Article contents
Breaking electrolyte symmetry in induced-charge electro-osmosis
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 October 2020
Abstract
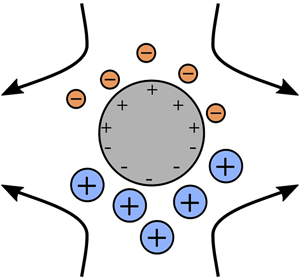
Induced-charge electro-osmotic (ICEO) flow caused by an alternating electric field applied around an infinitely long, ideally polarizable, uncharged circular cylinder in a binary electrolyte with unequal cation and anion diffusion coefficients is analysed. The thin-Debye-layer and weak-field approximations are invoked to compute the time-averaged, or rectified, quadrupolar ICEO flow around the cylinder. The inequality of ionic diffusion coefficients leads to transient ion concentration gradients, or concentration polarization, in the electroneutral bulk electrolyte outside the Debye layer. Consequently, the electric potential in the bulk is non-harmonic. Further, the concentration polarization alters the electro-osmotic slip at the surface of the cylinder and generates body forces in the bulk, both of which affect the rectified ICEO flow. Predictions for the strength of the rectified flow for varying ratio of ionic diffusion coefficients are in reasonable agreement with available experimental data. Our work highlights that an inequality in ionic diffusion coefficients – which all electrolytes possess to some extent – is an important factor in modelling ICEO flows.
JFM classification
Information
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2020. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
REFERENCES
- 12
- Cited by


