Article contents
Dynamic reconstruction and data reconstruction for subsampled or irregularly sampled data
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 July 2017
Abstract
The Nyquist–Shannon criterion indicates the sample rate necessary to identify information with particular frequency content from a dynamical system. However, in experimental applications such as the interrogation of a flow field using particle image velocimetry (PIV), it may be impracticable or expensive to obtain data at the desired temporal resolution. To address this problem, we propose a new approach to identify temporal information from undersampled data, using ideas from modal decomposition algorithms such as dynamic mode decomposition (DMD) and optimal mode decomposition (OMD). The novel method takes a vector-valued signal, such as an ensemble of PIV snapshots, sampled at random time instances (but at sub-Nyquist rate) and projects onto a low-order subspace. Subsequently, dynamical characteristics, such as frequencies and growth rates, are approximated by iteratively approximating the flow evolution by a low-order model and solving a certain convex optimisation problem. The methodology is demonstrated on three dynamical systems, a synthetic sinusoid, the cylinder wake at Reynolds number 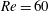 $Re=60$ and turbulent flow past the axisymmetric bullet-shaped body. In all cases the algorithm correctly identifies the characteristic frequencies and oscillatory structures present in the flow.
$Re=60$ and turbulent flow past the axisymmetric bullet-shaped body. In all cases the algorithm correctly identifies the characteristic frequencies and oscillatory structures present in the flow.
Information
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2017 Cambridge University Press
References
- 2
- Cited by


