No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 August 2015
The evolution of single stars on and away from the main sequence is well understood. A degenerate core is formed in a star as the star leaves the main sequence and expands to a giant with a radius typically 50 - 500 Ro . Observationally it is known that most stars are members of binary systems, and among these many have orbital periods less than 100 y. It can happen, therefore, that the expanding envelope of the primary of a binary system can reach to the secondary. As this happens, the primary fills its Roche tidal lobe and transfers matter to the secondary; if the primary has a radiative envelope the rate at which this occurs exceeds the Eddington limit of the secondary, which therefore repels the incoming gas, forming a common envelope around the two stars. Friction within the envelope causes the stars to spiral towards each other until the energy and angular momentum extracted from the binary orbit and transferred to the envelope are sufficient to eject the common envelope as a planetary nebula, leaving a short period binary  comprising a white dwarf and a main sequence star.
comprising a white dwarf and a main sequence star.
This mechanism of producing short period binaries containing white dwarfs, proposed by Ostriker and by Paczynski (1976), is the probable origin of the class of objects known as Cataclysmic Variable Stars (CVs), which encompass the classical novae, dwarf novae, novalike variables and a variety of related objects. Evidence has been accumulating for forty years (Crawford & Kraft 1956, Warner 1995a) that every CV consists of a secondary star (usually a dwarf, but a few systems contain giants) filling its Roche lobe and transferring mass to a white dwarf primary. In systems of normal chemical composition the orbital periods lie between 75 mins and ~250 d, with the majority having  . A few hydrogen-free systems are known for which 17 mins < Porb < 50 mins. It should be noted that CVs are very compact binary systems: for
. A few hydrogen-free systems are known for which 17 mins < Porb < 50 mins. It should be noted that CVs are very compact binary systems: for 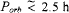 h such a binary would fit inside the Sun.
h such a binary would fit inside the Sun.