Article contents
Inertial-particle accelerations in turbulence: a Lagrangian closure
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 31 May 2016
Abstract
The distribution of particle accelerations in turbulence is intermittent, with non-Gaussian tails that are quite different for light and heavy particles. In this article we analyse a closure scheme for the acceleration fluctuations of light and heavy inertial particles in turbulence, formulated in terms of Lagrangian correlation functions of fluid tracers. We compute the variance and the flatness of inertial-particle accelerations and we discuss their dependency on the Stokes number. The closure incorporates effects induced by the Lagrangian correlations along the trajectories of fluid tracers, and its predictions agree well with results of direct numerical simulations of inertial particles in turbulence, provided that the effects induced by inertial preferential sampling of heavy/light particles outside/inside vortices are negligible. In particular, the scheme predicts the correct functional behaviour of the acceleration variance, as a function of 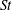 $St$ , as well as the presence of a minimum/maximum for the flatness of the acceleration of heavy/light particles, in good qualitative agreement with numerical data. We also show that the closure works well when applied to the Lagrangian evolution of particles using a stochastic surrogate for the underlying Eulerian velocity field. Our results support the conclusion that there exist important contributions to the statistics of the acceleration of inertial particles independent of the preferential sampling. For heavy particles we observe deviations between the predictions of the closure scheme and direct numerical simulations, at Stokes numbers of order unity. For light particles the deviation occurs for larger Stokes numbers.
$St$ , as well as the presence of a minimum/maximum for the flatness of the acceleration of heavy/light particles, in good qualitative agreement with numerical data. We also show that the closure works well when applied to the Lagrangian evolution of particles using a stochastic surrogate for the underlying Eulerian velocity field. Our results support the conclusion that there exist important contributions to the statistics of the acceleration of inertial particles independent of the preferential sampling. For heavy particles we observe deviations between the predictions of the closure scheme and direct numerical simulations, at Stokes numbers of order unity. For light particles the deviation occurs for larger Stokes numbers.
Information
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2016 Cambridge University Press
References
- 5
- Cited by


