Article contents
Computational and experimental study of an oil jet in crossflow: coupling population balance model with multifluid large eddy simulation
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 December 2021
Abstract
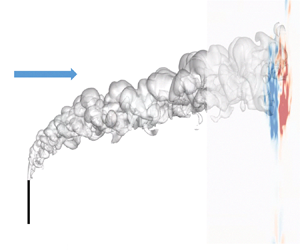
Understanding the size of oil droplets released from a jet in crossflow is crucial for estimating the trajectory of hydrocarbons and the rates of oil biodegradation/dissolution in the water column. We present experimental results of an oil jet with a jet-to-crossflow velocity ratio of 9.3. The oil was released from a vertical pipe 25 mm in diameter with a Reynolds number of 25 000. We measured the size of oil droplets near the top and bottom boundaries of the plume using shadowgraph cameras and we also filmed the whole plume. In parallel, we developed a multifluid large eddy simulation model to simulate the plume and coupled it with our VDROP population balance model to compute the local droplet size. We accounted for the slip velocity of oil droplets in the momentum equation and in the volume fraction equation of oil through the local, mass-weighted average droplet rise velocity. The top and bottom boundaries of the plume were captured well in the simulation. Larger droplets shaped the upper boundary of the plume, and the mean droplet size increased with elevation across the plume, most likely due to the individual rise velocity of droplets. At the same elevation across the plume, the droplet size was smaller at the centre axis as compared with the side boundaries of the plume due to the formation of the counter-rotating vortex pair, which induced upward velocity at the centre axis and downward velocity near the sides of the plume.
Information
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press
Footnotes
Work was completed while the author was a Postdoctoral Researcher at the New Jersey Institute of Technology.
References
REFERENCES
- 7
- Cited by


