Introduction
Dementia/major NCD is the second leading cause of death in older individuals. In the USA, approximately 47 million people have dementia/major NCD. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5 (DSM-5) identifies dementia/major NCD as a condition associated with a significant decline from a previous level of performance in one or more cognitive domains, including complex attention, executive function, learning, and memory, language, perceptual-motor, or social recognition (American Psychiatric Association, 2013. Mood disturbances, psychotic features, and agitation are the distinct behavioral features evidenced in NCDs (American Psychiatric Association, 2013).
Agitation and aggression are the most common disruptive neuropsychiatric symptoms seen in patients with dementia/major NCD (Cerejeira et al., Reference Cerejeira2012). It is reported that approximately 45–80% of patients who have dementia/major NCD exhibit these symptoms (Testad et al., Reference Testad2007). These contribute to increased cost of care, hospitalization, caregiver burden, and risk of premature institutionalization (Acharya et al., Reference Acharya2015). Agitation is characterized by disruptive motor or vocal activity. It could be moderate to severe in intensity and is most common, particularly in NCD. It often occurs in the setting of confusion and frustration and in the context of resisting the caregiver’s duties, such as bathing and dressing. There are currently no treatment options approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for aggression and agitation in patients with dementia/major NCD. Implementing environmental and behavioral interventions in nursing homes is challenging because of low staff-to-resident ratios (Acharya et al., Reference Acharya2015). Physicians utilize atypical antipsychotics to manage behavioral disturbances in patients with dementia/major NCD (Sutor and Rasmussen, Reference Sutor and Rasmussen2008). There are some concerns regarding the efficacy and safety of these medications, including tardive dyskinesia, cerebrovascular adverse events, sedation, and increased risk of mortality (Sutor and Rasmussen, Reference Sutor and Rasmussen2008). According to the FDA, an increased mortality risk is associated with antipsychotic use in a patient with dementia/major NCD complicated by agitation and psychosis (Lenzer Reference Lenzer2005). Given the concern about this risk, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) could be considered an alternative treatment with likely less risk.
ECT is effective and relatively safe in treating depression and mania in older adults, with or without dementia/major NCD (Sutor and Rasmussen, Reference Sutor and Rasmussen2008). A primary concern for using ECT in such patients is its adverse effect on cognitive functioning. There are few published reports, including case studies and retrospective chart reviews, that support the utility of ECT in individuals with dementia/major NCD as a safe and beneficial intervention (Roccaforte et al., Reference Roccaforte2000; Grant and Mohan, Reference Grant and Mohan2001a; Sutor and Rasmussen, Reference Sutor and Rasmussen2008; Ujkaj et al., Reference Ujkaj2012). However, little is known about the effects of these interventions on dementia/major NCD. Therefore, this study aims to review the impact of ECT on dementia/major NCD systematically.
Search strategy
This systematic review was conducted following the guidelines of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement (Figure 1) (Page et al., Reference Page2021). This review aims to evaluate the data on the efficacy and tolerability of ECT in individuals with dementia/major NCD. We performed a literature search of PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, and registry (ClinicalTrials.gov) collaboration databases through 30 March 2022, using the following keywords: ECT and dementia/major NCD. No language restrictions were imposed at the search and filtering stage. However, we only included studies published in English language journals or had official English translations in the final analysis. The search was not restricted by the age of the subjects. All studies, including clinical trials, case reports, case–control studies, case series, and retrospective chart reviews, were included if the participants were diagnosed with dementia/major NCD and were treated with ECT.
