Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Maehara, Hiroshi
1980.
On random simplices in product distributions.
Journal of Applied Probability,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 02,
p.
553.
Stam, A. J.
1982.
Limit theorems for uniform distributions on spheres in high-dimensional euclidean spaces.
Journal of Applied Probability,
Vol. 19,
Issue. 01,
p.
221.
Mathai, A.M.
and
Tracy, D.S.
1983.
On a random convex hull in an n-ball.
Communications in Statistics - Theory and Methods,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 15,
p.
1727.
Pederzoli, Giorgio
1985.
On uniformly distributed random points in an n-Ball.
Communications in Statistics - Theory and Methods,
Vol. 14,
Issue. 1,
p.
185.
Anderson, W.J
1986.
On certain random simplices in Rn.
Journal of Multivariate Analysis,
Vol. 19,
Issue. 2,
p.
265.
Pederzoli, Giorgio
1986.
A representation in beta series for the exact density of some random volume contents.
Communications in Statistics - Theory and Methods,
Vol. 15,
Issue. 11,
p.
3299.
Pederzoxi, Giorgio
1986.
Computable representations for the general density of random r–contents of beta distributed random points in an n–ball.
Statistics,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 3,
p.
445.
Schneider, Rolf
1988.
Random approximation of convex sets*.
Journal of Microscopy,
Vol. 151,
Issue. 3,
p.
211.
Affentranger, Fernando
1989.
Random circles in the d-dimensional unit ball.
Journal of Applied Probability,
Vol. 26,
Issue. 02,
p.
408.
Mathai, A. M.
and
Pederzoli, G.
1989.
Some Common Structures of Distribution Problems in Geometric Probabilities and Multivariate Statistical Analysis.
American Journal of Mathematical and Management Sciences,
Vol. 9,
Issue. 1-2,
p.
113.
Chu, David P.T.
1993.
Random r‐content of an r‐simplex from beta‐type‐2 random points.
Canadian Journal of Statistics,
Vol. 21,
Issue. 3,
p.
285.
WEIL, Wolfgang
and
WIEACKER, John A.
1993.
Handbook of Convex Geometry.
p.
1391.
Mathai, A.M.
2007.
Random volumes under a general matrix-variate model.
Linear Algebra and its Applications,
Vol. 425,
Issue. 1,
p.
162.
Grote, Julian
Kabluchko, Zakhar
and
Thäle, Christoph
2019.
Limit theorems for random simplices in high dimensions
.
Latin American Journal of Probability and Mathematical Statistics,
Vol. 16,
Issue. 1,
p.
141.
Alonso-Gutiérrez, D.
Besau, F.
Grote, J.
Kabluchko, Z.
Reitzner, M.
Thäle, C.
Vritsiou, B.-H.
and
Werner, E.
2020.
Asymptotic normality for random simplices and convex bodies in high dimensions.
Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society,
Vol. 149,
Issue. 1,
p.
355.
Gusakova, Anna
and
Thäle, Christoph
2021.
The volume of simplices in high-dimensional Poisson–Delaunay tessellations.
Annales Henri Lebesgue,
Vol. 4,
Issue. ,
p.
121.
Gusakova, Anna
Heiny, Johannes
and
Thäle, Christoph
2023.
The volume of random simplices from elliptical distributions in high dimension.
Stochastic Processes and their Applications,
Vol. 164,
Issue. ,
p.
357.

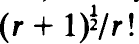 and
and  , respectively.
, respectively.