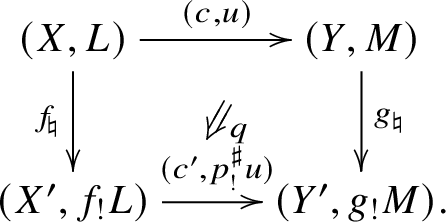
For a more explicit construction of
 $p^\sharp _!u$
, see [Reference ZhengZ, Construction 7.16]. We will often be interested in the case where f, g and p are proper. In this case, we write
$p^\sharp _!u$
, see [Reference ZhengZ, Construction 7.16]. We will often be interested in the case where f, g and p are proper. In this case, we write
 $p^\sharp _*u$
for
$p^\sharp _*u$
for
 $p^\sharp _!u$
.
$p^\sharp _!u$
.
This construction is compatible with horizontal and vertical compositions.
2.3 Dualisable objects
Let S and
![]() $\Lambda $
be as in Subsection 2.2. Next we study dualisable objects of
$\Lambda $
be as in Subsection 2.2. Next we study dualisable objects of
![]() $\mathcal {C}=\mathcal {C}_{S,\Lambda }$
.
$\mathcal {C}=\mathcal {C}_{S,\Lambda }$
.
Proposition 2.11. Let
![]() $(X,L)$
be a dualisable object of
$(X,L)$
be a dualisable object of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
.
$\mathcal {C}$
.
-
(a) The dual of
 $(X,L)$
is
$(X,L)$
is
 $(X,D_{X/S} L)$
and the biduality morphism
$(X,D_{X/S} L)$
and the biduality morphism
 $L\to D_{X/S}D_{X/S} L$
is an isomorphism. Moreover, for any object
$L\to D_{X/S}D_{X/S} L$
is an isomorphism. Moreover, for any object
 $(Y,M)$
of
$(Y,M)$
of
 $\mathcal {C}$
, the canonical morphisms (2.4)are isomorphisms. Here
$\mathcal {C}$
, the canonical morphisms (2.4)are isomorphisms. Here $$ \begin{align} &D_{X/S}L\boxtimes_S M\to R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_X^*L,p_Y^!M),\\ &\notag L\boxtimes_S D_{Y/S}M\to R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_Y^*M,p_X^!L),\\ &\notag D_{X/S} L\boxtimes_S D_{Y/S} M\to D_{X\times_S Y/S}(L\boxtimes_S M) \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} &D_{X/S}L\boxtimes_S M\to R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_X^*L,p_Y^!M),\\ &\notag L\boxtimes_S D_{Y/S}M\to R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_Y^*M,p_X^!L),\\ &\notag D_{X/S} L\boxtimes_S D_{Y/S} M\to D_{X\times_S Y/S}(L\boxtimes_S M) \end{align} $$
 $p_X\colon X\times _X Y\to X$
and
$p_X\colon X\times _X Y\to X$
and
 $p_Y\colon X\times _S Y\to Y$
are the projections.
$p_Y\colon X\times _S Y\to Y$
are the projections.
-
(b) For every morphism of schemes
 $g\colon Y\to Y'$
separated of finite type over S and all
$g\colon Y\to Y'$
separated of finite type over S and all
 $M\in D(Y,\Lambda )$
,
$M\in D(Y,\Lambda )$
,
 $M'\in D(Y',\Lambda )$
, the canonical morphisms are isomorphisms. Moreover, for morphisms of schemes
$M'\in D(Y',\Lambda )$
, the canonical morphisms are isomorphisms. Moreover, for morphisms of schemes $$ \begin{align*} L\boxtimes_S g_*M&\to (\mathrm{id}_X\times_S g)_* (L\boxtimes_S M),\\ L\boxtimes_S g^! M'&\to (\mathrm{id}_X\times_S g)^! (L\boxtimes_S M') \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} L\boxtimes_S g_*M&\to (\mathrm{id}_X\times_S g)_* (L\boxtimes_S M),\\ L\boxtimes_S g^! M'&\to (\mathrm{id}_X\times_S g)^! (L\boxtimes_S M') \end{align*} $$
 $f\colon X\to X'$
and
$f\colon X\to X'$
and
 $f'\colon X''\to X$
separated of finite type over S such that
$f'\colon X''\to X$
separated of finite type over S such that
 $(X',f_!D_{X/S}L)$
and
$(X',f_!D_{X/S}L)$
and
 $(X'',f^{\prime }*D_{X/S}L)$
are dualisable and
$(X'',f^{\prime }*D_{X/S}L)$
are dualisable and
 $M\in D(Y,\Lambda )$
, the canonical morphisms are isomorphisms.
$M\in D(Y,\Lambda )$
, the canonical morphisms are isomorphisms. $$ \begin{align*} f_*L\boxtimes_S M&\to (f\times_S \mathrm{id}_Y)_* (L\boxtimes_S M),\\ f^{\prime}!L\boxtimes_S M&\to (f'\times_S \mathrm{id}_Y)^! (L\boxtimes_S M) \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} f_*L\boxtimes_S M&\to (f\times_S \mathrm{id}_Y)_* (L\boxtimes_S M),\\ f^{\prime}!L\boxtimes_S M&\to (f'\times_S \mathrm{id}_Y)^! (L\boxtimes_S M) \end{align*} $$
-
(c) If
 $L\in D^+(X,\Lambda )$
, then L is locally acyclic over S.
$L\in D^+(X,\Lambda )$
, then L is locally acyclic over S. -
(d) If
 $R\Delta ^!$
commutes with small direct sums and U has finite
$R\Delta ^!$
commutes with small direct sums and U has finite
 $\Lambda $
-cohomological dimension for every affine scheme U étale over X, then L is c-perfect. Here
$\Lambda $
-cohomological dimension for every affine scheme U étale over X, then L is c-perfect. Here
 $\Delta \colon X\to X\times _S X$
is the diagonal.
$\Delta \colon X\to X\times _S X$
is the diagonal.
Following [Reference Illusie, Laszlo and OrgogozoILO, XVII Définition 7.7.1] we say
![]() $L\in D(X,\Lambda )$
is c-perfect if there exists a finite stratification
$L\in D(X,\Lambda )$
is c-perfect if there exists a finite stratification
![]() $(X_i)$
of X by constructible subschemes such that for each i,
$(X_i)$
of X by constructible subschemes such that for each i,
![]() $L|_{X_i}\in D(X_i,\Lambda )$
is locally constant of perfect values. For
$L|_{X_i}\in D(X_i,\Lambda )$
is locally constant of perfect values. For
![]() $\Lambda $
Noetherian, ‘c-perfect’ is equivalent to ‘
$\Lambda $
Noetherian, ‘c-perfect’ is equivalent to ‘
![]() $\in D_{c\mathrm {ft}}$
’.
$\in D_{c\mathrm {ft}}$
’.
The condition that
![]() $R\Delta ^!$
commutes with small direct sums is satisfied if
$R\Delta ^!$
commutes with small direct sums is satisfied if
(*) S is Noetherian finite-dimensional and
![]() $m\Lambda =0$
with m invertible on S,
$m\Lambda =0$
with m invertible on S,
by Lemma 2.13 and [Reference Illusie, Laszlo and OrgogozoILO, XVIIIA Corollary 1.4]. Moreover, the proof below shows that the assumption
![]() $L\in D^+(X,\Lambda )$
in (c) can be removed under condition (*).
$L\in D^+(X,\Lambda )$
in (c) can be removed under condition (*).
Proof. (a) follows from Remarks 1.2, 1.3 and the identification of internal mapping objects (Lemma 2.8). Via biduality and (2.4), the morphisms in (b) can be identified with the isomorphisms

