Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Craske, John
and
van Reeuwijk, Maarten
2015.
Energy dispersion in turbulent jets. Part 1. Direct simulation of steady and unsteady jets.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 763,
Issue. ,
p.
500.
van Reeuwijk, Maarten
and
Craske, John
2015.
Energy-consistent entrainment relations for jets and plumes.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 782,
Issue. ,
p.
333.
Woodhouse, Mark J.
Hogg, Andrew J.
and
Phillips, Jeremy C.
2016.
A global sensitivity analysis of the PlumeRise model of volcanic plumes.
Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,
Vol. 326,
Issue. ,
p.
54.
Burridge, H.C.
Partridge, J.L.
and
Linden, P.F.
2016.
The Fluxes and Behaviour of Plumes Inferred from Measurements of Coherent Structures within Images of the Bulk Flow.
Atmosphere-Ocean,
Vol. 54,
Issue. 4,
p.
403.
Hunt, Gary R.
and
Debugne, Antoine L. R.
2016.
Forced fountains.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 802,
Issue. ,
p.
437.
Fabregat Tomàs, Alexandre
Poje, Andrew C.
Özgökmen, Tamay M.
and
Dewar, William K.
2016.
Dynamics of multiphase turbulent plumes with hybrid buoyancy sources in stratified environments.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 9,
Woodhouse, M. J.
Phillips, J. C.
and
Hogg, A. J.
2016.
Unsteady turbulent buoyant plumes.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 794,
Issue. ,
p.
595.
Rooney, G. G.
2016.
Merging of two or more plumes arranged around a circle.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 796,
Issue. ,
p.
712.
Burridge, H. C.
and
Hunt, G. R.
2016.
Entrainment by turbulent fountains.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 790,
Issue. ,
p.
407.
van Reeuwijk, Maarten
Salizzoni, Pietro
Hunt, Gary R.
and
Craske, John
2016.
Turbulent transport and entrainment in jets and plumes: A DNS study.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 1,
Issue. 7,
Burridge, H. C.
and
Hunt, G. R.
2017.
From free jets to clinging wall jets: The influence of a horizontal boundary on a horizontally forced buoyant jet.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 2,
Carlotti, P.
and
Hunt, G. R.
2017.
An entrainment model for lazy turbulent plumes.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 811,
Issue. ,
p.
682.
Craske, John
Salizzoni, Pietro
and
van Reeuwijk, Maarten
2017.
The turbulent Prandtl number in a pure plume is 3/5.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 822,
Issue. ,
p.
774.
Yannopoulos, Panayotis C.
2017.
Unique Superposition Solution of Multiple Plumes’ Flow via Mean Kinetic Energy Fluxes.
Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,
Vol. 143,
Issue. 9,
Ezhova, Ekaterina
Cenedese, Claudia
and
Brandt, Luca
2017.
Dynamics of a Turbulent Buoyant Plume in a Stratified Fluid: An Idealized Model of Subglacial Discharge in Greenland Fjords.
Journal of Physical Oceanography,
Vol. 47,
Issue. 10,
p.
2611.
López, Pilar
Tarquis, Ana M.
Matulka, Ania
Skadden, Benjamin
and
Redondo, José M.
2017.
Multiscaling properties on sequences of turbulent plumes images.
Chaos, Solitons & Fractals,
Vol. 105,
Issue. ,
p.
128.
Burridge, H. C.
Parker, D. A.
Kruger, E. S.
Partridge, J. L.
and
Linden, P. F.
2017.
Conditional sampling of a high Péclet number turbulent plume and the implications for entrainment.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 823,
Issue. ,
p.
26.
Cao, Zhixuan
Patra, Abani
Bursik, Marcus
Pitman, E. Bruce
and
Jones, Matthew
2018.
Plume-SPH 1.0: a three-dimensional, dusty-gas volcanic plume model based on smoothed particle hydrodynamics.
Geoscientific Model Development,
Vol. 11,
Issue. 7,
p.
2691.
Clément, Simon A.
Guillemain, Anaïs
McCleney, Amy B.
and
Bardet, Philippe M.
2018.
Options for refractive index and viscosity matching to study variable density flows.
Experiments in Fluids,
Vol. 59,
Issue. 2,
Jiang, Lei
Creyssels, Mathieu
Mos, Antoine
and
Salizzoni, Pietro
2018.
Critical velocity in ventilated tunnels in the case of fire plumes and densimetric plumes.
Fire Safety Journal,
Vol. 101,
Issue. ,
p.
53.
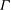 ${\it\Gamma}$ . In addition, we analyse the similarity of one-point and two-point second-order velocity statistics, and we discuss the role of
${\it\Gamma}$ . In addition, we analyse the similarity of one-point and two-point second-order velocity statistics, and we discuss the role of 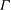 ${\it\Gamma}$ on the vertical development of the bulk dynamical parameters of the plume, namely, the turbulent viscosity, the turbulent Prandtl number and the entrainment coefficient
${\it\Gamma}$ on the vertical development of the bulk dynamical parameters of the plume, namely, the turbulent viscosity, the turbulent Prandtl number and the entrainment coefficient 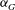 ${\it\alpha}_{G}$ . Comparison with previous experimental results and with estimates of the entrainment coefficient based on the mean kinetic energy budget allow us to conclude on the influence of
${\it\alpha}_{G}$ . Comparison with previous experimental results and with estimates of the entrainment coefficient based on the mean kinetic energy budget allow us to conclude on the influence of 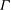 ${\it\Gamma}$ on the entrainment process and to explain possible physical reasons for the high scatter in estimates of
${\it\Gamma}$ on the entrainment process and to explain possible physical reasons for the high scatter in estimates of 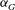 ${\it\alpha}_{G}$ in the literature.
${\it\alpha}_{G}$ in the literature.