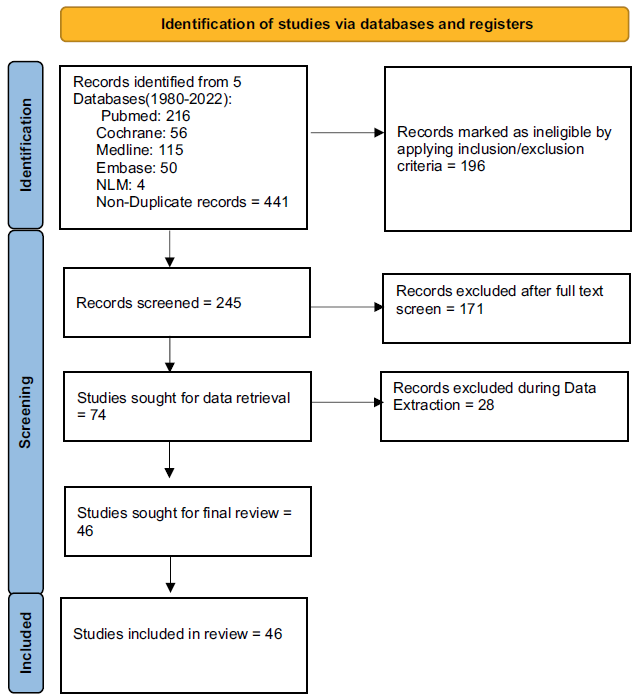
Figure 1. PRISMA 2020 flow diagram for new systematic review.
Four authors reviewed all the abstracts and full-text papers from the citations obtained via the search of the databases. The decision on which studies to be included or excluded from the final analysis was made after reviewing the full-text papers by all the authors. Disagreements between the authors were resolved by a consensus.
Results
This systematic review of the literature identified 445 published papers and 4 clinical trials using our search strategy for the evidence for using ECT among individuals with dementia/major NCD. After removing duplicates, abstracts of 242 papers and 3 clinical trials were reviewed by all the authors. Among them, 171 full-text papers were assessed for eligibility. Forty-three published papers and three clinical trials were eligible for a full-text review. We excluded 10 non-English papers without translations, letters to the editor, review papers, medical hypotheses, and 2 with pseudo-dementia/major NCD as a primary diagnosis. Of the 43 papers and 3 trials that were included in our systematic review, 22 were case reports, 14 were case series, 1 were retrospective case–control studies, 4 were retrospective chart reviews, 3 were randomized control trials (RCTs), 1 observational trial, and 1 single-group interventional trial was identified for the use of ECT among individuals with dementia/major NCD (Tables 1, 2, and 3).
Table 1. Study type and distribution of 46 studies included in the systematic review

Table 2. Number of studies by isolated presenting symptoms

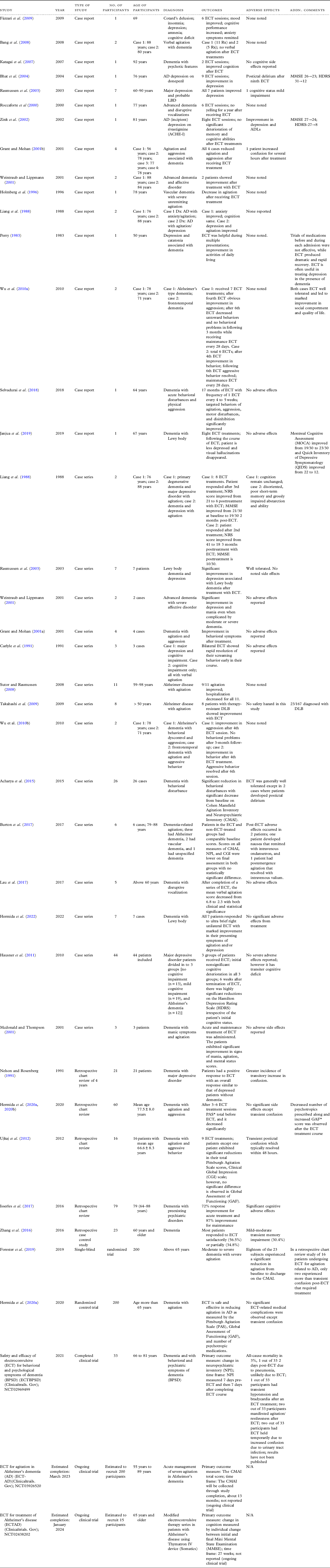
Table 3. The type of study, age of participants, diagnosis, outcomes, and adverse events for all 46 studies
Case reports
The case reports included male and female patients ranging from a 48-year-old male with frontotemporal dementia/major NCD and major depressive disorder to a 92-year-old female with dementia/major NCD and psychosis (Katagai et al., Reference Katagai2007). Five patients received ECT for symptoms of depression (Amison and Foster, Reference Amison and Foster2005; Bhat et al., Reference Bhat2004; Arrsland and Odberg, Reference Arrsland and Odberg1996; Fàzzari et al., Reference Fàzzari2009; Zink et al., Reference Zink2002) and showed significant improvement in scores on several rating scales, including HAM-D (Amison and Foster, Reference Amison and Foster2005), Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS) (Bhat et al., Reference Bhat2004; Zink et al., Reference Zink2002), Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) (Amison and Foster, Reference Amison and Foster2005; Bhat et al., Reference Bhat2004; Zink et al., Reference Zink2002), and the Cornell scale for depression in dementia/major NCD (Arrsland and Odberg, Reference Arrsland and Odberg1996) after ECT.