where
,
![]() $g_X=\mathrm {id}_X\times _S g$
,
$g_X=\mathrm {id}_X\times _S g$
,
![]() $f_Y=f\times _S \mathrm {id}_Y$
,
$f_Y=f\times _S \mathrm {id}_Y$
,
![]() $f^{\prime }_{Y}=f'\times _S \mathrm {id}_Y$
and
$f^{\prime }_{Y}=f'\times _S \mathrm {id}_Y$
and
![]() $p^{\prime }_X\colon X\times _S Y'\to X$
,
$p^{\prime }_X\colon X\times _S Y'\to X$
,
![]() $p^{\prime }_Y\colon X'\times _S Y\to X'$
,
$p^{\prime }_Y\colon X'\times _S Y\to X'$
,
![]() $p^{\prime \prime }_Y\colon X''\times _S Y\to X''$
are the projection. (c) follows from the first isomorphism in (b) and Lemma 2.12. For (d), note that for
$p^{\prime \prime }_Y\colon X''\times _S Y\to X''$
are the projection. (c) follows from the first isomorphism in (b) and Lemma 2.12. For (d), note that for
![]() $M\in D(X,\Lambda )$
,
$M\in D(X,\Lambda )$
,
![]() $\mathrm {Hom}(\Lambda _X,\Delta ^! (D_{X/S} L\boxtimes _S M))\simeq \mathrm {Hom}(L,M)$
by (2.4). Since
$\mathrm {Hom}(\Lambda _X,\Delta ^! (D_{X/S} L\boxtimes _S M))\simeq \mathrm {Hom}(L,M)$
by (2.4). Since
![]() $\Delta ^{!}$
commutes with small direct sums and
$\Delta ^{!}$
commutes with small direct sums and
![]() $\Lambda _X$
is a compact object of
$\Lambda _X$
is a compact object of
![]() $D(X,\Lambda )$
, it follows that L is a compact object, which is equivalent to being c-perfect by [Reference Bhatt and ScholzeBS, Proposition 6.4.8].
$D(X,\Lambda )$
, it follows that L is a compact object, which is equivalent to being c-perfect by [Reference Bhatt and ScholzeBS, Proposition 6.4.8].
The following is a variant of [Reference FuF, Theorem 7.6.9] and [Reference SaitoS, Proposition 8.11].
Lemma 2.12. Let
![]() $X\to S$
be a morphism of coherent schemes and let
$X\to S$
be a morphism of coherent schemes and let
![]() $L\in D(X,\Lambda )$
. Assume that for every quasi-finite morphism
$L\in D(X,\Lambda )$
. Assume that for every quasi-finite morphism
![]() $g\colon Y\to Y'$
of affine schemes with
$g\colon Y\to Y'$
of affine schemes with
![]() $Y'$
étale over S, the canonical morphism
$Y'$
étale over S, the canonical morphism
![]() $L\boxtimes _S g_*\Lambda _Y\to (\mathrm {id}_X\times _S g)_* (L\boxtimes _S \Lambda _Y)$
is an isomorphism. Assume either
$L\boxtimes _S g_*\Lambda _Y\to (\mathrm {id}_X\times _S g)_* (L\boxtimes _S \Lambda _Y)$
is an isomorphism. Assume either
![]() $L\in D^+(X,\Lambda )$
or that
$L\in D^+(X,\Lambda )$
or that
![]() $(\mathrm {id}_X\times _S g)_*$
has bounded
$(\mathrm {id}_X\times _S g)_*$
has bounded
![]() $\Lambda $
-cohomological dimension. Then L is locally acyclic over S.
$\Lambda $
-cohomological dimension. Then L is locally acyclic over S.
Proof. Let
![]() $s\to S$
be a geometric point and let
$s\to S$
be a geometric point and let
![]() $g\colon t\to S_{(s)}$
be an algebraic geometric point. Consider the diagram
$g\colon t\to S_{(s)}$
be an algebraic geometric point. Consider the diagram

obtained by base change. By the assumption and passing to the limit, the morphism
![]() $L|_{X_s}\to i_X^*g_{X*}(L|_{X_t})$
can be identified with
$L|_{X_s}\to i_X^*g_{X*}(L|_{X_t})$
can be identified with
![]() $L\boxtimes _S-$
applied to
$L\boxtimes _S-$
applied to
![]() $\Lambda _s\to i^*g_*\Lambda _t$
, which is an isomorphism.
$\Lambda _s\to i^*g_*\Lambda _t$
, which is an isomorphism.
Lemma 2.13. Let
![]() $i\colon Y\to X$
be a closed immersion of finite presentation. Assume that
$i\colon Y\to X$
be a closed immersion of finite presentation. Assume that
![]() $i^!$
has finite
$i^!$
has finite
![]() $\Lambda $
-cohomological dimension; then
$\Lambda $
-cohomological dimension; then
![]() $Ri^!$
commutes with small direct sums.
$Ri^!$
commutes with small direct sums.
Proof. Let j be the complementary open immersion. It suffices to show that
![]() $Rj_*$
commutes with small direct sums under the condition that
$Rj_*$
commutes with small direct sums under the condition that
![]() $j_*$
has finite
$j_*$
has finite
![]() $\Lambda $
-cohomological dimension. This is standard. See, for example, [Reference Lu and ZhengLZ, Lemma 1.10].
$\Lambda $
-cohomological dimension. This is standard. See, for example, [Reference Lu and ZhengLZ, Lemma 1.10].
Lemma 2.14. An object
![]() $(X,L)$
of
$(X,L)$
of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
is dualisable if and only if the canonical morphism
$\mathcal {C}$
is dualisable if and only if the canonical morphism
 $L\boxtimes _S D_{X/S} L\to R\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(p_2^*L,p_1^!L)$
is an isomorphism. Here
$L\boxtimes _S D_{X/S} L\to R\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(p_2^*L,p_1^!L)$
is an isomorphism. Here
![]() $p_1$
and
$p_1$
and
![]() $p_2$
are the projections
$p_2$
are the projections
![]() $X\times _S X\to X$
.
$X\times _S X\to X$
.
Proof. The ‘only if’ part is a special case of Proposition 2.11 (a). The ‘if’ part follows from Lemma 1.4 and the identification of the internal mapping objects (Lemma 2.8).
Remark 2.15. The evaluation and coevaluation maps for a dualisable object
![]() $(X,L)$
of
$(X,L)$
of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
can be given explicitly as follows. The evaluation map
$\mathcal {C}$
can be given explicitly as follows. The evaluation map
![]() $(X\times _S X, D_{X/S} L\boxtimes _S L)\to (S,\Lambda )$
is given by
$(X\times _S X, D_{X/S} L\boxtimes _S L)\to (S,\Lambda )$
is given by
 $X\times _S X\xleftarrow {\Delta } X\to S$
and the usual evaluation map
$X\times _S X\xleftarrow {\Delta } X\to S$
and the usual evaluation map
where
![]() $\Delta $
denotes the diagonal. The coevaluation map
$\Delta $
denotes the diagonal. The coevaluation map
![]() $(S,\Lambda )\to (X\times _S X, L\boxtimes _S D_{X/S} L)$
is given by
$(S,\Lambda )\to (X\times _S X, L\boxtimes _S D_{X/S} L)$
is given by
 $S\leftarrow X\xrightarrow {\Delta }X\times _S X$
and
$S\leftarrow X\xrightarrow {\Delta }X\times _S X$
and
![]() $\mathrm {id}_L$
considered as a morphism
$\mathrm {id}_L$
considered as a morphism
 $$ \begin{align*}\Lambda_X\to R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(L,L)\simeq \Delta^!R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_2^*L,p_1^!L)\simeq \Delta^!(L\boxtimes_S D_{X/S} L). \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\Lambda_X\to R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(L,L)\simeq \Delta^!R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_2^*L,p_1^!L)\simeq \Delta^!(L\boxtimes_S D_{X/S} L). \end{align*} $$
We can identify dualisable objects of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
under mild assumptions.
$\mathcal {C}$
under mild assumptions.
Theorem 2.16. Let S be a Noetherian scheme and
![]() $\Lambda $
a Noetherian commutative ring with
$\Lambda $
a Noetherian commutative ring with
![]() $m\Lambda =0$
for m invertible on S. Let X be a scheme separated of finite type over S,
$m\Lambda =0$
for m invertible on S. Let X be a scheme separated of finite type over S,
![]() $L\in D_{{c\mathrm {ft}}}(X,\Lambda )$
. Then
$L\in D_{{c\mathrm {ft}}}(X,\Lambda )$
. Then
![]() $(X,L)$
is a dualisable object of
$(X,L)$
is a dualisable object of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
if and only if L is locally acyclic over S. In this case, the dual of
$\mathcal {C}$
if and only if L is locally acyclic over S. In this case, the dual of
![]() $(X,L)$
is
$(X,L)$
is
![]() $(X,D_{X/S}L)$
.
$(X,D_{X/S}L)$
.
We will use Gabber’s theorem that for X of finite type over S,
![]() $L\in D^b_c(X,\Lambda )$
is locally acyclic if and only if it is universally locally acyclic [Reference Lu and ZhengLZ, Corollary 6.6].
$L\in D^b_c(X,\Lambda )$
is locally acyclic if and only if it is universally locally acyclic [Reference Lu and ZhengLZ, Corollary 6.6].
Proof. We have already seen the last assertion and the ‘only if’ part of the first assertion in Parts (a) and (c) of Proposition 2.11. The ‘if’ part of the first assertion follows from Lemma 2.14, Proposition 2.5 and Gabber’s theorem.
Remark 2.17. Without invoking Gabber’s theorem, our proof and Proposition 2.26 show that for
![]() $L\in D_{c\mathrm {ft}}(X,L)$
,
$L\in D_{c\mathrm {ft}}(X,L)$
,
![]() $(X,L)$
is dualisable if and only if L is universally locally acyclic over S.
$(X,L)$
is dualisable if and only if L is universally locally acyclic over S.
Corollary 2.18. For S,
![]() $\Lambda $
and X as in Theorem 2.16 and
$\Lambda $
and X as in Theorem 2.16 and
![]() $L\in D_{{c\mathrm {ft}}}(X,\Lambda )$
locally acyclic over S,
$L\in D_{{c\mathrm {ft}}}(X,\Lambda )$
locally acyclic over S,
![]() $D_{X/S} L$
is locally acyclic over S.
$D_{X/S} L$
is locally acyclic over S.
This was known under the additional assumption that S is regular (and excellent) [Reference Lu and ZhengLZ, Corollary 5.13] (see also [Reference Braverman and GaitsgoryBG, Section B.6 2)] for S smooth over a field). Our proof here is different from the one in [Reference Lu and ZhengLZ]. In fact, without invoking Gabber’s theorem, our proof here shows that
![]() $D_{X/S}$
preserves universal local acyclicity and makes no use of oriented topoi.
$D_{X/S}$
preserves universal local acyclicity and makes no use of oriented topoi.
Proof. By Theorem 2.16 and Remark 1.2,
![]() $(X,D_{X/S}L)$
is dualisable. We conclude by Proposition 2.11 (c).
$(X,D_{X/S}L)$
is dualisable. We conclude by Proposition 2.11 (c).
Corollary 2.19. Let S be an Artinian scheme,
![]() $\Lambda $
and X as in Theorem 2.16, and
$\Lambda $
and X as in Theorem 2.16, and
![]() $L\in D(X,\Lambda )$
. Then
$L\in D(X,\Lambda )$
. Then
![]() $(X,L)$
is a dualisable object of
$(X,L)$
is a dualisable object of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
if and only if
$\mathcal {C}$
if and only if
![]() $L\in D_{{c\mathrm {ft}}}(X,\Lambda )$
.
$L\in D_{{c\mathrm {ft}}}(X,\Lambda )$
.
Proof. For
![]() $L\in D_{{c\mathrm {ft}}}(X,\Lambda )$
, L is locally acyclic over S by [Reference DeligneD, Th. finitude, Corollaire 2.16] and thus
$L\in D_{{c\mathrm {ft}}}(X,\Lambda )$
, L is locally acyclic over S by [Reference DeligneD, Th. finitude, Corollaire 2.16] and thus
![]() $(X,L)$
is dualisable by the theorem. (Alternatively, one can apply Lemma 2.14 and [Reference GrothendieckSGA5, III Formule (3.1.1)].) For the converse, we may assume that S is the spectrum of a separably closed field by Proposition 2.26. In this case, Proposition 2.11 (d) applies.
$(X,L)$
is dualisable by the theorem. (Alternatively, one can apply Lemma 2.14 and [Reference GrothendieckSGA5, III Formule (3.1.1)].) For the converse, we may assume that S is the spectrum of a separably closed field by Proposition 2.26. In this case, Proposition 2.11 (d) applies.
2.4 The relative Lefschetz–Verdier pairing
Let S be a coherent scheme and
![]() $\Lambda $
a torsion commutative ring.
$\Lambda $
a torsion commutative ring.
Notation 2.20. For objects
![]() $(X,L)$
and
$(X,L)$
and
![]() $(Y,M)$
of
$(Y,M)$
of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
with
$\mathcal {C}$
with
![]() $(X,L)$
dualisable and morphisms
$(X,L)$
dualisable and morphisms
![]() $(c,u)\colon (X,L)\to (Y,M)$
and
$(c,u)\colon (X,L)\to (Y,M)$
and
![]() $(d,v)\colon (Y,M)\to (X,L)$
, we write the pairing
$(d,v)\colon (Y,M)\to (X,L)$
, we write the pairing
![]() $\langle (c,u),(d,v)\rangle \in \Omega \mathcal {C}$
in Construction 1.6 as
$\langle (c,u),(d,v)\rangle \in \Omega \mathcal {C}$
in Construction 1.6 as
![]() $(F,\langle u,v\rangle )$
, where
$(F,\langle u,v\rangle )$
, where
![]() $F=C\times _{X\times _S Y} D$
. We call
$F=C\times _{X\times _S Y} D$
. We call
![]() $\langle u,v\rangle \in H^0(F,K_{F/S})$
the relative Lefschetz–Verdier pairing. The pairing is symmetric:
$\langle u,v\rangle \in H^0(F,K_{F/S})$
the relative Lefschetz–Verdier pairing. The pairing is symmetric:
![]() $\langle u,v\rangle $
can be identified with
$\langle u,v\rangle $
can be identified with
![]() $\langle v,u\rangle $
via the canonical isomorphism
$\langle v,u\rangle $
via the canonical isomorphism
![]() $\langle c,d\rangle \simeq \langle d,c\rangle $
.
$\langle c,d\rangle \simeq \langle d,c\rangle $
.
For an endomorphism
![]() $(e,w)$
of a dualisable object
$(e,w)$
of a dualisable object
![]() $(X,L)$
of
$(X,L)$
of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
, we write
$\mathcal {C}$
, we write
![]() $\mathrm {tr}(e,w)=(X^e,\mathrm {tr}(w))$
, where
$\mathrm {tr}(e,w)=(X^e,\mathrm {tr}(w))$
, where
![]() $X^e=E\times _{e,X\times _S X,\Delta } X$
and
$X^e=E\times _{e,X\times _S X,\Delta } X$
and
![]() $\mathrm {tr}(w)=\langle w,\mathrm {id}_L \rangle \in H^0(X^e,K_{X^e/S})$
. We define the characteristic class
$\mathrm {tr}(w)=\langle w,\mathrm {id}_L \rangle \in H^0(X^e,K_{X^e/S})$
. We define the characteristic class
![]() $\mathrm {cc}_{X/S}(L)$
to be
$\mathrm {cc}_{X/S}(L)$
to be
![]() $\mathrm {tr}(\mathrm {id}_L)=\langle \mathrm {id}_L,\mathrm {id}_L\rangle \in H^0(X,K_{X/S})$
. In other words,
$\mathrm {tr}(\mathrm {id}_L)=\langle \mathrm {id}_L,\mathrm {id}_L\rangle \in H^0(X,K_{X/S})$
. In other words,
![]() $\dim (X,L)=(X,\mathrm {cc}_{X/S}(L))$
.
$\dim (X,L)=(X,\mathrm {cc}_{X/S}(L))$
.
Theorem 2.21 Relative Lefschetz–Verdier
Let

