Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Mandal, Shubhadeep
Bandopadhyay, Aditya
and
Chakraborty, Suman
2016.
Dielectrophoresis of a surfactant-laden viscous drop.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 6,
Mandal, Shubhadeep
Bandopadhyay, Aditya
and
Chakraborty, Suman
2016.
The effect of uniform electric field on the cross-stream migration of a drop in plane Poiseuille flow.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 809,
Issue. ,
p.
726.
Mandal, Shubhadeep
Bandopadhyay, Aditya
and
Chakraborty, Suman
2017.
The effect of surface charge convection and shape deformation on the settling velocity of drops in nonuniform electric field.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 1,
Zabarankin, Michael
2017.
Liquid toroidal drop under uniform electric field.
Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,
Vol. 473,
Issue. 2202,
p.
20160633.
Tyatyushkin, Alexander N.
2017.
Unsteady electrorotation of a drop in a constant electric field.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 9,
Mikkelsen, Alexander
Wojciechowski, Jarosław
Rajňák, Michal
Kurimský, Juraj
Khobaib, Khobaib
Kertmen, Ahmet
and
Rozynek, Zbigniew
2017.
Electric Field-Driven Assembly of Sulfonated Polystyrene Microspheres.
Materials,
Vol. 10,
Issue. 4,
p.
329.
Sengupta, Rajarshi
Walker, Lynn M.
and
Khair, Aditya S.
2017.
The role of surface charge convection in the electrohydrodynamics and breakup of prolate drops.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 833,
Issue. ,
p.
29.
Huang, Y.
Wang, Y. L.
and
Wong, T. N.
2017.
AC electric field controlled non-Newtonian filament thinning and droplet formation on the microscale.
Lab on a Chip,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 17,
p.
2969.
Mikkelsen, Alexander
Rozynek, Zbigniew
Khobaib, Khobaib
Dommersnes, Paul
and
Fossum, Jon Otto
2017.
Transient deformation dynamics of particle laden droplets in electric field.
Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,
Vol. 532,
Issue. ,
p.
252.
Mandal, Shubhadeep
Chakrabarti, Suryapratim
and
Chakraborty, Suman
2017.
Effect of nonuniform electric field on the electrohydrodynamic motion of a drop in Poiseuille flow.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 5,
Das, Debasish
and
Saintillan, David
2017.
Electrohydrodynamics of viscous drops in strong electric fields: numerical simulations.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 829,
Issue. ,
p.
127.
Mandal, Shubhadeep
and
Chakraborty, Suman
2017.
Effect of uniform electric field on the drop deformation in simple shear flow and emulsion shear rheology.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 7,
Mandal, Shubhadeep
Sinha, Sudipta
Bandopadhyay, Aditya
and
Chakraborty, Suman
2018.
Drop deformation and emulsion rheology under the combined influence of uniform electric field and linear flow.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 841,
Issue. ,
p.
408.
Lanauze, Javier A.
Sengupta, Rajarshi
Bleier, Blake J.
Yezer, Benjamin A.
Khair, Aditya S.
and
Walker, Lynn M.
2018.
Colloidal stability dictates drop breakup under electric fields.
Soft Matter,
Vol. 14,
Issue. 46,
p.
9351.
Santra, Somnath
Mandal, Shubhadeep
and
Chakraborty, Suman
2018.
Electrohydrodynamics of confined two-dimensional liquid droplets in uniform electric field.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 6,
Mori, Yoichiro
and
Young, Y.-N.
2018.
From electrodiffusion theory to the electrohydrodynamics of leaky dielectrics through the weak electrolyte limit.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 855,
Issue. ,
p.
67.
Bandopadhyay, Aditya
and
Ghosh, Uddipta
2018.
Electrohydrodynamic Phenomena.
Journal of the Indian Institute of Science,
Vol. 98,
Issue. 2,
p.
201.
Alidoost, Mohammadali
and
Reza Pishevar, Ahmad
2018.
On Importance of the Surface Charge Transport Equation in Numerical Simulation of Drop Deformation in a Direct Current Field.
Journal of Fluids Engineering,
Vol. 140,
Issue. 12,
Esmaeeli, A.
and
Halim, Md. Abdul
2018.
Electrohydrodynamics of a liquid drop in AC electric fields.
Acta Mechanica,
Vol. 229,
Issue. 9,
p.
3943.
Huang, Yi
Yin, Shuai
Chong, Wen Han
Wong, Teck Neng
and
Ooi, Kim Tiow
2019.
Precise morphology control and fast merging of a complex multi-emulsion system: the effects of AC electric fields.
Soft Matter,
Vol. 15,
Issue. 28,
p.
5614.
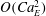 $O(Ca_{E}^{2})$ for the complete Melcher–Taylor model that includes transient charge relaxation, charge convection by the flow, as well as transient shape deformation. The main result of the paper is the derivation of coupled evolution equations for the induced electric multipoles and for the shape functions describing the deformations on the basis of spherical harmonics. Our results, which are consistent with previous models in the appropriate limits, show excellent agreement with fully nonlinear numerical simulations based on an axisymmetric boundary element formulation and with existing experimental data in the small-deformation regime.
$O(Ca_{E}^{2})$ for the complete Melcher–Taylor model that includes transient charge relaxation, charge convection by the flow, as well as transient shape deformation. The main result of the paper is the derivation of coupled evolution equations for the induced electric multipoles and for the shape functions describing the deformations on the basis of spherical harmonics. Our results, which are consistent with previous models in the appropriate limits, show excellent agreement with fully nonlinear numerical simulations based on an axisymmetric boundary element formulation and with existing experimental data in the small-deformation regime.