Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Maurer, P.
Ghaemsaidi, S. J.
Joubaud, S.
Peacock, T.
and
Odier, P.
2017.
An axisymmetric inertia-gravity wave generator.
Experiments in Fluids,
Vol. 58,
Issue. 10,
Arthur, Robert S.
Koseff, Jeffrey R.
and
Fringer, Oliver B.
2017.
Local versus volume-integrated turbulence and mixing in breaking internal waves on slopes.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 815,
Issue. ,
p.
169.
Hogg, Charlie A. R.
Egan, Galen C.
Ouellette, Nicholas T.
and
Koseff, Jeffrey R.
2018.
Shoaling internal waves may reduce gravity current transport.
Environmental Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 18,
Issue. 2,
p.
383.
Sinnett, Gregory
Feddersen, Falk
Lucas, Andrew J.
Pawlak, Geno
and
Terrill, Eric
2018.
Observations of Nonlinear Internal Wave Run-Up to the Surfzone.
Journal of Physical Oceanography,
Vol. 48,
Issue. 3,
p.
531.
Zhu, Hai
Lin, Chang
Wang, Lingling
Kao, Mingjer
Tang, Hongwu
and
Williams, J. J. R.
2018.
Numerical investigation of internal solitary waves of elevation type propagating on a uniform slope.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 11,
Navrotsky, V. V.
Liapidevskii, V. Yu.
Pavlova, E. P.
and
Khrapchenkov, F. F.
2019.
TRANSFORMATIONS AND EFFECTS OF INTERNAL WAVES IN THE NEARSHORE REGION OF SEA.
Journal of Oceanological Research,
Vol. 47,
Issue. 2,
p.
230.
Reid, Emma C.
DeCarlo, Thomas M.
Cohen, Anne L.
Wong, George T. F.
Lentz, Steven J.
Safaie, Aryan
Hall, Austin
and
Davis, Kristen A.
2019.
Internal waves influence the thermal and nutrient environment on a shallow coral reef.
Limnology and Oceanography,
Vol. 64,
Issue. 5,
p.
1949.
Kukarin, V. F.
Liapidevskii, V. Yu.
Khrapchenkov, F. F.
and
Yaroshchuk, I. O.
2019.
Nonlinear Internal Waves in the Shelf Zone of the Sea.
Fluid Dynamics,
Vol. 54,
Issue. 3,
p.
329.
Morozov, E. G.
Frey, D. I.
Gladyshev, S. V.
and
Gladyshev, V. S.
2020.
Hydrodynamics of the Bottom-Water Flow from the Arctic to the Atlantic through the Strait of Denmark.
Izvestiya, Atmospheric and Oceanic Physics,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 5,
p.
479.
Deepwell, David
Sapède, Raphaël
Buchart, Liam
Swaters, Gordon E.
and
Sutherland, Bruce R.
2020.
Particle transport and resuspension by shoaling internal solitary waves.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 5,
Allshouse, Michael R.
and
Swinney, Harry L.
2020.
Dependence of Internal Wave Bolus Transport on Pycnocline Thickness.
Geophysical Research Letters,
Vol. 47,
Issue. 14,
Vieira, Guilherme S.
and
Allshouse, Michael R.
2020.
Internal wave boluses as coherent structures in a continuously stratified fluid.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 885,
Issue. ,
Bachman, Scott D.
Shakespeare, Callum J.
Kleypas, Joan
Castruccio, Frederic S.
and
Curchitser, Enrique
2020.
Particle‐Based Lagrangian Filtering for Locating Wave‐Generated Thermal Refugia for Coral Reefs.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans,
Vol. 125,
Issue. 7,
Tanimoto, Yukinobu
Ouellette, Nicholas T.
and
Koseff, Jeffrey R.
2020.
Interaction between an inclined gravity current and a pycnocline in a two-layer stratification.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 887,
Issue. ,
Tanimoto, Yukinobu
Ouellette, Nicholas T.
and
Koseff, Jeffrey R.
2021.
Secondary generation of breaking internal waves in confined basins by gravity currents.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 917,
Issue. ,
Morozov, Eugene G.
Tarakanov, Roman Y.
and
Frey, Dmitry I.
2021.
Bottom Gravity Currents and Overflows in Deep Channels of the Atlantic Ocean.
p.
443.
Tanimoto, Yukinobu
Ouellette, Nicholas T.
and
Koseff, Jeffrey R.
2022.
On the interaction between oncoming internal waves and a dense gravity current in a two-layer stratification.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 932,
Issue. ,
Sinnett, Gregory
Ramp, Steven R.
Yang, Yiing J.
Chang, Ming-Huei
Jan, Sen
and
Davis, Kristen A.
2022.
Large-Amplitude Internal Wave Transformation into Shallow Water.
Journal of Physical Oceanography,
Vol. 52,
Issue. 10,
p.
2539.
Ghassemi, Amin
Zahedi, Saeid
and
Boegman, Leon
2022.
Bolus formation from fission of nonlinear internal waves over a mild slope.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 932,
Issue. ,
2023.
Mechanism analysis of internal solitary waves breaking encountering submarine ridges based on laboratory experiments.
AIP Advances,
Vol. 13,
Issue. 7,
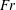 $Fr$ , a wave Reynolds number
$Fr$ , a wave Reynolds number 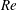 $Re$ and a wave steepness parameter
$Re$ and a wave steepness parameter 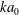 $ka_{0}$ , are used to relate initial wave forcing to a dominant bolus formation mechanism. Bolus characteristics, including the bolus propagation speed and turbulent components, are also related to wave forcing. Results indicate that for
$ka_{0}$ , are used to relate initial wave forcing to a dominant bolus formation mechanism. Bolus characteristics, including the bolus propagation speed and turbulent components, are also related to wave forcing. Results indicate that for 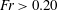 $Fr>0.20$ and
$Fr>0.20$ and 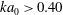 $ka_{0}>0.40$ , the generated boluses become more turbulent in nature. As wave forcing continues to increase further, boluses are no longer able to form.
$ka_{0}>0.40$ , the generated boluses become more turbulent in nature. As wave forcing continues to increase further, boluses are no longer able to form.