be a commutative diagram of schemes separated of finite type over S, with p and
![]() $D\to D'\times _{Y'} Y$
proper. Let
$D\to D'\times _{Y'} Y$
proper. Let
![]() $L\in D(X,\Lambda )$
such that
$L\in D(X,\Lambda )$
such that
![]() $(X,L)$
and
$(X,L)$
and
![]() $(X',f_!L)$
are dualisable objects of
$(X',f_!L)$
are dualisable objects of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
. Let
$\mathcal {C}$
. Let
![]() $M\in D(Y,\Lambda )$
,
$M\in D(Y,\Lambda )$
,
![]() $u\colon \overleftarrow {c}^*L\to \overrightarrow {c}^! M$
,
$u\colon \overleftarrow {c}^*L\to \overrightarrow {c}^! M$
,
![]() $v\colon \overleftarrow {d}^*M\to \overrightarrow {d}^! L$
. Then
$v\colon \overleftarrow {d}^*M\to \overrightarrow {d}^! L$
. Then
![]() $s\colon C\times _{X\times _S Y} D\to C'\times _{X'\times _S Y'} D'$
is proper and
$s\colon C\times _{X\times _S Y} D\to C'\times _{X'\times _S Y'} D'$
is proper and
 $$ \begin{align*}s_*\langle u,v\rangle = \langle p^\sharp_!u,q^\sharp_!v\rangle.\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}s_*\langle u,v\rangle = \langle p^\sharp_!u,q^\sharp_!v\rangle.\end{align*} $$
Combining this with Theorem 2.16, we obtain Theorem 0.1.
Proof. By Construction 2.10 applied to the right half of (2.5) and to the decomposition (which was used in the proof of [Reference ZhengZ, Proposition 8.11])

of the left half of (2.5), we get a diagram in
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
$\mathcal {C}$

