Article contents
ROUNDNESS PROPERTIES OF ULTRAMETRIC SPACES
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 August 2013
Abstract
Motivated by a classical theorem of Schoenberg, we prove that an n + 1 point finite metric space has strict 2-negative type if and only if it can be isometrically embedded in the Euclidean space 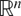 $\mathbb{R}^{n}$ of dimension n but it cannot be isometrically embedded in any Euclidean space
$\mathbb{R}^{n}$ of dimension n but it cannot be isometrically embedded in any Euclidean space 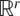 $\mathbb{R}^{r}$ of dimension r < n. We use this result as a technical tool to study ‘roundness’ properties of additive metrics with a particular focus on ultrametrics and leaf metrics. The following conditions are shown to be equivalent for a metric space (X,d): (1) X is ultrametric, (2) X has infinite roundness, (3) X has infinite generalized roundness, (4) X has strict p-negative type for all p ≥ 0 and (5) X admits no p-polygonal equality for any p ≥ 0. As all ultrametric spaces have strict 2-negative type by (4) we thus obtain a short new proof of Lemin's theorem: Every finite ultrametric space is isometrically embeddable into some Euclidean space as an affinely independent set. Motivated by a question of Lemin, Shkarin introduced the class
$\mathbb{R}^{r}$ of dimension r < n. We use this result as a technical tool to study ‘roundness’ properties of additive metrics with a particular focus on ultrametrics and leaf metrics. The following conditions are shown to be equivalent for a metric space (X,d): (1) X is ultrametric, (2) X has infinite roundness, (3) X has infinite generalized roundness, (4) X has strict p-negative type for all p ≥ 0 and (5) X admits no p-polygonal equality for any p ≥ 0. As all ultrametric spaces have strict 2-negative type by (4) we thus obtain a short new proof of Lemin's theorem: Every finite ultrametric space is isometrically embeddable into some Euclidean space as an affinely independent set. Motivated by a question of Lemin, Shkarin introduced the class 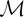 $\mathcal{M}$ of all finite metric spaces that may be isometrically embedded into ℓ2 as an affinely independent set. The results of this paper show that Shkarin's class
$\mathcal{M}$ of all finite metric spaces that may be isometrically embedded into ℓ2 as an affinely independent set. The results of this paper show that Shkarin's class 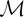 $\mathcal{M}$ consists of all finite metric spaces of strict 2-negative type. We also note that it is possible to construct an additive metric space whose generalized roundness is exactly ℘ for each ℘ ∈ [1, ∞].
$\mathcal{M}$ consists of all finite metric spaces of strict 2-negative type. We also note that it is possible to construct an additive metric space whose generalized roundness is exactly ℘ for each ℘ ∈ [1, ∞].
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Glasgow Mathematical Journal Trust 2013
References
REFERENCES
- 13
- Cited by