Roccaforte et al. (Reference Roccaforte2000) reported the use of ECT for “screaming” in a 77-year-old female with advanced dementia/major NCD, which improved subsequently following treatment. ECT was used to treat two patients with dementia/major NCD with comorbid psychotic depression (Borisovskaya et al., Reference Borisovskaya2014) with remission of symptoms and no worsening of cognition. In a case reported by Rodríguez-Sosa et al. (Reference Rodríguez-Sosa2013), ECT was used to treat a 65-year-old female patient presenting first with refractory psychotic depression and later with catatonic symptoms who was diagnosed with frontotemporal dementia/major NCD. In this patient, the symptoms improved transiently. In a case reported by Katagai et al. (Reference Katagai2007), ECT was used to treat a 92-year-old demented female with delusions, and the psychotic symptoms resolved following ECT treatment. No cardiac adverse effects or cognitive decline was reported in the case by Katagai et al. (Reference Katagai2007). Authors (Aksay et al., Reference Aksay2014; Holmberg et al., Reference Holmberg1996) described two separate case reports illustrating the use of ECT for agitation and physical aggression in patients with vascular dementia/major NCD and early-onset Alzheimer’s dementia/major NCD with remission of symptoms and improved scores on the Pittsburg Agitation Scale (PAS).
Selvadurai et al. (Reference Selvadurai2018) reported the use of ECT in a 64-year-old male diagnosed with a major neurocognitive disorder with acute behavioral disturbances and physical aggression. M-ECT was administered and was continued for 17 months at a frequency of 1 ECT every 4 to 5 weeks. The patient showed significant improvement in agitation, aggression, motor disturbances, and disinhibition with no reported adverse effects. Janjua et al. (Reference Janjua2019) described another case report which elicited using ECT to treat dementia/major NCD with Lewy body (DLB) in a 67-year-old male with depression, Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep behavior disorder, bradykinesia, cognitive impairment, and visual hallucination. After receiving eight right unilateral ultra-brief pulse treatments of ECT over 3 weeks, the patient showed marked improvement in his MOCA and QIDS after the eighth ECT treatment. The patient did not experience any significant side effects.
ECT was generally well tolerated in all these cases except for the development of ST-segment depression in the electrocardiogram of one patient (Borisovskaya et al., Reference Borisovskaya2014), and high fever with liver dysfunction in another patient (Suzuki et al., Reference Suzuki2009) after the sixth ECT session, which resolved within a week and the ECT series was continued.