where
![]() $e=(f\overleftarrow {c},\overrightarrow {c})$
and
$e=(f\overleftarrow {c},\overrightarrow {c})$
and
![]() $w=(f,\mathrm {id}_C,\mathrm {id}_Y)_!u$
. By Construction 1.8, we then get a morphism
$w=(f,\mathrm {id}_C,\mathrm {id}_Y)_!u$
. By Construction 1.8, we then get a morphism
 $(F,\langle u,v\rangle )\to (F',\langle p^\sharp _!u,q^\sharp _! v\rangle )$
in
$(F,\langle u,v\rangle )\to (F',\langle p^\sharp _!u,q^\sharp _! v\rangle )$
in
![]() $\Omega \mathcal {C}$
given by
$\Omega \mathcal {C}$
given by
![]() $s\colon F\to F'$
.
$s\colon F\to F'$
.
In the case where f is proper, the dualisability of
![]() $(X',f_*L)$
follows from that of
$(X',f_*L)$
follows from that of
![]() $(X,L)$
by Proposition 2.23. Moreover, in this case, by Lemma 2.9,
$(X,L)$
by Proposition 2.23. Moreover, in this case, by Lemma 2.9,
![]() $f_\natural $
is right adjointable and it suffices in the above proof to apply the more direct Construction 1.7 in place of Construction 1.8.
$f_\natural $
is right adjointable and it suffices in the above proof to apply the more direct Construction 1.7 in place of Construction 1.8.
Corollary 2.22. Let
![]() $f\colon X\to X'$
be a proper morphism of schemes separated of finite type over S and let
$f\colon X\to X'$
be a proper morphism of schemes separated of finite type over S and let
![]() $L\in D(X,\Lambda )$
such that
$L\in D(X,\Lambda )$
such that
![]() $(X,L)$
is a dualisable object of
$(X,L)$
is a dualisable object of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
. Then
$\mathcal {C}$
. Then
![]() $f_*\mathrm {cc}_{X/S}(L)=\mathrm {cc}_{X'/S}(f_* L)$
.
$f_*\mathrm {cc}_{X/S}(L)=\mathrm {cc}_{X'/S}(f_* L)$
.
Proof. This follows from Theorem 2.21 applied to
![]() $c=d=(\mathrm {id}_X,\mathrm {id}_X)$
,
$c=d=(\mathrm {id}_X,\mathrm {id}_X)$
,
![]() $c'=d'=(\mathrm {id}_{X'},\mathrm {id}_{X'})$
and
$c'=d'=(\mathrm {id}_{X'},\mathrm {id}_{X'})$
and
![]() $u=v=\mathrm {id}_L$
.
$u=v=\mathrm {id}_L$
.
Proposition 2.23. Let
![]() $f\colon X\to Y$
be a proper morphism of schemes separated of finite type over S. Let
$f\colon X\to Y$
be a proper morphism of schemes separated of finite type over S. Let
![]() $(X,L)$
be a dualisable object of
$(X,L)$
be a dualisable object of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
. Then
$\mathcal {C}$
. Then
![]() $(Y,f_*L)$
is dualisable.
$(Y,f_*L)$
is dualisable.
Proof. This follows formally from Remark 1.12 (b). We can also argue using internal mapping objects as follows. By Proposition 2.11 and Lemma 2.14, the canonical morphism
 $$ \begin{align*}\alpha\colon D_{X/S}L\boxtimes_S M\to R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_X^*L,p_Z^! M)\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\alpha\colon D_{X/S}L\boxtimes_S M\to R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_X^*L,p_Z^! M)\end{align*} $$
is an isomorphism for every object
![]() $(Z,M)$
of
$(Z,M)$
of
![]() $\mathcal {C}$
, and it suffices to show that the canonical morphism
$\mathcal {C}$
, and it suffices to show that the canonical morphism
 $$ \begin{align*}\beta\colon D_{Y/S} f_* L\boxtimes_S M\to R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(q_Y^*f_*L,q_Z^!M)\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\beta\colon D_{Y/S} f_* L\boxtimes_S M\to R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(q_Y^*f_*L,q_Z^!M)\end{align*} $$
is an isomorphism. Here
![]() $p_X,p_Z,q_Y,q_Z$
are the projections as shown in the commutative diagram
$p_X,p_Z,q_Y,q_Z$
are the projections as shown in the commutative diagram

Via the isomorphisms
![]() $D_{Y/S} f_* L\boxtimes _S M\simeq (f\times _S \mathrm {id}_Z)_*(D_{X/S}L\boxtimes _S M)$
and
$D_{Y/S} f_* L\boxtimes _S M\simeq (f\times _S \mathrm {id}_Z)_*(D_{X/S}L\boxtimes _S M)$
and
 $$ \begin{align*} R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(q_Y^*f_*L,q_Z^!M) \simeq R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}((f\times_S \mathrm{id}_Z)_*p_X^*L,q_Z^!M)\simeq (f\times_S \mathrm{id}_Z)_*R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_X^*L,p_Z^!M), \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(q_Y^*f_*L,q_Z^!M) \simeq R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}((f\times_S \mathrm{id}_Z)_*p_X^*L,q_Z^!M)\simeq (f\times_S \mathrm{id}_Z)_*R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_X^*L,p_Z^!M), \end{align*} $$
![]() $\beta $
can be identified with
$\beta $
can be identified with
![]() $(f\times _S \mathrm {id}_Z)_*\alpha $
.
$(f\times _S \mathrm {id}_Z)_*\alpha $
.
Remark 2.24. The relative Lefschetz–Verdier formula and the proof given above hold for Artin stacks of finite type over an Artin stack S, with proper morphisms replaced by a suitable class of morphisms equipped with canonical isomorphisms
![]() $f_!\simeq f_*$
(such as proper representable morphisms). The characteristic class lives in
$f_!\simeq f_*$
(such as proper representable morphisms). The characteristic class lives in
 $H^0(I_{X/S},K_{I_{X/S}/S})$
, where
$H^0(I_{X/S},K_{I_{X/S}/S})$
, where
![]() $I_{X/S}=X\times _{\Delta ,X\times _S X,\Delta } X$
is the inertia stack of X over S.
$I_{X/S}=X\times _{\Delta ,X\times _S X,\Delta } X$
is the inertia stack of X over S.
Theorem 2.21 does not cover the twisted Lefschetz–Verdier formula in [Reference Xiao and ZhuXZ, Section A.2.19].
Remark 2.25. Scholze remarked that arguments of this article also apply in the étale cohomology of diamonds and imply the equivalence between dualisability and universal local acyclicity in this situation. This fact and applications are discussed in his work with Fargues on the geometrisation of the Langlands correspondence [Reference Fargues and ScholzeFS]. In [Reference Hansen, Kaletha and WeinsteinHKW, Section 4], Hansen, Kaletha and Weinstein adapt our formalism and prove a Lefschetz–Verdier formula for diamonds and v-stacks.
2.5 Base change and duals
We conclude this section with a result on the preservation of duals by base change.
Let
![]() $g\colon S\to T$
be a morphism of coherent schemes and let
$g\colon S\to T$
be a morphism of coherent schemes and let
![]() $\Lambda $
be a torsion commutative ring.
$\Lambda $
be a torsion commutative ring.
Proposition 2.26. Let
![]() $(Y,M)$
be a dualisable object of
$(Y,M)$
be a dualisable object of
![]() $\mathcal {C}_{T,\Lambda }$
. Then
$\mathcal {C}_{T,\Lambda }$
. Then
![]() $(Y_S, g_Y^*M)$
is a dualisable object of
$(Y_S, g_Y^*M)$
is a dualisable object of
![]() $\mathcal {C}_{S,\Lambda }$
and the canonical morphism
$\mathcal {C}_{S,\Lambda }$
and the canonical morphism
![]() $g_Y^*D_{Y/T} M\to D_{Y_S/S} g_Y^* M$
is an isomorphism. Here
$g_Y^*D_{Y/T} M\to D_{Y_S/S} g_Y^* M$
is an isomorphism. Here
![]() $Y_S=Y\times _T S$
and
$Y_S=Y\times _T S$
and
![]() $g_Y\colon Y_S\to Y$
is the projection.
$g_Y\colon Y_S\to Y$
is the projection.
We prove the proposition by constructing a symmetric monoidal functor
![]() $g^*\colon \mathcal {C}_{T,\Lambda }\to \mathcal {C}_{S,\Lambda }$
as follows. We take
$g^*\colon \mathcal {C}_{T,\Lambda }\to \mathcal {C}_{S,\Lambda }$
as follows. We take
![]() $g^*(Y,M)=(Y_S,g_Y^*M)$
. For
$g^*(Y,M)=(Y_S,g_Y^*M)$
. For
![]() $(d,v)\colon (Y,M)\to (Z,N)$
, we take
$(d,v)\colon (Y,M)\to (Z,N)$
, we take
![]() $g^*(d,v)=(d_S,v_S)$
, where
$g^*(d,v)=(d_S,v_S)$
, where
![]() $d_S$
is the base change of d by g and
$d_S$
is the base change of d by g and
![]() $v_S$
is the composite
$v_S$
is the composite
 $$ \begin{align*}\overleftarrow{d}^*_S g_Y^*M\simeq g_D^*\overleftarrow{d}^* M\xrightarrow{g_D^* v} g_D^*\overrightarrow{d}^! M\to \overrightarrow{d}_S^!g_Z^* M,\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\overleftarrow{d}^*_S g_Y^*M\simeq g_D^*\overleftarrow{d}^* M\xrightarrow{g_D^* v} g_D^*\overrightarrow{d}^! M\to \overrightarrow{d}_S^!g_Z^* M,\end{align*} $$
where D is the source of
![]() $\overleftarrow {d}$
and
$\overleftarrow {d}$
and
![]() $\overrightarrow {d}$
,
$\overrightarrow {d}$
,
![]() $g_D$
and
$g_D$
and
![]() $g_Z$
are defined similar to
$g_Z$
are defined similar to
![]() $g_Y$
. For every
$g_Y$
. For every
![]() $2$
-morphism p of
$2$
-morphism p of
![]() $\mathcal {C}_{T,\Lambda }$
, we take
$\mathcal {C}_{T,\Lambda }$
, we take
![]() $g^*(p)=p\times _T S$
. The symmetric monoidal structure on
$g^*(p)=p\times _T S$
. The symmetric monoidal structure on
![]() $g^*$
is obvious. Proposition 2.26 then follows from the fact that
$g^*$
is obvious. Proposition 2.26 then follows from the fact that
![]() $g^*\colon \mathcal {C}_{T,\Lambda }\to \mathcal {C}_{S,\Lambda }$
preserves duals (Remark 1.9).
$g^*\colon \mathcal {C}_{T,\Lambda }\to \mathcal {C}_{S,\Lambda }$
preserves duals (Remark 1.9).
The construction above is a special case of Construction 1.16 (applied to
![]() $H\colon \mathcal {B}_T\to \mathcal {B}_S$
given by base change by g and
$H\colon \mathcal {B}_T\to \mathcal {B}_S$
given by base change by g and
![]() $\alpha _Y$
given by
$\alpha _Y$
given by
![]() $g_Y^*$
).
$g_Y^*$
).
Corollary 2.27. Let
![]() $g\colon S\to T$
be a morphism of coherent schemes with T Noetherian and let
$g\colon S\to T$
be a morphism of coherent schemes with T Noetherian and let
![]() $\Lambda $
be a Noetherian commutative ring with
$\Lambda $
be a Noetherian commutative ring with
![]() $m\Lambda =0$
for m invertible on T. Then for any scheme Y separated of finite type over T and any
$m\Lambda =0$
for m invertible on T. Then for any scheme Y separated of finite type over T and any
![]() $M\in D_{{c\mathrm {ft}}}(Y,\Lambda )$
locally acyclic over T, the canonical morphism
$M\in D_{{c\mathrm {ft}}}(Y,\Lambda )$
locally acyclic over T, the canonical morphism
![]() $g_Y^*D_{Y/T} M\to D_{Y_S/S} g_Y^* M$
is an isomorphism. Here
$g_Y^*D_{Y/T} M\to D_{Y_S/S} g_Y^* M$
is an isomorphism. Here
![]() $Y_S=Y\times _T S$
and
$Y_S=Y\times _T S$
and
![]() $g_Y\colon Y_S\to Y$
is the projection.
$g_Y\colon Y_S\to Y$
is the projection.
Note that the statement does not involve cohomological correspondences.
3 Nearby cycles over Henselian valuation rings
Let R be a Henselian valuation ring and let
![]() $S=\mathrm {Spec}(R)$
. We do not assume that the valuation is discrete. In other words, we do not assume S Noetherian. Let
$S=\mathrm {Spec}(R)$
. We do not assume that the valuation is discrete. In other words, we do not assume S Noetherian. Let
![]() $\eta $
be the generic point and let s be the closed point. Let X be a scheme of finite type over S. Let
$\eta $
be the generic point and let s be the closed point. Let X be a scheme of finite type over S. Let
![]() $X_\eta =X\times _S \eta $
,
$X_\eta =X\times _S \eta $
,
![]() $X_s=X\times _S s$
. We consider the morphisms of topoi
$X_s=X\times _S s$
. We consider the morphisms of topoi

