Article contents
ON GENERALISED PRONORMAL SUBGROUPS OF FINITE GROUPS
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 22 August 2014
Abstract
For a formation 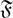 $\mathfrak F$, a subgroup M of a finite group G is said to be
$\mathfrak F$, a subgroup M of a finite group G is said to be 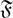 $\mathfrak F$-pronormal in G if for each g ∈ G, there exists x ∈ 〈U,Ug〉
$\mathfrak F$-pronormal in G if for each g ∈ G, there exists x ∈ 〈U,Ug〉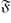 $\mathfrak F$ such that Ux = Ug. Let f be a subgroup embedding functor such that f(G) contains the set of normal subgroups of G and is contained in the set of Sylow-permutable subgroups of G for every finite group G. Given such an f, let fT denote the class of finite groups in which f(G) is the set of subnormal subgroups of G; this is the class of all finite groups G in which to be in f(G) is a transitive relation in G. A subgroup M of a finite group G is said to be
$\mathfrak F$ such that Ux = Ug. Let f be a subgroup embedding functor such that f(G) contains the set of normal subgroups of G and is contained in the set of Sylow-permutable subgroups of G for every finite group G. Given such an f, let fT denote the class of finite groups in which f(G) is the set of subnormal subgroups of G; this is the class of all finite groups G in which to be in f(G) is a transitive relation in G. A subgroup M of a finite group G is said to be 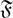 $\mathfrak F$-normal in G if G/CoreG(M) belongs to
$\mathfrak F$-normal in G if G/CoreG(M) belongs to 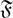 $\mathfrak F$. A subgroup U of a finite group G is called K-
$\mathfrak F$. A subgroup U of a finite group G is called K-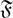 $\mathfrak F$-subnormal in G if either U = G or there exist subgroups U = U0 ≤ U1 ≤ . . . ≤ Un = G such that Ui–1 is either normal or
$\mathfrak F$-subnormal in G if either U = G or there exist subgroups U = U0 ≤ U1 ≤ . . . ≤ Un = G such that Ui–1 is either normal or 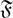 $\mathfrak F$-normal in Ui, for i = 1,2, …, n. We call a finite group G an
$\mathfrak F$-normal in Ui, for i = 1,2, …, n. We call a finite group G an 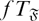 $fT_{\mathfrak F}$-group if every K-
$fT_{\mathfrak F}$-group if every K-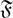 $\mathfrak F$-subnormal subgroup of G is in f(G). In this paper, we analyse for certain formations
$\mathfrak F$-subnormal subgroup of G is in f(G). In this paper, we analyse for certain formations 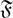 $\mathfrak F$ the structure of
$\mathfrak F$ the structure of 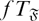 $fT_{\mathfrak F}$-groups. We pay special attention to the
$fT_{\mathfrak F}$-groups. We pay special attention to the 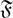 $\mathfrak F$-pronormal subgroups in this analysis.
$\mathfrak F$-pronormal subgroups in this analysis.
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Glasgow Mathematical Journal Trust 2014
References
REFERENCES
- 1
- Cited by