Case series
Out of the 14 case series, ECT was used to treat depression in six studies (Rasmussen et al., Reference Rasmussen2003; Takahashi et al., Reference Takahashi2009; Weintraub and Lippmann, Reference Weintraub and Lippmann2001; Hausner et al., Reference Hausner2011; Hermida et al., Reference Hermida2022; Liang et al., Reference Liang1988). Seven studies targeted agitation and yelling (Bang et al., Reference Bang2008; Grant and Mohan, Reference Grant and Mohan2001b; Acharya et al., Reference Acharya2015; Burton et al., Reference Burton2017; Carlyle et al., Reference Carlyle1991; Lau et al., Reference Lau2017; Wu et al., Reference Wu2010a), and ECT was used to treat mania in one case series (Mcdonald and Thompson, Reference Mcdonald and Thompson2001). The mean age group for the individuals was 50–95 years, with most patients being females. Most of the patients were diagnosed with Alzheimer’s dementia/major NCD, and two case series of patients were diagnosed with Lewy body dementia/major NCD.
Rasmussen et al. (Reference Rasmussen2003) described a case series of seven individuals with probable Lewy body dementia/major NCD, all showing improved depression following ECT treatments. Takahashi et al. (Reference Takahashi2009) described similar results in their case series of eight patients with dementia/major NCD with Lewy bodies and treatment-resistant depression. Pathological yelling diminished significantly in two patients with dementia/major NCD using ECT described in a case series by Bang et al. (Reference Bang2008). Similarly, three demented patients showed rapid resolution of their screaming behavior with ECT (Carlyle et al., Reference Carlyle1991). In an open-label, noncontrolled trial, Hausner et al. (Reference Hausner2011) compared cognitive changes between three groups of patients with no cognitive impairment (n = 13), mild cognitive impairment (n = 19), and Alzheimer’s dementia/major NCD (n = 12) who received ECT for depression after they had failed at least two sufficient trials with antidepressants. It was determined that 6 weeks after the termination of ECT, there were highly significant reductions on the HDRS, irrespective of the patient’s initial cognitive status.
A prospective study conducted by Acharya et al. (Reference Acharya2015) to investigate the safety and efficacy of ECT as a treatment for agitation and aggression in patients with dementia/major NCD included 23 patients. The results reported a significant reduction in behavioral disturbances with a substantial decrease from baseline on Cohen Mansfield Agitation Inventory and Neuropsychiatric Inventory (CMAI). ECT was generally well tolerated except in two cases where patients developed postictal delirium (Acharya et al., Reference Acharya2015). Only one case series by Mcdonald and Thompson (Reference Mcdonald and Thompson2001) was done on three elderly patients with dementia/major NCD associated with agitation and mania. Patients showed significant improvement in signs of mania and agitation.
Burton et al. (Reference Burton2017) described case series of nine patients with dementia/major NCD-related agitation, out of which six received ECT, and three did not receive ECT. Patients in both groups had comparable CMAI, Neuropsychiatric inventory (NPI), and Clinical Global Impression (CGI) scores. The scores were lower on the final assessment in both groups, with no statistically significant difference.
Lau et al. (Reference Lau2017) conducted a case series of five patients with dementia/major NCD with disruptive vocalization who completed a series of ECT. The mean verbal agitation score showed statistically significant improvement. Hermida et al. (Reference Hermida2022) conducted a case series on seven patients with DLB who received ultra-brief right unilateral ECT to treat agitation and depressive symptoms. All seven patients elicited marked improvement in their presenting symptoms of agitation and depression without significant adverse effects from treatment.
Retrospective chart reviews
After reviewing the literature, four retrospective chart reviews were included in this systematic review. A retrospective chart review by Nelson and Rosenberg (Reference Nelson and Rosenberg1991) reported treatment with ECT for 21 patients with dementia/major NCD and depression. Out of these 21 patients, 12 had refractory depression, 4 had medical contraindications to the use of antidepressants, 2 had life-threatening depression and refused to eat, and 4 had a history of good response to ECT. All patients had a positive response to ECT, with an overall response similar to depressed patients without dementia/major NCD but with a greater incidence of transitory increase in confusion.
Another retrospective chart review conducted by Ujkaj et al. (Reference Ujkaj2012) included 16 patients diagnosed with dementia/major NCD based on DSM IV-TR who received ECT for agitation and aggressive behaviors. Patients, on average, received nine ECT treatments ranging from 2 to 15. All patients except one showed significant reductions in their total PAS scores from pre- to post-ECT measurements. The CGI scale improved after ECT treatment. The change in the Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF) was clinically and statistically insignificant. The most common side effect was transient postictal confusion which typically resolved within 48 hours.