where
denotes the oriented product of topoi [Reference Illusie, Laszlo and OrgogozoILO, Exposé XI] and
![]() $\mathbin {\bar {\times }}$
denotes the fibre product of topoi. Let
$\mathbin {\bar {\times }}$
denotes the fibre product of topoi. Let
![]() $\Lambda $
be a commutative ring such that
$\Lambda $
be a commutative ring such that
![]() $m\Lambda =0$
for some m invertible on S. We will study the composite functor
$m\Lambda =0$
for some m invertible on S. We will study the composite functor

Let
![]() $\bar s$
be an algebraic geometric point above s and let
$\bar s$
be an algebraic geometric point above s and let
![]() $\bar \eta \to S_{(\bar s)}$
be an algebraic geometric point above
$\bar \eta \to S_{(\bar s)}$
be an algebraic geometric point above
![]() $\eta $
. The restriction of
$\eta $
. The restriction of
![]() $\Psi _X L$
to
$\Psi _X L$
to
![]() $X_{\bar s}\simeq X_{\bar s}\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_{\bar s} \bar \eta $
can be identified with
$X_{\bar s}\simeq X_{\bar s}\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_{\bar s} \bar \eta $
can be identified with
![]() $(j_* L)|_{X_{\bar s}}$
, where
$(j_* L)|_{X_{\bar s}}$
, where
![]() $j\colon X_{\bar \eta }\to X_{(\bar s)}$
and was studied by Huber [Reference HuberH, Section 4.2]. We do not need Huber’s results in this article.
$j\colon X_{\bar \eta }\to X_{(\bar s)}$
and was studied by Huber [Reference HuberH, Section 4.2]. We do not need Huber’s results in this article.
In Subsection 3.1, we study the symmetric monoidal functor given by
![]() $\Psi $
and cohomological correspondences. We deduce that
$\Psi $
and cohomological correspondences. We deduce that
![]() $\Psi $
commutes with duals (Corollary 3.8), generalising a theorem of Gabber. We also obtain a new proof of the theorems of Deligne and Huber that
$\Psi $
commutes with duals (Corollary 3.8), generalising a theorem of Gabber. We also obtain a new proof of the theorems of Deligne and Huber that
![]() $\Psi $
preserves constructibility (Corollary 3.9). In Subsection 3.2, extending results of Vidal, we use the compatibility of specialisation with proper pushforward to deduce a fixed point result.
$\Psi $
preserves constructibility (Corollary 3.9). In Subsection 3.2, extending results of Vidal, we use the compatibility of specialisation with proper pushforward to deduce a fixed point result.
3.1 Künneth formulas and duals
Proposition 3.1 Künneth formulas
Let X and Y be schemes of finite type over S and let
![]() $L\in D(X_\eta ,\Lambda )$
,
$L\in D(X_\eta ,\Lambda )$
,
![]() $M\in D(Y_\eta ,\Lambda )$
; then the canonical morphisms
$M\in D(Y_\eta ,\Lambda )$
; then the canonical morphisms
 $$ \begin{align*}\overleftarrow{\Psi}_{X} L\boxtimes \overleftarrow{\Psi}_{Y} M\to \overleftarrow{\Psi}_{X\times_S Y}(L\boxtimes M),\quad \Psi_X L\boxtimes \Psi_Y M\to \Psi_{X\times_S Y}(L\boxtimes M), \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\overleftarrow{\Psi}_{X} L\boxtimes \overleftarrow{\Psi}_{Y} M\to \overleftarrow{\Psi}_{X\times_S Y}(L\boxtimes M),\quad \Psi_X L\boxtimes \Psi_Y M\to \Psi_{X\times_S Y}(L\boxtimes M), \end{align*} $$
are isomorphisms.
The Künneth formula for
![]() $\Psi $
over a Henselian discrete valuation ring is a theorem of Gabber ([Reference IllusieI1, Théorème 4.7], [Reference Beĭlinson and BernsteinBB, Lemma 5.1.1]).
$\Psi $
over a Henselian discrete valuation ring is a theorem of Gabber ([Reference IllusieI1, Théorème 4.7], [Reference Beĭlinson and BernsteinBB, Lemma 5.1.1]).
Proof. It suffices to show that the first morphism is an isomorphism. By passing to the limit and the finiteness of cohomological dimensions, it suffices to show that
 satisfies Künneth formula for each open subscheme
satisfies Künneth formula for each open subscheme
![]() $U\subseteq S$
. We then reduce to the case
$U\subseteq S$
. We then reduce to the case
![]() $U=S$
, where the Künneth formula is [Reference IllusieI2, Theorem A.3]. The
$U=S$
, where the Künneth formula is [Reference IllusieI2, Theorem A.3]. The
![]() $\Psi $
-goodness is satisfied by Orgogozo’s theorem ([Reference OrgogozoO, Théorème 2.1], [Reference Lu and ZhengLZ, Example 4.26 (2)]).
$\Psi $
-goodness is satisfied by Orgogozo’s theorem ([Reference OrgogozoO, Théorème 2.1], [Reference Lu and ZhengLZ, Example 4.26 (2)]).
Construction 3.2. Let
![]() $f\colon X\to Y$
be a separated morphism of schemes of finite type over S. Then we have canonical natural transformations
$f\colon X\to Y$
be a separated morphism of schemes of finite type over S. Then we have canonical natural transformations
 $$ \begin{align} \Psi_{Y}f_\eta^!\to f_s^!\Psi_{Y}. \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} \Psi_{Y}f_\eta^!\to f_s^!\Psi_{Y}. \end{align} $$
Here we denoted
![]() $f_s\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta $
by
$f_s\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta $
by
![]() $f_s$
. (3.1) is the base change
$f_s$
. (3.1) is the base change

