No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Union results for thin sets
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 18 May 2009
Extract
Core share and HTML view are not available for this content. However, as you have access to this content, a full PDF is available via the ‘Save PDF’ action button.
Let G be a compact abelian group and let Γ be its (discrete) dual group. Denote by M(G) the space of complex regular Borel measures on G.
Let E be a subset of Γ. Then:
(i) E is called a Rajchman set if, for all μ ∈M(G) 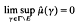 implies
implies 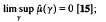
(ii) E is called a set of continuity if given ε > 0 there exists δ > 0 such that if 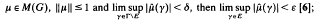 and
and
(iii) E is called a parallelepiped of dimension N if |E| = 2N and there are two-element sets 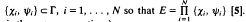 . (The multiplication indicated here is the group operation.)
. (The multiplication indicated here is the group operation.)
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Glasgow Mathematical Journal Trust 1990
References
REFERENCES
1.Blei, R., Fractional Cartesian products of sets, Ann. last. Fourier (Grenoble) 29 (1979), 79–105.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
2.De Leeuw, K. and Katznelson, Y., The two sides of a Fourier-Stieltjes transform and almost idempotent measures, Israel J. Math. 8 (1970), 213–229.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
3.Edwards, R. E. and Ross, K. A., p-Sidon sets, J. Fund. Anal. 15 (1974), 404–427.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
4.Erdös, P. and Rényi, A., Additive properties of random sequences of positive integers, Ada Arith. 6 (1960), 83–110.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
5.Fournier, J. and Pigno, L., Analytic and arithmetic properties of thin sets, Pacific J. Math. 105 (1983), 115–141.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
6.Gardner, P. and Pigno, L., The two sides of a Fourier-Stieltjes transform, Arch. Math. (Basel) 32 (1979), 75–78.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
7.Hajela, D., Construction techniques for some thin sets in duals of compact abelian groups, Ann. Inst. Fourier (Grenoble) 36 (1986), 137–166.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
9.Hare, K. E., Arithmetic properties of thin sets, Pacific J. Math. 131 (1988), 143–155.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
10.Host, B. and Parreau, F., Ensembles de Rajchman et ensembles de continuity, C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris Sir. I Math. 288 (1979), 899–902.Google Scholar
11.Host, B. and Parreau, F., Sur les mesures dont la transformed de Fourier Stieltjes ne tend pas vers zero a l'infini, Colloq. Math. 41 (1979), 285–289.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
12.Johnson, G. W. and Woodward, G. S., Onp-Sidon sets, Indiana Univ. Math. J. 24 (1974), 161–167.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
13.Lopez, J. and Ross, K., Sidon sets, Lecture notes in Pure and Applied Mathematics 13 (Marcel Dekker, 1975).Google Scholar
15.Pigno, L., Fourier transforms which vanish at infinity off certain sets, Glasgow Math. J. 19 (1978), 49–56.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
16.Rajchman, A., Une classe de series trigonom6triques qui convergent presque partout vers zéro, Math. Ann. 101 (1929), 686–700.CrossRefGoogle Scholar