All cognitive side effects were reversible and transient, even in dementia/major NCD subjects. Out of 11 patients with Alzheimer’s dementia/major NCD treated with ECT for agitation, nine showed improved symptoms and were associated with fewer hospitalizations in the year after an ECT series (Sutor and Rasmussen, Reference Sutor and Rasmussen2008).
Hermida et al. (Reference Hermida2020a) conducted a retrospective chart review of 60 elderly patients with dementia/major NCD presenting with symptoms of aggression or agitation and who received ECT treatments. The baseline PAS total decreased significantly after 3–6 ECT treatments. No significant ECT-related medical complications were observed except transient confusion.
Isserles et al. (Reference Isserles2017) conducted a retrospective chart review on 25 patients with dementia/major NCD and a preexisting psychiatric disorder treated with ECT. Twenty-nine acute ECT courses and 15 maintenance courses were reviewed. ECT showed clinically significant improvement in acute and maintenance treatment courses. Cognitive adverse effects affecting functioning were reported in 7% of the acute treatment courses, and two reports showed significant cognitive adverse effects in the maintenance treatment courses.
Retrospective case–control studies
After reviewing the literature, the systematic review included one retrospective case–control study by Zhang et al. (Reference Zhang2016). This case–control study comprised 23 patients with dementia/major NCD treated with ECT, and 71 matched controls were treated for 8 years (2007–2014). Most patients responded to ECT satisfactorily (65%) or partially (34–8%), with only mild–moderate transient memory impairment as a side effect.
Clinical trials
This systematic review included three RCTs and two ongoing trials.
Published trials
Forester et al. (Reference Forester2019) conducted a multi-site, single-blinded, randomized trial in 200 in-patients with severe agitation and moderate-to-severe treatment-resistant dementia/major NCD. The preliminary open-label data suggested that acute ECT treatment was safe and effective in reducing agitation in this population. Hermida et al. (Reference Hermida2020a) conducted a RCT on 200 randomized patients with Alzheimer’s dementia/major NCD and severe agitation. The authors reported that ECT is safe and effective in reducing agitation in AD as measured by the PAS and GAF. There were no significant ECT-related medical complications observed except for transient confusion.
Completed clinical trial
The clinical trial (Clinicaltrails. Gov, National Library of Medicine (U.S.), 2016-2020) studied the safety and efficacy of ECT for behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia/major NCD. NPI measured 7 days pre-ECT and 7 days after completing the ECT course as the primary outcome. The results have yet to be published.
Ongoing clinical trials
Two ongoing clinical trials were included in this systematic review. One trial (Clinicaltrails. Gov, National Library of Medicine (U.S.), 2021-2024) studies ECT for agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia/major NCD (AD) (ECT-AD) with an estimated completion date of March 2023. The Primary Outcome Measure is CMAI. The total score will be collected after study completion in about 13 months. Another ongoing clinical trial (Clinicaltrials. Gov, National Library of Medicine (U.S.), 2024-2027) studies the utility of ECT to treat Alzheimer’s disease (ECTAD) with an estimated completion date of January 2024. The primary outcome measure is change in cognition measured by the individual change between the initial and final MMSE within a time frame of 27 weeks. The results of these two ongoing trials are not yet reported.
Discussion
Agitation and aggression in demented patients may be due to numerous conditions (psychosis, disorientation, confusion, sensory loss, etc.). Behavioral disturbances may also be secondary to mood disorders, and the diagnosis of depression may be quite difficult in such patients (Grant and Mohan, Reference Grant and Mohan2001b). The etiology of behavioral disturbances in neurocognitive disorder is poorly understood. These may be due to abnormalities of neurotransmission, especially GABAergic and dopaminergic dysfunction, cholinergic and serotonergic deficiency, and noradrenergic hyperactivity, which further promotes agitation and aggression (Aksay et al., Reference Aksay2014). It has been postulated that ECT may mediate its beneficial effects through its known enhancement of GABAergic transmission and inhibition.