and (3.4) is defined similar to [Reference Lu and ZhengLZ, Formula (4.9)] as

(3.1) and (3.2) correspond to each other by adjunction. The same holds for (3.3) and (3.4). For f proper, (3.2) and (3.3) are inverse to each other.
Construction 3.3. We construct symmetric monoidal
![]() $2$
-categories
$2$
-categories
![]() $\mathcal {C}_1$
and
$\mathcal {C}_1$
and
![]() $\mathcal {C}_2$
and a symmetric monoidal functor
$\mathcal {C}_2$
and a symmetric monoidal functor
![]() $\psi \colon \mathcal {C}_1\to \mathcal {C}_2$
as follows.
$\psi \colon \mathcal {C}_1\to \mathcal {C}_2$
as follows.
The construction of
![]() $\mathcal {C}_1$
is identical to that of
$\mathcal {C}_1$
is identical to that of
![]() $\mathcal {C}_{S,\Lambda }$
(Construction 2.6) except that we replace the derived category
$\mathcal {C}_{S,\Lambda }$
(Construction 2.6) except that we replace the derived category
![]() $D(-,\Lambda )$
by
$D(-,\Lambda )$
by
![]() $D((-)_\eta ,\Lambda )$
. Thus, an object of
$D((-)_\eta ,\Lambda )$
. Thus, an object of
![]() $\mathcal {C}_1$
is a pair
$\mathcal {C}_1$
is a pair
![]() $(X,L)$
, where X is a scheme separated of finite type over S and
$(X,L)$
, where X is a scheme separated of finite type over S and
![]() $L\in D(X_\eta ,\Lambda )$
. A morphism
$L\in D(X_\eta ,\Lambda )$
. A morphism
![]() $(X,L)\to (Y,M)$
is a pair
$(X,L)\to (Y,M)$
is a pair
![]() $(c,u)$
, where
$(c,u)$
, where
![]() $c\colon X\to Y$
is a correspondence over S and
$c\colon X\to Y$
is a correspondence over S and
![]() $(c_\eta ,u)$
is a cohomological correspondence over
$(c_\eta ,u)$
is a cohomological correspondence over
![]() $\eta $
. A
$\eta $
. A
![]() $2$
-morphism
$2$
-morphism
![]() $(c,u)\to (d,v)$
is a
$(c,u)\to (d,v)$
is a
![]() $2$
-morphism
$2$
-morphism
![]() $p\colon c\to d$
such that
$p\colon c\to d$
such that
![]() $p_\eta $
is a
$p_\eta $
is a
![]() $2$
-morphism
$2$
-morphism
![]() $(c_\eta ,u)\to (d_\eta ,v)$
. We have
$(c_\eta ,u)\to (d_\eta ,v)$
. We have
![]() $(X,L)\boxtimes (Y,M)= (X\times _S Y,L\boxtimes _\eta M)$
. The monoidal unit is
$(X,L)\boxtimes (Y,M)= (X\times _S Y,L\boxtimes _\eta M)$
. The monoidal unit is
![]() $(S,\Lambda _\eta )$
.
$(S,\Lambda _\eta )$
.
The construction of
![]() $\mathcal {C}_2$
is identical to that of
$\mathcal {C}_2$
is identical to that of
![]() $\mathcal {C}_{s,\Lambda }$
except that we replace the derived category
$\mathcal {C}_{s,\Lambda }$
except that we replace the derived category
![]() $D(-,\Lambda )$
by
$D(-,\Lambda )$
by
![]() $D((-)\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta ,\Lambda )$
. Thus, an object of
$D((-)\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta ,\Lambda )$
. Thus, an object of
![]() $\mathcal {C}_2$
is a pair
$\mathcal {C}_2$
is a pair
![]() $(X,L)$
, where X is a scheme separated of finite type over s and
$(X,L)$
, where X is a scheme separated of finite type over s and
![]() $L\in D(X\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta ,\Lambda )$
. The monoidal unit is
$L\in D(X\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta ,\Lambda )$
. The monoidal unit is
![]() $(s,\Lambda _\eta )$
.
$(s,\Lambda _\eta )$
.
We define
![]() $\psi $
by
$\psi $
by
![]() $\psi (X,L)=(X_s,\Psi _{X} L)$
,
$\psi (X,L)=(X_s,\Psi _{X} L)$
,
![]() $\psi (c,u)=(c_s,\psi u)$
, where
$\psi (c,u)=(c_s,\psi u)$
, where
![]() $\psi u$
is specialisation of u defined as the composite
$\psi u$
is specialisation of u defined as the composite
 $$ \begin{align*}\overleftarrow{c}_s^* \Psi_{X} L\xrightarrow{(3.1)} \Psi_{C} \overleftarrow{c}_\eta^*L \xrightarrow{\Psi_{C} (u)} \Psi_{C}\overrightarrow{c}_\eta^! M \xrightarrow{(3.4)} \overrightarrow{c}_s^!\Psi_{Y} M. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\overleftarrow{c}_s^* \Psi_{X} L\xrightarrow{(3.1)} \Psi_{C} \overleftarrow{c}_\eta^*L \xrightarrow{\Psi_{C} (u)} \Psi_{C}\overrightarrow{c}_\eta^! M \xrightarrow{(3.4)} \overrightarrow{c}_s^!\Psi_{Y} M. \end{align*} $$
For every
![]() $2$
-morphism p,
$2$
-morphism p,
![]() $\psi p=p_s$
. The symmetric monoidal structure is given by the Künneth formula (Proposition 3.1) and the canonical isomorphism
$\psi p=p_s$
. The symmetric monoidal structure is given by the Künneth formula (Proposition 3.1) and the canonical isomorphism
![]() $\Psi _{S} \Lambda _S \simeq \Lambda _\eta $
.
$\Psi _{S} \Lambda _S \simeq \Lambda _\eta $
.
Remark 3.4. The symmetric monoidal
![]() $2$
-category
$2$
-category
![]() $\mathcal {C}_1$
(respectively
$\mathcal {C}_1$
(respectively
![]() $\mathcal {C}_2$
) is obtained via the Grothendieck construction (Construction 1.10) from the right-lax symmetric monoidal functor
$\mathcal {C}_2$
) is obtained via the Grothendieck construction (Construction 1.10) from the right-lax symmetric monoidal functor
![]() $\mathcal {B}_S\to \mathcal {C}\mathit {at}^{\mathrm {co}}$
(respectively
$\mathcal {B}_S\to \mathcal {C}\mathit {at}^{\mathrm {co}}$
(respectively
![]() $\mathcal {B}_s\to \mathcal {C}\mathit {at}^{\mathrm {co}}$
) carrying X to
$\mathcal {B}_s\to \mathcal {C}\mathit {at}^{\mathrm {co}}$
) carrying X to
![]() $D(X_\eta ,\Lambda )$
(respectively
$D(X_\eta ,\Lambda )$
(respectively
![]() $D(X\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta ,\Lambda )$
). The symmetric monoidal functor
$D(X\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta ,\Lambda )$
). The symmetric monoidal functor
![]() $\psi $
is a special case of Construction 1.16 (with
$\psi $
is a special case of Construction 1.16 (with
![]() $H\colon \mathcal {B}_S\to \mathcal {B}_s$
given by taking special fibre). More explicitly, if
$H\colon \mathcal {B}_S\to \mathcal {B}_s$
given by taking special fibre). More explicitly, if
![]() $\mathcal {C}^{\prime }_2$
denotes the symmetric monoidal
$\mathcal {C}^{\prime }_2$
denotes the symmetric monoidal
![]() $2$
-category obtained from the right-lax symmetric monoidal functor
$2$
-category obtained from the right-lax symmetric monoidal functor
![]() $\mathcal {B}_S\to \mathcal {C}\mathit {at}^{\mathrm {co}}$
carrying X to
$\mathcal {B}_S\to \mathcal {C}\mathit {at}^{\mathrm {co}}$
carrying X to
![]() $D(X_s\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta ,\Lambda )$
, then
$D(X_s\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta ,\Lambda )$
, then
![]() $\psi $
decomposes into
$\psi $
decomposes into
 $\mathcal {C}_1\xrightarrow {\psi _1} \mathcal {C}^{\prime }_2\xrightarrow {\psi _2}\mathcal {C}_2$
, where
$\mathcal {C}_1\xrightarrow {\psi _1} \mathcal {C}^{\prime }_2\xrightarrow {\psi _2}\mathcal {C}_2$
, where
![]() $\psi _1$
carries
$\psi _1$
carries
![]() $(X,L)$
to
$(X,L)$
to
![]() $(X,\Psi _{X} L)$
and
$(X,\Psi _{X} L)$
and
![]() $\psi _2$
carries
$\psi _2$
carries
![]() $(X,L)$
to
$(X,L)$
to
![]() $(X_s,L)$
.
$(X_s,L)$
.
The proof of the following lemma is identical to that of Lemma 2.8.
Lemma 3.5. The symmetric monoidal structures
![]() $\otimes $
on
$\otimes $
on
![]() $\mathcal {C}_1$
(respectively
$\mathcal {C}_1$
(respectively
![]() $\mathcal {C}_2$
) are closed, with mapping object
$\mathcal {C}_2$
) are closed, with mapping object
 $$ \begin{align*} &\qquad\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}((X,L),(Y,M))=(X\times_S Y,R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_{X_\eta}^*L,p_{Y_\eta}^!M))\\ &(\text{respectively}\ \mathcal{H}\mathit{om}((X,L),(Y,M))=(X\times_s Y,R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_X^*L,p_Y^!M))). \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} &\qquad\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}((X,L),(Y,M))=(X\times_S Y,R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_{X_\eta}^*L,p_{Y_\eta}^!M))\\ &(\text{respectively}\ \mathcal{H}\mathit{om}((X,L),(Y,M))=(X\times_s Y,R\mathcal{H}\mathit{om}(p_X^*L,p_Y^!M))). \end{align*} $$
Remark 3.6. It follows from Remark 1.3 and Lemma 3.5 that the dual of a dualisable object
![]() $(X,L)$
in
$(X,L)$
in
![]() $\mathcal {C}_1$
(respectively
$\mathcal {C}_1$
(respectively
![]() $\mathcal {C}_2$
) is
$\mathcal {C}_2$
) is
![]() $(X,D_{X_\eta } L)$
(respectively
$(X,D_{X_\eta } L)$
(respectively
![]() $(X,D_{X\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta } L)$
). Here, for
$(X,D_{X\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta } L)$
). Here, for
![]() $a\colon U\to \eta $
and
$a\colon U\to \eta $
and
![]() $b\colon V\to s$
separated of finite type, we write
$b\colon V\to s$
separated of finite type, we write
![]() $K_U=K_{U/\eta }$
,
$K_U=K_{U/\eta }$
,
![]() $D_U=D_{U/\eta }$
and
$D_U=D_{U/\eta }$
and
 $K_{V\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta }=(b\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta )^!\Lambda _\eta $
,
$K_{V\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta }=(b\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta )^!\Lambda _\eta $
,
![]() $D_{V\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta }=R\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(-,K_{V\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta })$
.
$D_{V\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta }=R\mathcal {H}\mathit {om}(-,K_{V\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta })$
.
In the rest of Subsection 3.1, we assume that
![]() $\Lambda $
is Noetherian.
$\Lambda $
is Noetherian.
Proposition 3.7. An object
![]() $(X,L)$
in
$(X,L)$
in
![]() $\mathcal {C}_1$
or
$\mathcal {C}_1$
or
![]() $\mathcal {C}_2$
is dualisable if and only if
$\mathcal {C}_2$
is dualisable if and only if
![]() $L\in D_{c\mathrm {ft}}$
.
$L\in D_{c\mathrm {ft}}$
.
Proof. By Lemma 1.4 and the identification of internal mapping objects (Lemmas 2.8 and 3.5),
![]() $(X,L)$
in
$(X,L)$
in
![]() $\mathcal {C}_1$
is dualisable if and only if
$\mathcal {C}_1$
is dualisable if and only if
![]() $(X_\eta ,L)$
in
$(X_\eta ,L)$
in
![]() $\mathcal {C}_\eta $
is dualisable. The latter condition is equivalent to
$\mathcal {C}_\eta $
is dualisable. The latter condition is equivalent to
![]() $L\in D_{c\mathrm {ft}}$
by Corollary 2.19.
$L\in D_{c\mathrm {ft}}$
by Corollary 2.19.
Similarly,
![]() $(X,L)$
in
$(X,L)$
in
![]() $\mathcal {C}_2$
is dualisable if and only if
$\mathcal {C}_2$
is dualisable if and only if
![]() $(X_{\bar s},L|_{X_{\bar s}})$
in
$(X_{\bar s},L|_{X_{\bar s}})$
in
![]() $\mathcal {C}_{\bar s}$
is dualisable, by [Reference Lu and ZhengLZ, Lemma 1.29]. The latter condition is equivalent to
$\mathcal {C}_{\bar s}$
is dualisable, by [Reference Lu and ZhengLZ, Lemma 1.29]. The latter condition is equivalent to
![]() $L|_{X_{\bar s}}\in D_{c\mathrm {ft}}$
, which is in turn equivalent to
$L|_{X_{\bar s}}\in D_{c\mathrm {ft}}$
, which is in turn equivalent to
![]() $L\in D_{c\mathrm {ft}}$
.
$L\in D_{c\mathrm {ft}}$
.
Corollary 3.8. Let X be a scheme separated of finite type over S and let
![]() $L\in D^-_c(X_\eta ,\Lambda )$
. The canonical morphism
$L\in D^-_c(X_\eta ,\Lambda )$
. The canonical morphism
![]() $\Psi _X D_{X_\eta } L \to D_{X_s\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta }\Psi _X L$
is an isomorphism in
$\Psi _X D_{X_\eta } L \to D_{X_s\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta }\Psi _X L$
is an isomorphism in
![]() $D(X_s\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta ,\Lambda )$
.
$D(X_s\mathbin {\bar {\times }}_s \eta ,\Lambda )$
.
This generalises a theorem of Gabber for Henselian discrete valuation rings [Reference IllusieI1, Théorème 4.2]. Our proof here is different from that of Gabber. One can also deduce Corollary 3.8 from the commutation of duality with sliced nearby cycles over general bases [Reference Lu and ZhengLZ, Theorem 0.1].
Proof. The cohomological dimension of
![]() $\Psi _X$
is bounded by
$\Psi _X$
is bounded by
![]() $\dim (X_\eta )$
. Thus, we may assume that L is of the form
$\dim (X_\eta )$
. Thus, we may assume that L is of the form
![]() $u_!\Lambda _U$
, where
$u_!\Lambda _U$
, where
![]() $u\colon U\to X_\eta $
is an étale morphism of finite type. In particular, we may assume
$u\colon U\to X_\eta $
is an étale morphism of finite type. In particular, we may assume
![]() $L\in D_{{c\mathrm {ft}}}(X_\eta ,\Lambda )$
. In this case,
$L\in D_{{c\mathrm {ft}}}(X_\eta ,\Lambda )$
. In this case,
![]() $(X,L)$
is dualisable by Proposition 3.7. We conclude by the fact that
$(X,L)$
is dualisable by Proposition 3.7. We conclude by the fact that
![]() $\psi $
preserve duals (Remark 1.9) and the identification of duals (Remark 3.6).
$\psi $
preserve duals (Remark 1.9) and the identification of duals (Remark 3.6).
We also deduce a new proof of the following finiteness theorem of Deligne (for Henselian discrete valuation rings) [Reference DeligneD, Th. finitude, Théorème 3.2] and Huber [Reference HuberH, Proposition 4.2.5]. Our proof relies on Deligne’s theorem on local acyclicity over a field [Reference DeligneD, Th. finitude, Corollaire 2.16].
Corollary 3.9. Let X be a scheme of finite type over S. Then
![]() $\Psi _X$
preserves
$\Psi _X$
preserves
![]() $D^b_c$
and
$D^b_c$
and
![]() $D_{c\mathrm {ft}}$
.
$D_{c\mathrm {ft}}$
.
Proof. We may assume that X is separated. As in the proof of Corollary 3.8, we are reduced to the case of
![]() $D_{c\mathrm {ft}}$
. This case follows from Proposition 3.7 and the fact that
$D_{c\mathrm {ft}}$
. This case follows from Proposition 3.7 and the fact that
![]() $\psi $
preserves dualisable objects (Remark 1.9).
$\psi $
preserves dualisable objects (Remark 1.9).
By Remark 1.9,
![]() $\psi $
also preserves pairings, and we obtain the following generalisation of [Reference VarshavskyV1, Proposition 1.3.5].
$\psi $
also preserves pairings, and we obtain the following generalisation of [Reference VarshavskyV1, Proposition 1.3.5].
Corollary 3.10. Consider morphisms of schemes separated of finite type over S:

