Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Zhao, Majie
Ye, Taohong
Cao, Changmin
Zhou, Taotao
and
Zhu, Minming
2016.
Study of sonic injection from circular injector into a supersonic cross-flow using large eddy simulation.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,
Vol. 41,
Issue. 39,
p.
17657.
Issakhov, Alibek
and
Baitureyeva, Aiymzhan
2017.
Numerical simulation of a passive scalar transport from thermal power plants.
Vol. 1836,
Issue. ,
p.
020019.
André, T.
Durant, A.
and
Fedioun, I.
2017.
Numerical Study of Supersonic Boundary-Layer Transition due to Sonic Wall Injection.
AIAA Journal,
Vol. 55,
Issue. 5,
p.
1530.
Huang, Wei
Li, Lang-quan
Chen, Xiao-qian
and
Yan, Li
2017.
Parametric effect on the flow and mixing properties of transverse gaseous injection flow fields with streamwise slot: A numerical study.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,
Vol. 42,
Issue. 2,
p.
1252.
Yu, Xinyu
Chen, Tianwen
Zhang, Qi
and
Wang, Tiefeng
2017.
Mixing Behaviors of Jets in Cross-Flow for Heat Recovery of Partial Oxidation Process.
International Journal of Chemical Reactor Engineering,
Vol. 15,
Issue. 1,
Sun, Ming-bo
and
Hu, Zhi-wei
2018.
Mixing in nearwall regions downstream of a sonic jet in a supersonic crossflow at Mach 2.7.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 10,
Issakhov, Alibek
and
Baitureyeva, Aiymzhan R
2018.
Numerical modelling of a passive scalar transport from thermal power plants to air environment.
Advances in Mechanical Engineering,
Vol. 10,
Issue. 10,
Sun, Mingbo
and
Hu, Zhiwei
2018.
Formation of surface trailing counter-rotating vortex pairs downstream of a sonic jet in a supersonic cross-flow.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 850,
Issue. ,
p.
551.
Beresh, Steven J.
Henfling, John F.
Spillers, Russell W.
and
Pruett, Brian
2018.
Influence of the Fluctuating Velocity Field on the Surface Pressures in a Jet/Fin Interaction.
Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets,
Vol. 55,
Issue. 5,
p.
1098.
Sun, M. B.
and
Hu, Z. W.
2018.
Generation of Upper Trailing Counter-Rotating Vortices of a Sonic Jet in a Supersonic Crossflow.
AIAA Journal,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 3,
p.
1047.
Beresh, Steven J.
Henfling, John
Spillers, Russell
and
Pruett, Brian O.
2018.
Influence of the Fluctuating Velocity Field on the Surface Pressures in a Jet/Fin Interaction.
Pourhashem, Hamideh
Kalkhoran, Iraj M.
and
Kumar, Sunil
2018.
Interaction of Vortex with Bow Shock Wave: Computational Model, Experimental Validation, Enhanced Mixing.
AIAA Journal,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 8,
p.
3071.
Liang, Chang-hai
Sun, Ming-bo
Liu, Yuan
and
Yang, Yi-xin
2018.
Shock wave structures in the wake of sonic transverse jet into a supersonic crossflow.
Acta Astronautica,
Vol. 148,
Issue. ,
p.
12.
Huang, Wei
Li, Yong
Yan, Li
and
Moradi, R.
2018.
Mixing enhancement mechanism induced by the cascaded fuel injectors in supersonic flows: A numerical study.
Acta Astronautica,
Vol. 152,
Issue. ,
p.
18.
Gao, Meng
Huai, Wenxin
Xiao, Yizhou
Yang, Zhonghua
and
Ji, Bin
2018.
Large eddy simulation of a vertical buoyant jet in a vegetated channel.
International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow,
Vol. 70,
Issue. ,
p.
114.
Miller, Warrick A.
Medwell, Paul R.
Doolan, Con J.
and
Kim, Minkwan
2018.
Transient interaction between a reaction control jet and a hypersonic crossflow.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 4,
Miller, Warrick A.
Medwell, Paul R.
Doolan, Con J.
and
Kim, Minkwan
2018.
Numerical investigation of a pulsed reaction control jet in hypersonic crossflow.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 10,
Zheng, Qinmin
and
Alam, Md. Mahbub
2019.
Evolution of the wake of three inline square prisms.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 4,
Issue. 10,
Dong, Min-zhou
Liao, Jun
Choubey, Gautam
and
Huang, Wei
2019.
Influence of the secondary flow control on the transverse gaseous injection flow field properties in a supersonic flow.
Acta Astronautica,
Vol. 165,
Issue. ,
p.
150.
Du, Zhao-bo
Huang, Wei
Yan, Li
Li, Lang-quan
Chen, Zheng
and
Li, Shi-bin
2019.
RANS study of steady and pulsed gaseous jets into a supersonic crossflow.
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,
Vol. 136,
Issue. ,
p.
157.
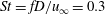 $St=fD/u_{\infty }=0.3$. For supersonic jet flow, no such global frequency is observed. Dynamic mode decomposition of the three-dimensional pressure field obtained from LES is performed and shows the same behaviour. The DMD results indicate that the
$St=fD/u_{\infty }=0.3$. For supersonic jet flow, no such global frequency is observed. Dynamic mode decomposition of the three-dimensional pressure field obtained from LES is performed and shows the same behaviour. The DMD results indicate that the 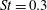 $St=0.3$ mode is dominant between the upstream barrel shock and the bow shock for the sonic jet, while the roll up of the upstream shear layer is dominant for the supersonic jet.
$St=0.3$ mode is dominant between the upstream barrel shock and the bow shock for the sonic jet, while the roll up of the upstream shear layer is dominant for the supersonic jet.