Our systematic review indicates that, to date, there are three RCTs, one observational, and one single-group trial for using ECT in individuals with dementia/major NCD. Current evidence from 41 nonrandomized studies reported symptomatic benefits from ECT in individuals with dementia/major NCD, including depression, mania, yelling and screaming agitation, and a combination of these symptoms. Multiple case reports, case series, and retrospective studies suggest that of all the modalities, including behavioral strategies and antipsychotics, ECT remains the most effective, rapidly acting, and safe method for treating mood symptoms in patients with dementia/major NCD.
Notably, there were significant reductions in behavioral disturbances with ECT. One study showed significant reductions in behavioral disturbances by the third, and most participants dramatically improved by the ninth ECT session (Acharya et al., Reference Acharya2015). Although transient post-ECT confusion may be more significant in depressed patients with dementia/major NCD, the treatment course is reported to be well tolerated overall. Performing neurocognitive testing pre- and post-ECT sessions in patients with dementia/major NCD would help evaluate them effectively (Berman et al., Reference Berman2008).
The strengths of this systematic review include using guidelines from PRISMA and a literature search from five major databases, including case reports, case series, retrospective case–control studies, retrospective chart reviews, and clinical trials only. Limitations of this review are that there is no measure of heterogeneity, and several studies were underpowered and had short treatment duration. Studies (Sackeim et al., Reference Sackeim2008) suggest that ECT can significantly impact cardiac health, particularly in the elderly, where receiving ECT had a higher risk of adverse cardiovascular events, such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and even death, compared to younger patients. ECT increases heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen demand and acts like a treadmill test for the heart. Patients at risk of cardiovascular disease or with a history of heart conditions may experience complications from ECT.
Conclusion
Current evidence from a systematic review of 46 studies indicates that ECT is beneficial in specific individuals with dementia/major NCD and behavioral symptoms. Still, sometimes adverse events may limit its use in these vulnerable individuals. Although ECT is useful for treating agitation and aggression for a short period, no data suggest when the treatment should be initiated and which patients would benefit the most. Even though it is not FDA-approved for treating agitation in patients with dementia/major NCD, it can be preferred as a treatment option to alleviate the behavioral symptoms. Providing adequate, comprehensive, and timely information about risks and benefits associated with ECT treatment will provide insight to the patient’s family and allow the healthcare professionals to act in the patient’s best interest.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Dr. Silpa Balachandran, MD, and Dr. Sujan Barua, MD, for initial contribution of the study, and data collection.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Source of funding
Dr. Youssef discloses that in the last 5 years, he received research support from the National Institute of Health (NIH), the Department of Veteran Affairs, the Department of Defense, and research support but not salary support from MECTA Corporation, Vistagen, and Merck. He receives royalties from Elsevier Publishing. The opinions or assertions contained herein are the private views of the authors. They are not to be construed as reflecting views of the US government or the Department of Defense. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Description of authors’ roles
Anil Bachu, MD, conceived and designed the study, collected the data, contributed to the systematic review of literature, wrote the manuscript, edited the manuscript, and oversaw and coordinated the workflow with other authors.
Vijaya Padma Kotapati, MD, collected and updated the data, contributed to the systematic review of literature, wrote the manuscript, and revised/edited the manuscript.
Tejasvi Kainth, MD, collected and updated the data, contributed to the systematic review of literature, wrote the manuscript, and revised/edited the manuscript.
Rikin Patel, MD, updated the data collection, contributed to the systematic review of literature, wrote the manuscript, and revised and edited the manuscript.
Nagy A. Youssef, MD, Ph.D., provided the final edits and corrections, and oversaw and coordinated the workflow with other authors.
Rajesh R. Tampi, MD, MS, DFAPA, DFAAGP, conceived and designed the study, provided the revisions and corrections, oversaw and coordinated the workflow with other authors, and provided expert-level guidance and final approval of the study.