Let
![]() $L\in D_{c\mathrm {ft}}(X_\eta ,\Lambda )$
,
$L\in D_{c\mathrm {ft}}(X_\eta ,\Lambda )$
,
![]() $M\in D(Y_\eta ,\Lambda )$
,
$M\in D(Y_\eta ,\Lambda )$
,
 $u\colon \overleftarrow {c}_\eta ^*L\to \overrightarrow {c}_\eta ^!M$
,
$u\colon \overleftarrow {c}_\eta ^*L\to \overrightarrow {c}_\eta ^!M$
,
 $v\colon \overleftarrow {d}_\eta ^* M\to \overrightarrow {d}_\eta ^! L$
. Then
$v\colon \overleftarrow {d}_\eta ^* M\to \overrightarrow {d}_\eta ^! L$
. Then
![]() $\mathrm {sp}\langle u,v\rangle =\langle \psi u,\psi v\rangle $
, where
$\mathrm {sp}\langle u,v\rangle =\langle \psi u,\psi v\rangle $
, where
![]() $\mathrm {sp}$
is the composition
$\mathrm {sp}$
is the composition
 $$ \begin{align*}H^0(F_\eta,K_{F_\eta})\to H^0(F_s\mathbin{\bar{\times}}_s \eta,\Psi_F K_{F_\eta})\to H^0(F_s\mathbin{\bar{\times}}_s \eta,K_{F_s\mathbin{\bar{\times}}_s \eta}) \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}H^0(F_\eta,K_{F_\eta})\to H^0(F_s\mathbin{\bar{\times}}_s \eta,\Psi_F K_{F_\eta})\to H^0(F_s\mathbin{\bar{\times}}_s \eta,K_{F_s\mathbin{\bar{\times}}_s \eta}) \end{align*} $$
and
![]() $F=C\times _{X\times Y}D$
.
$F=C\times _{X\times Y}D$
.
3.2 Pushforward and fixed points
Construction 3.11
 $!$
-Pushforward in
$!$
-Pushforward in
 $\mathcal {C}_2$
$\mathcal {C}_2$
Consider a commutative diagram (2.3) in
![]() $\mathcal {B}_s$
such that
$\mathcal {B}_s$
such that
![]() $q\colon C\to X\times _{X'} C'$
is proper. Let
$q\colon C\to X\times _{X'} C'$
is proper. Let
![]() $(c,u)\colon (X,L)\to (Y,M)$
be a morphism in
$(c,u)\colon (X,L)\to (Y,M)$
be a morphism in
![]() $\mathcal {C}_2$
above c. By Lemma 1.11, we have a unique morphism
$\mathcal {C}_2$
above c. By Lemma 1.11, we have a unique morphism
 $(c',p^\sharp _{!}u)\colon (X',f_{!}l’)\to (Y',g_{!}M')$
in
$(c',p^\sharp _{!}u)\colon (X',f_{!}l’)\to (Y',g_{!}M')$
in
![]() $\mathcal {C}_2$
above
$\mathcal {C}_2$
above
![]() $c'$
such that q defines a
$c'$
such that q defines a
![]() $2$
-morphism in
$2$
-morphism in
![]() $\mathcal {C}_2$
:
$\mathcal {C}_2$
:

For f, g, p proper, we write
 $p^\sharp _*u$
for
$p^\sharp _*u$
for
 $p^\sharp _!u$
.
$p^\sharp _!u$
.
Applying Lemma 1.14 to the functor
![]() $\psi _1$
in Remark 3.4, we obtain the following.
$\psi _1$
in Remark 3.4, we obtain the following.
Proposition 3.12. Consider a commutative diagram of schemes separated of finite type over S

such that
![]() $C\to X\times _{X'} C'$
is proper. Let
$C\to X\times _{X'} C'$
is proper. Let
![]() $L\in D(X_\eta ,\Lambda )$
,
$L\in D(X_\eta ,\Lambda )$
,
![]() $M\in D(Y_\eta ,\Lambda )$
,
$M\in D(Y_\eta ,\Lambda )$
,
 $u\colon \overleftarrow {c}_\eta ^* L\to \overrightarrow {c}_\eta ^! M$
. Then the square
$u\colon \overleftarrow {c}_\eta ^* L\to \overrightarrow {c}_\eta ^! M$
. Then the square

commutes. Here the vertical arrows are given by (3.3). In particular, in the case where f, g, p are proper,
 $p^\sharp _{s*} \psi u$
can be identified with
$p^\sharp _{s*} \psi u$
can be identified with
 $\psi p^\sharp _{\eta *}u$
via the isomorphisms
$\psi p^\sharp _{\eta *}u$
via the isomorphisms
![]() $f_{s*}\Psi _X\simeq \Psi _{X'} f_{\eta *}$
and
$f_{s*}\Psi _X\simeq \Psi _{X'} f_{\eta *}$
and
![]() $g_{s*}\Psi _{Y}\simeq \Psi _{Y'} g_{\eta *}$
.
$g_{s*}\Psi _{Y}\simeq \Psi _{Y'} g_{\eta *}$
.
This generalises a result of Vidal [Reference VidalV2, Théorème 7.5.1] for certain Henselian valuation rings of rank
![]() $1$
. As in [Reference VidalV2, Sections 7.5, 7.6], Proposition 3.12 implies the following fixed point result, generalising [Reference VidalV2, Proposition 5.1, Corollaire 7.5.3].
$1$
. As in [Reference VidalV2, Sections 7.5, 7.6], Proposition 3.12 implies the following fixed point result, generalising [Reference VidalV2, Proposition 5.1, Corollaire 7.5.3].
Corollary 3.13. Assume that
![]() $\eta $
is separably closed. Consider a commutative diagram of schemes
$\eta $
is separably closed. Consider a commutative diagram of schemes

with f proper and
![]() $\sigma $
fixing s. Assume that
$\sigma $
fixing s. Assume that
![]() $g_s$
does not fix any point of
$g_s$
does not fix any point of
![]() $X_s$
. Then
$X_s$
. Then
![]() $\mathrm {tr}(g,R\Gamma (X_\eta ,\Lambda ))=0$
. If, moreover, g is an isomorphism and
$\mathrm {tr}(g,R\Gamma (X_\eta ,\Lambda ))=0$
. If, moreover, g is an isomorphism and
![]() $U\subseteq X_\eta $
is an open subscheme such that
$U\subseteq X_\eta $
is an open subscheme such that
![]() $g(U)=U$
, then
$g(U)=U$
, then
![]() $\mathrm {tr}(g,R\Gamma _c(U,\Lambda ))=0$
.
$\mathrm {tr}(g,R\Gamma _c(U,\Lambda ))=0$
.
Proof. For completeness, we recall the arguments of [Reference VidalV2, Corollaire 7.5.2]. We may assume
![]() $\Lambda =\mathbb {Z}/m\mathbb {Z}$
. We decompose the commutative diagram into
$\Lambda =\mathbb {Z}/m\mathbb {Z}$
. We decompose the commutative diagram into

Consider the cohomological correspondences
![]() $((\mathrm {id}_{X_s},\mathrm {id}_{X_s}),\sigma )\colon (X_s,\Psi _{X}\Lambda )\to (X_s,\Psi _{\sigma ^* X}\Lambda )$
and
$((\mathrm {id}_{X_s},\mathrm {id}_{X_s}),\sigma )\colon (X_s,\Psi _{X}\Lambda )\to (X_s,\Psi _{\sigma ^* X}\Lambda )$
and
![]() $(c_\eta ,u)\colon (\sigma ^*X_\eta ,\Lambda )\to (X_\eta ,\Lambda )$
, where
$(c_\eta ,u)\colon (\sigma ^*X_\eta ,\Lambda )\to (X_\eta ,\Lambda )$
, where
![]() $c=(\gamma ,\mathrm {id}_{X})$
and
$c=(\gamma ,\mathrm {id}_{X})$
and
![]() $u=\mathrm {id}_{\Lambda _{X_\eta }}$
. We have a commutative diagram
$u=\mathrm {id}_{\Lambda _{X_\eta }}$
. We have a commutative diagram

where the square on the right commutes by Proposition 3.12. The composite of the upper horizontal arrows is the action of g. Thus, by the Lefschetz–Verdier formula over s, we have
 $$ \begin{align*}\mathrm{tr}(g,R\Gamma(X_\eta,\Lambda))=\int_{X_s^{g_s}} \langle \sigma,\psi u\rangle=0,\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\mathrm{tr}(g,R\Gamma(X_\eta,\Lambda))=\int_{X_s^{g_s}} \langle \sigma,\psi u\rangle=0,\end{align*} $$
where
 $\int _{F}\colon H^0(F,K_{F})\to \Lambda $
denotes the trace map. For the last assertion of the corollary, it suffices to note that
$\int _{F}\colon H^0(F,K_{F})\to \Lambda $
denotes the trace map. For the last assertion of the corollary, it suffices to note that
where Z is the closure of
![]() $X_\eta \backslash U$
in X, equipped with the reduced subscheme structure.
$X_\eta \backslash U$
in X, equipped with the reduced subscheme structure.
Acknowledgments
We learned categorical traces from lectures by Xinwen Zhu and David Nadler. We thank Ning Guo, Luc Illusie, Yifeng Liu, François Petit, Takeshi Saito, Peter Scholze, Yakov Varshavsky, Cong Xue, Enlin Yang and Xinwen Zhu for discussions and comments. We are grateful for the support of Princeton University, where part of this work was done during a visit. This work was partially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2020YFA0712600), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 12125107, 11822110, 11688101, 11621061), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 1202014), Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities of China and China Scholarship Council.
Conflicts of interest
None.